Technology and Innovation
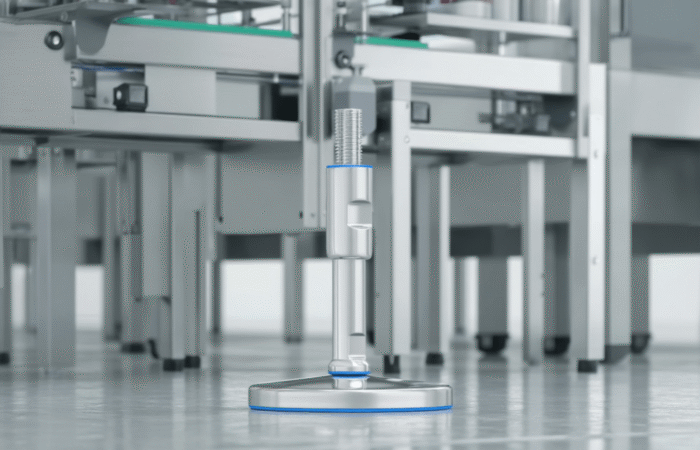
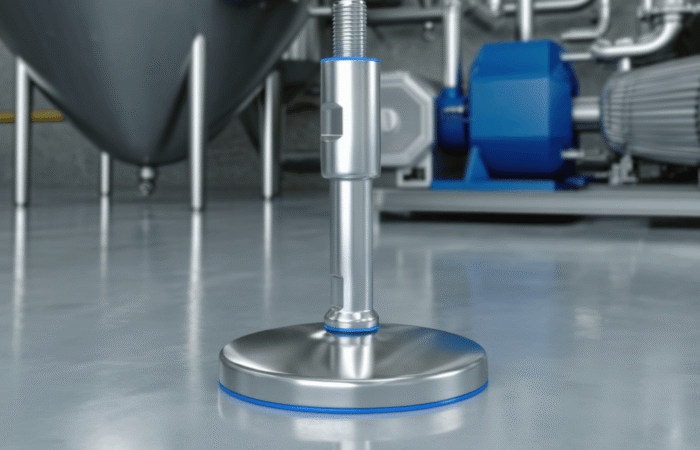
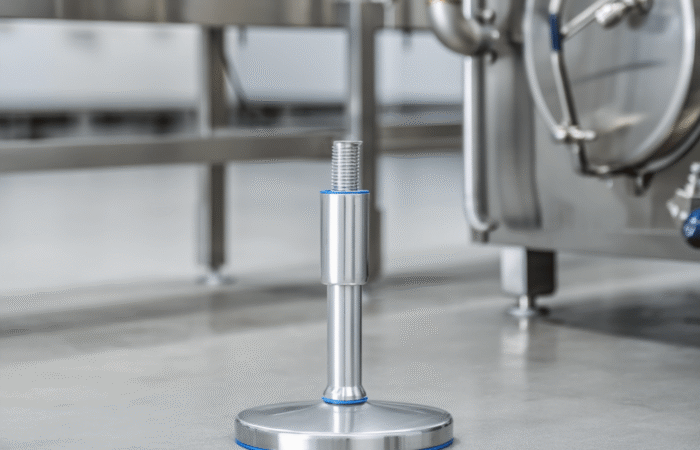
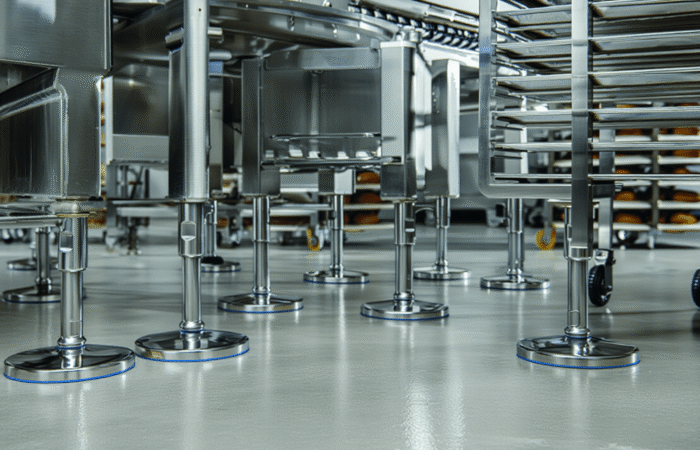
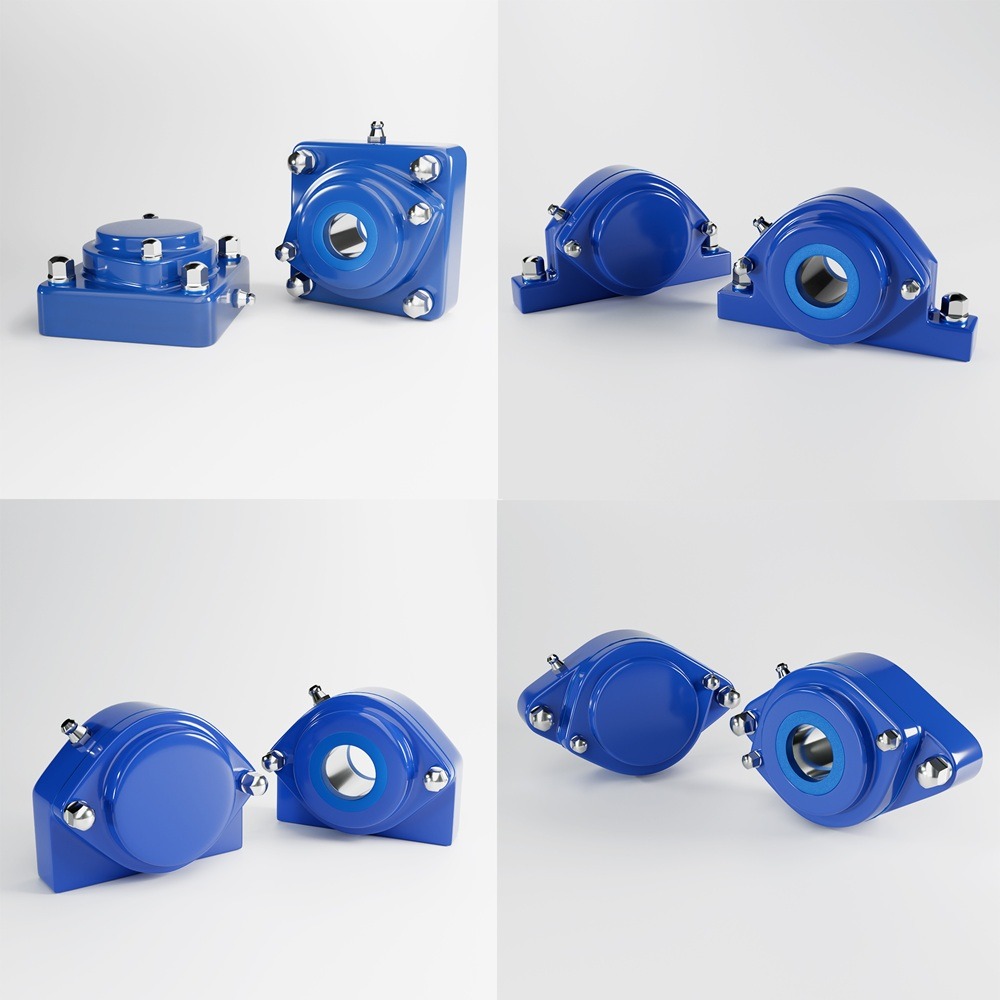
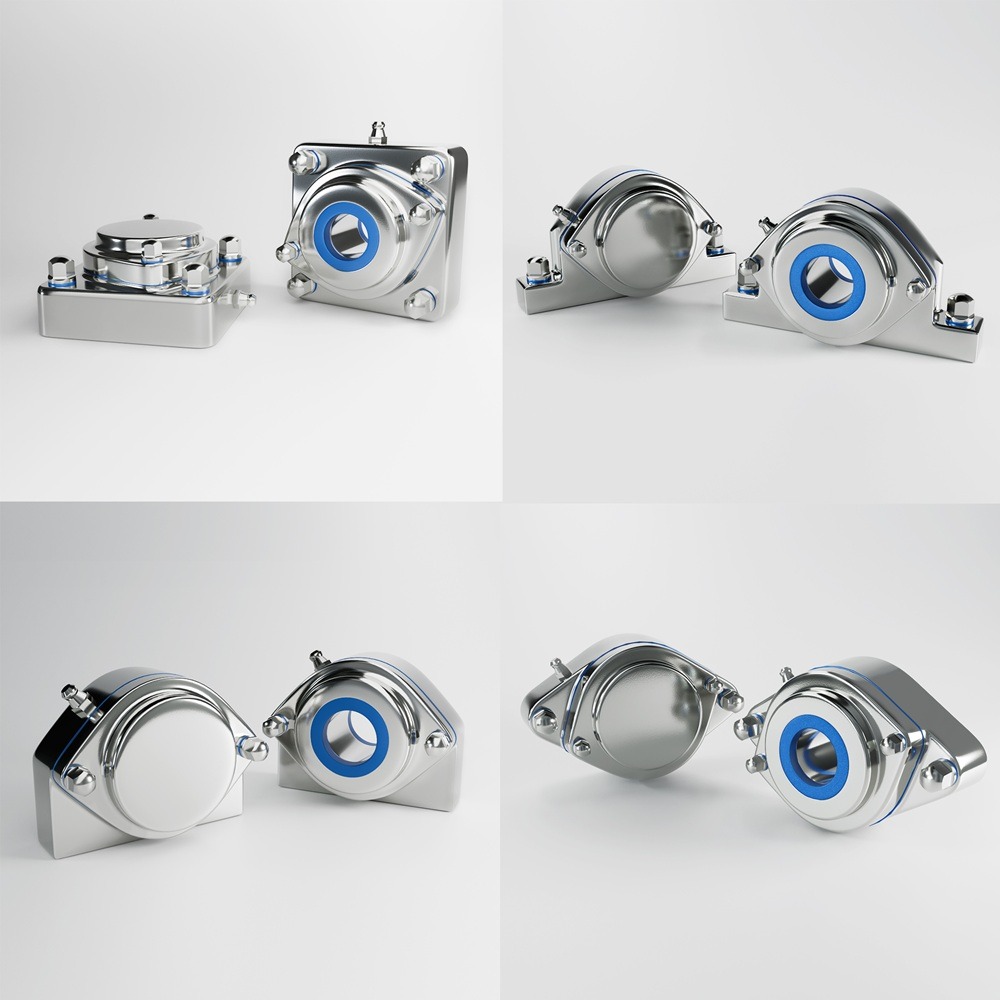
In today’s fast-paced global market, the supply chain is the backbone of numerous industries, ensuring that products are developed, manufactured, and delivered efficiently and transparently. Recent advancements in technology, particularly Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain, have revolutionized the supply chain landscape. These innovations have not only enhanced transparency and efficiency but also significantly impacted product development. This article delves into how these technologies are reshaping the supply chain and presents four case studies demonstrating their real-world applications. Artificial Intelligence has been a game-changer in supply chain management. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, predict trends, and optimize processes. AI-powered predictive analytics enable companies to anticipate demand, manage inventory, and reduce waste. Machine learning models continuously improve over time, offering more precise insights and better decision-making capabilities. The Internet of Things (IoT) involves interconnected devices that communicate and share data in real time. In the supply chain, IoT devices can track goods, monitor environmental conditions, and provide real-time updates. This connectivity enhances visibility, allowing companies to manage their logistics more effectively and respond promptly to any issues. Blockchain technology offers an immutable ledger for recording transactions. In the supply chain, blockchain can track every step of a product’s journey, from raw materials to the end consumer. This transparency ensures authenticity, reduces fraud, and builds trust among stakeholders. Smart contracts on blockchain platforms can automate processes, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency. Walmart has implemented blockchain technology to enhance food safety and traceability. By partnering with IBM, Walmart developed a blockchain system that tracks the journey of food products from farms to store shelves. This system allows Walmart to trace contaminated products quickly, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensuring consumer safety. DHL, a global logistics leader, leverages IoT to improve its supply chain operations. IoT sensors monitor the condition and location of shipments in real-time. This data allows DHL to optimize routes, reduce delays, and ensure the integrity of sensitive goods. The enhanced visibility provided by IoT has significantly improved DHL’s operational efficiency. Amazon utilizes AI to predict customer demand and manage inventory. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical sales data, customer behavior, and external factors to forecast demand accurately. This predictive capability enables Amazon to maintain optimal inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize excess inventory, ensuring a smooth supply chain. Maersk, a leading shipping company, has embraced blockchain technology to streamline its shipping processes. In collaboration with IBM, Maersk developed TradeLens, a blockchain-based platform that digitizes the entire shipping process. TradeLens enhances transparency, reduces paperwork, and expedites transactions, resulting in a more efficient and secure supply chain. The integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain into supply chain management has revolutionized the industry. These technologies offer unprecedented levels of transparency, efficiency, and security, ultimately enhancing product development and delivery. As companies continue to innovate and adopt these technologies, the future of supply chain management looks promising, with the potential for even greater advancements on the horizon. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Block Units and Flange Bearings is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. 440C Steel and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.The Role of AI, IoT, and Blockchain in Improving Supply Chain Transparency, Efficiency, and Product Development
The Role of AI in Supply Chain Management
IoT: Connecting the Supply Chain
Blockchain: Ensuring Transparency and Security
Case Study 1: Walmart’s Use of Blockchain for Food Safety
Case Study 2: DHL’s IoT-Enabled Logistics
Case Study 3: Amazon’s AI-Driven Demand Forecasting
Case Study 4: Maersk’s Blockchain-Powered Shipping
Conclusion


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards