Safe Food Production Needs Hygienic Design
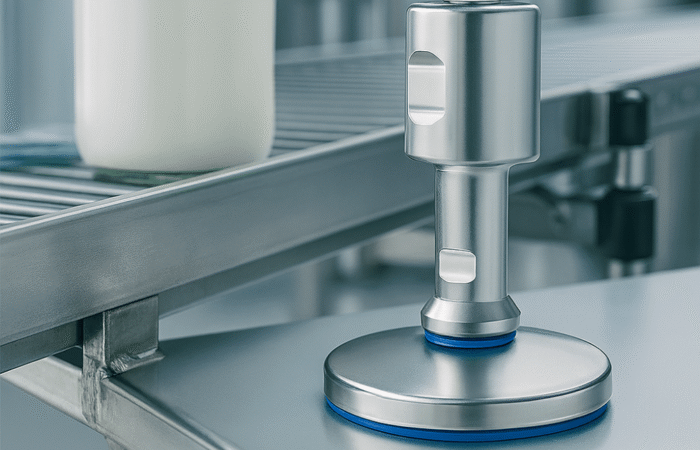
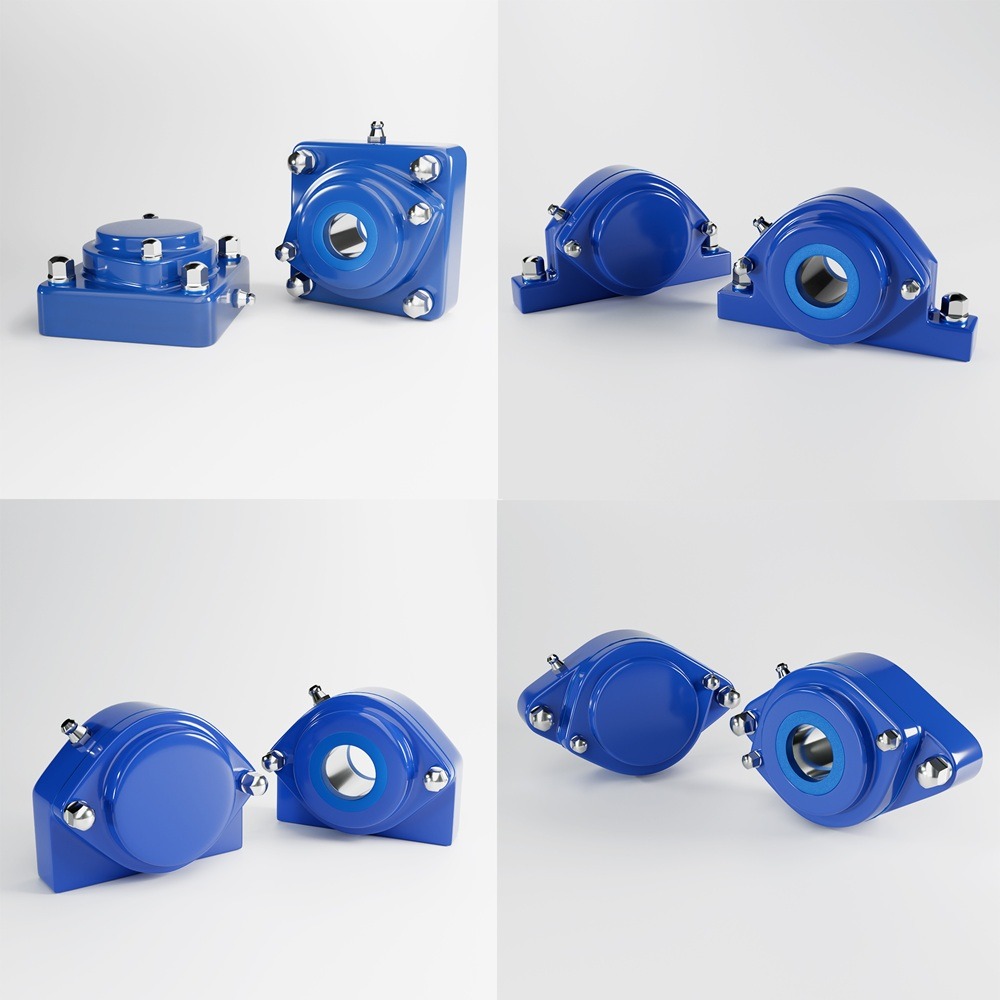
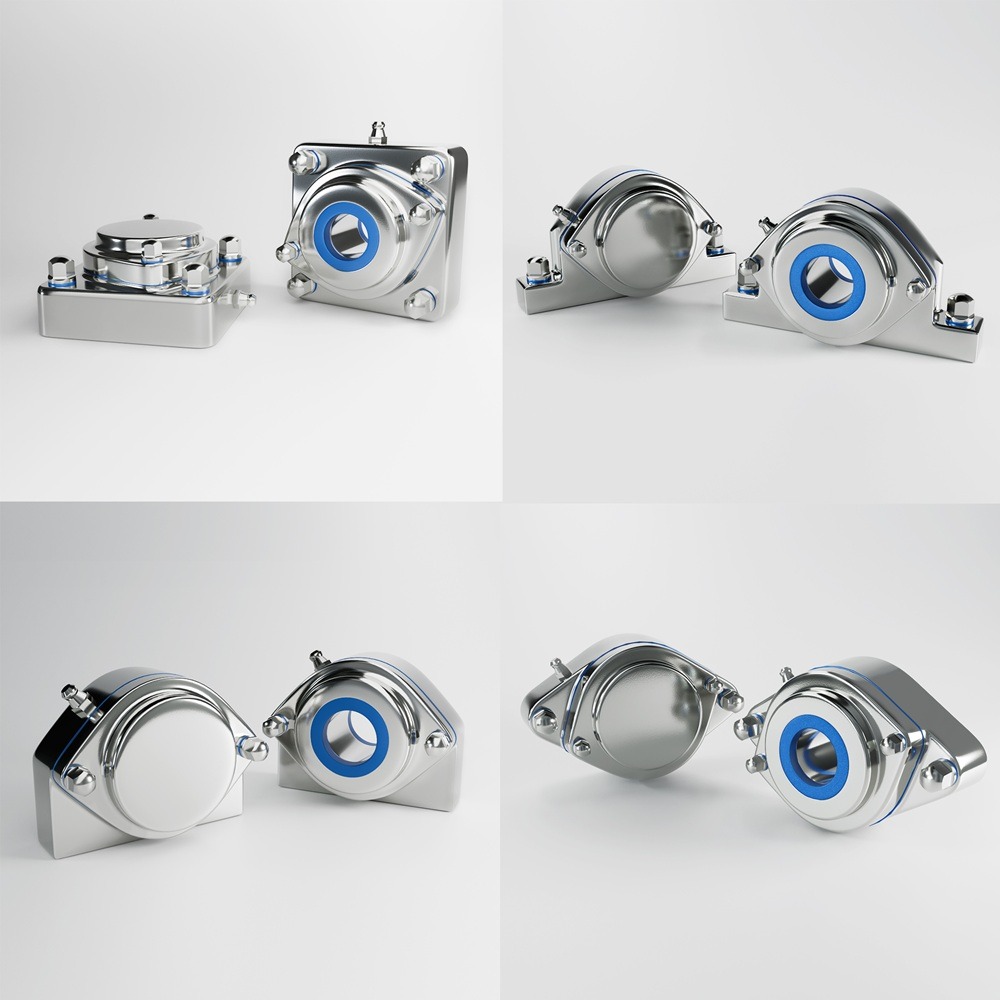
In the modern food processing industry, safety is paramount. Consumers demand high-quality products free from contamination, and regulatory bodies impose strict guidelines to ensure food safety. One of the most crucial aspects of food safety is hygienic design, which involves engineering food processing equipment and facilities to prevent contamination, facilitate cleaning, and comply with food safety standards. This article explores the importance of hygienic design in food production, key principles, benefits, and challenges. In the realm of food production, ensuring safety is paramount. A critical component in achieving this is the implementation of hygienic design principles. Hygienic design refers to the thoughtful engineering of food processing facilities and equipment to minimize contamination risks and facilitate effective cleaning. By integrating these principles, manufacturers can uphold product integrity, protect consumer health, and comply with stringent regulatory standards. The primary objective of hygienic design is to prevent contamination from biological, chemical, and physical hazards. This involves designing equipment and facilities that are easy to clean, reducing the likelihood of microbial growth, and ensuring that all surfaces in contact with food are smooth and non-porous. Such designs not only enhance food safety but also improve operational efficiency by reducing downtime during cleaning processes. Implementing hygienic design involves adhering to several core principles: Adhering to hygienic design principles offers numerous advantages: While the benefits are clear, implementing hygienic design can present challenges: Recent incidents underscore the critical need for hygienic design in food production: In the pursuit of safe food production, hygienic design stands as a cornerstone. By thoughtfully designing facilities and equipment to minimize contamination risks and facilitate effective cleaning, food manufacturers can ensure product safety, comply with regulatory standards, and maintain consumer trust. While challenges exist, the long-term benefits of implementing hygienic design principles far outweigh the initial hurdles, leading to a safer and more efficient food production environment. Hygienic design plays a vital role in minimizing risks associated with foodborne illnesses, product recalls, and regulatory non-compliance. Food safety hazards, such as biological, chemical, and physical contaminants, can lead to severe consequences, including public health risks and reputational damage for manufacturers. By implementing hygienic design principles, food processing companies can: To ensure safe food production, hygienic design must be incorporated into equipment, facilities, and processing environments. The following principles are essential: Food processing equipment should be made of materials that are non-toxic, corrosion-resistant, and easy to clean. Stainless steel (304 and 316 grades) is the preferred material due to its durability and resistance to harsh cleaning chemicals. Surfaces that come into contact with food should be free from cracks, crevices, and rough textures to prevent microbial growth. Polished stainless steel with a Ra (Roughness Average) value of 0.8 µm or less is recommended. Welded joints should be continuous and smooth to eliminate bacteria traps. Bolted or riveted connections should be minimized, as they create hard-to-clean areas where food residues can accumulate. Equipment should be designed to prevent water accumulation, which can harbor bacteria and biofilms. Sloped surfaces and self-draining designs help in effective liquid removal. All parts of the equipment must be easily accessible for cleaning and maintenance. This includes removable panels, tool-free disassembly, and open-frame designs. Hollow tubing and enclosed spaces can trap moisture and contaminants. Instead, solid bars or sealed tubing should be used in construction to ensure no hidden bacterial growth. Food processing facilities must adhere to internationally recognized hygienic design standards, such as: Adopting hygienic design principles leads to multiple advantages: Hygienic design significantly reduces the risk of microbial contamination, ensuring that food products meet safety standards. Companies that implement hygienic design can more easily pass HACCP audits, ISO 22000 certification, and FDA inspections. Using corrosion-resistant materials and sanitary design principles extends the lifespan of food processing equipment. Hygienic design simplifies cleaning processes, reducing water, energy, and chemical consumption. This leads to lower operational costs and increased production uptime. Consumers are more likely to purchase products from brands that prioritize food safety and hygiene. While the benefits of hygienic design are clear, food manufacturers may face some challenges: A leading dairy processing plant in Europe implemented EHEDG-certified stainless steel equipment, resulting in a 40% reduction in cleaning time and improved product safety. A global meat processing company redesigned its equipment with self-draining surfaces and hygienic conveyors, reducing cross-contamination risks by 60%. A soft drink manufacturer upgraded its bottling lines with hygienic pumps and sealed bearings, leading to fewer product recalls and improved shelf life. Hygienic design is a non-negotiable factor in modern food production. By prioritizing cleanability, material selection, and regulatory compliance, food manufacturers can enhance food safety, reduce operational costs, and build consumer trust. Investing in hygienic design today leads to a safer, more efficient, and more profitable food processing operation. With foodborne illnesses and recalls on the rise, now is the time for the food industry to embrace hygienic design as a fundamental pillar of safe food production. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Plummer Blocks and Direct Mount Bearings is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. Stainless Steel 440 and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Ensuring Food Safety and Compliance
Hygienic Design: The Key to Safe, Efficient and Compliant Food Production
The Imperative of Hygienic Design
Key Principles of Hygienic Design
Benefits of Hygienic Design
Challenges in Implementing Hygienic Design
Case Studies Highlighting the Importance of Hygienic Design
The Importance of Hygienic Design in Food Production
Key Principles of Hygienic Design
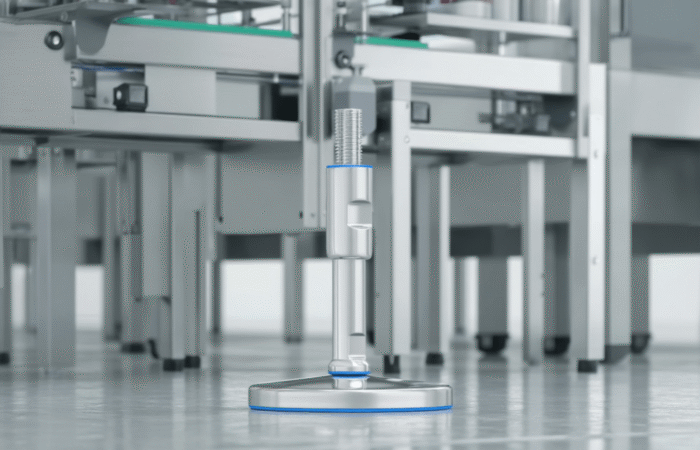
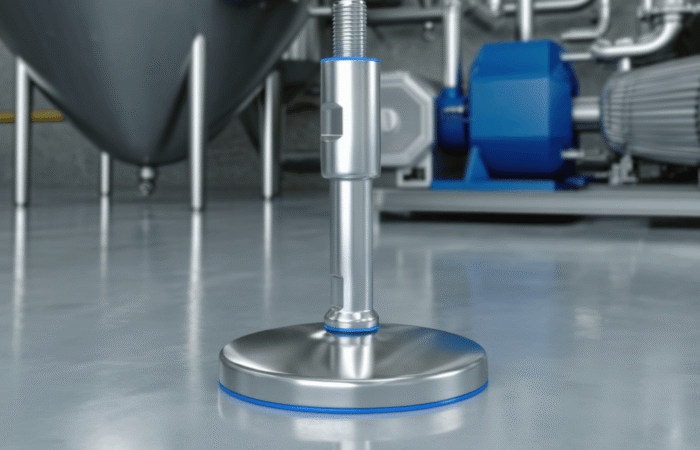
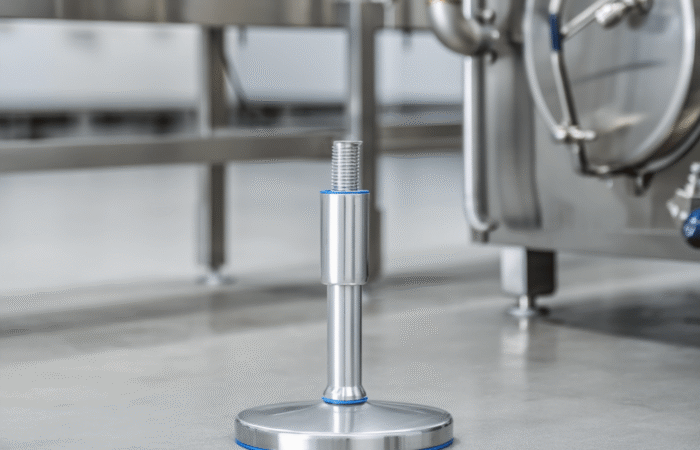
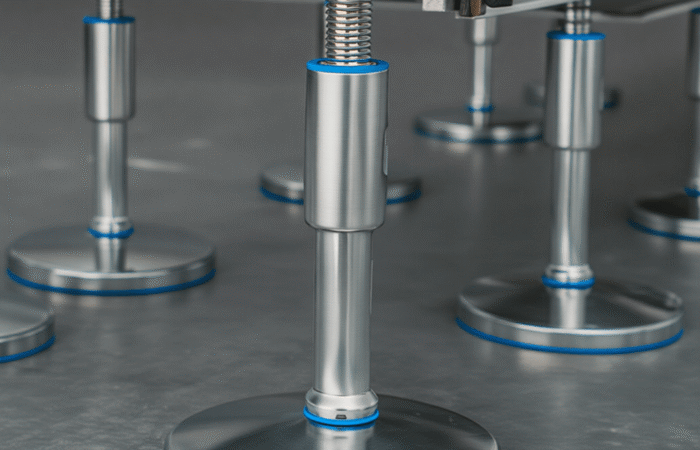
1. Use of Hygienic Materials
2. Smooth and Non-Porous Surfaces
3. Seamless Construction
4. Proper Drainage Systems
5. Accessible and Easy-to-Clean Design
6. Avoidance of Hollow Bodies
7. Compliance with Food Safety Standards
Benefits of Hygienic Design in Food Production
1. Improved Food Safety
2. Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
3. Increased Equipment Longevity
4. Reduced Cleaning Time and Costs
5. Improved Consumer Trust
Challenges in Implementing Hygienic Design
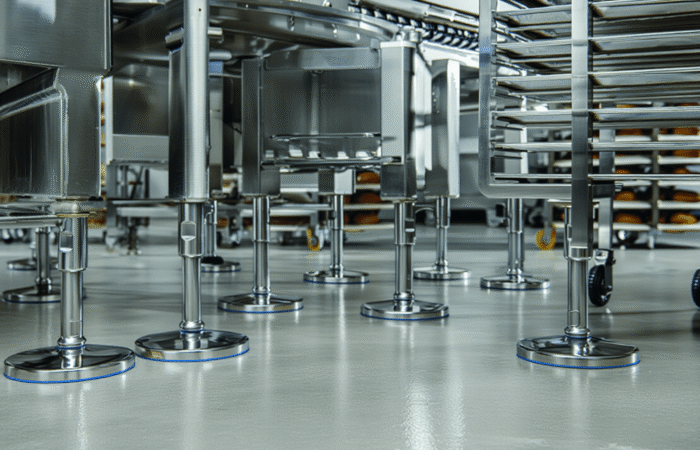
Case Studies: Hygienic Design in Action
1. The Dairy Industry
2. Meat Processing Facilities
3. Beverage Manufacturing
Safe Food Production Starts with Hygienic Design
Ensuring Quality and Compliance”



Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards