Regulatory Changes and Compliance
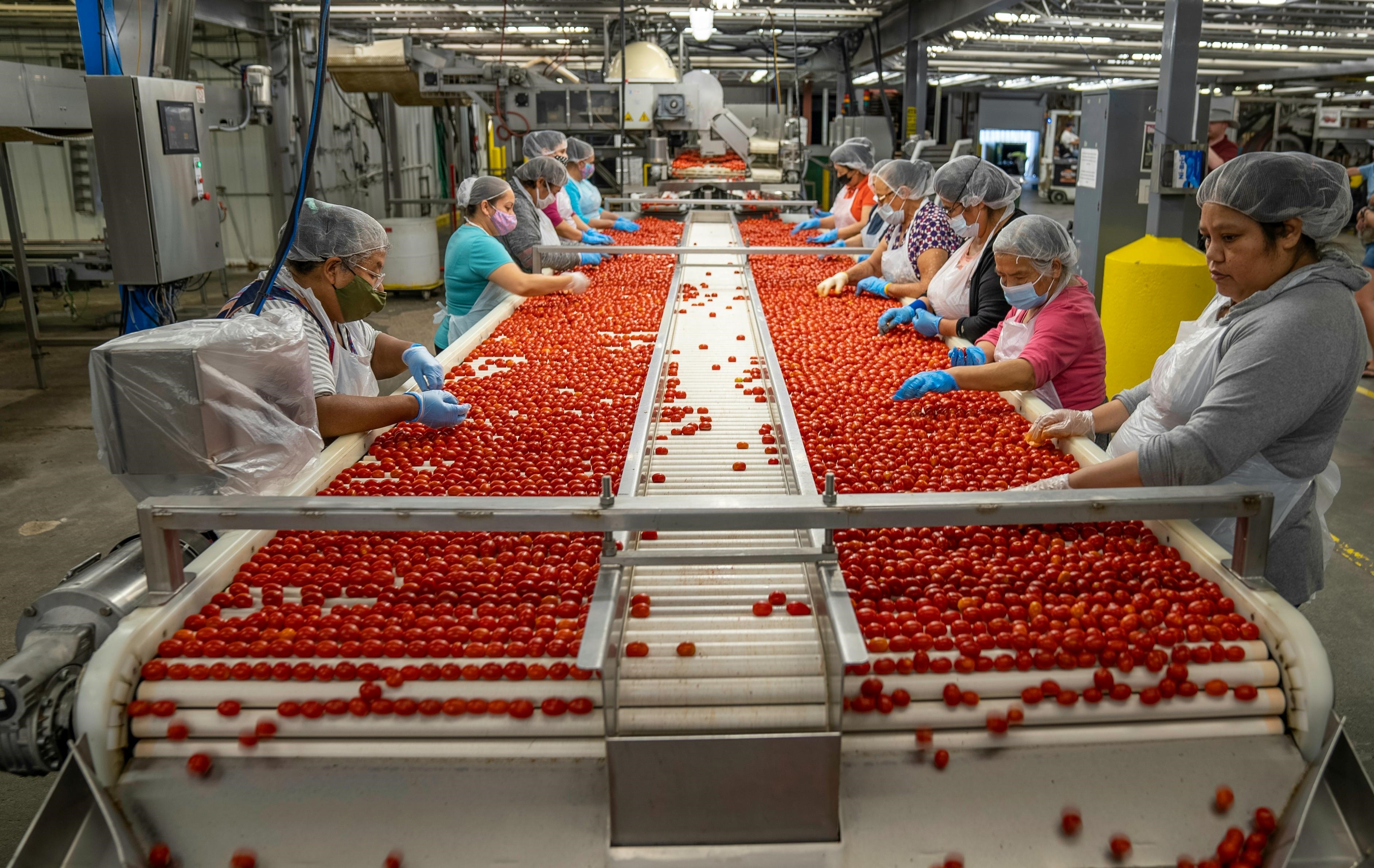
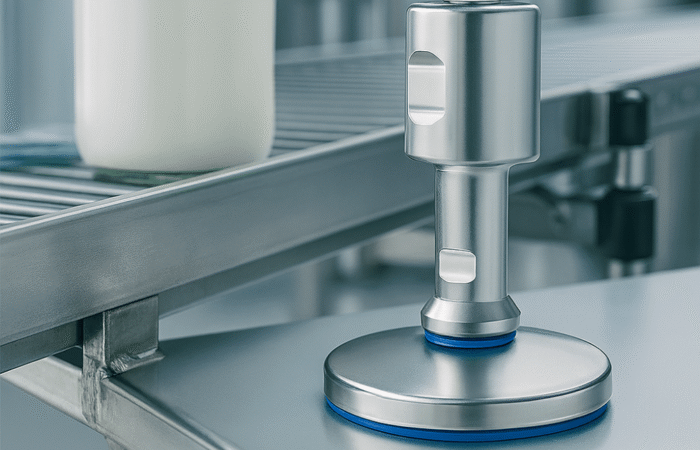
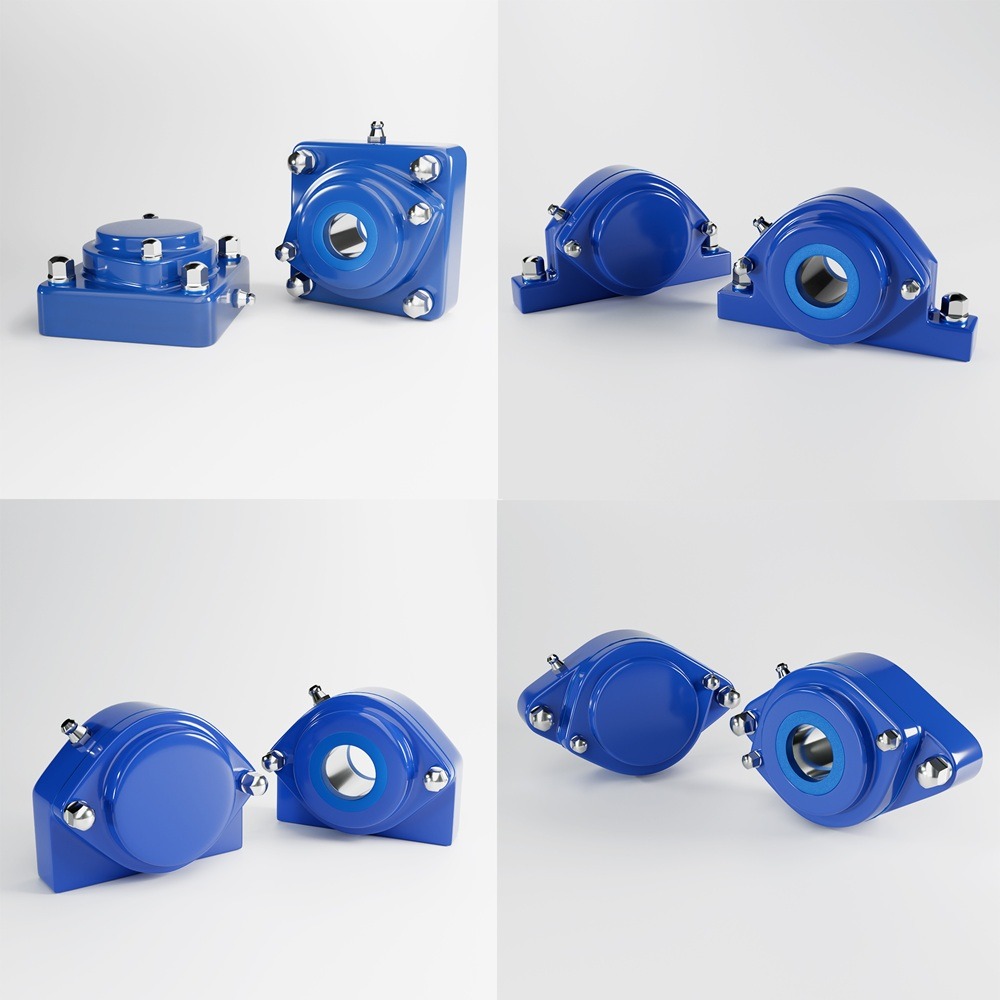
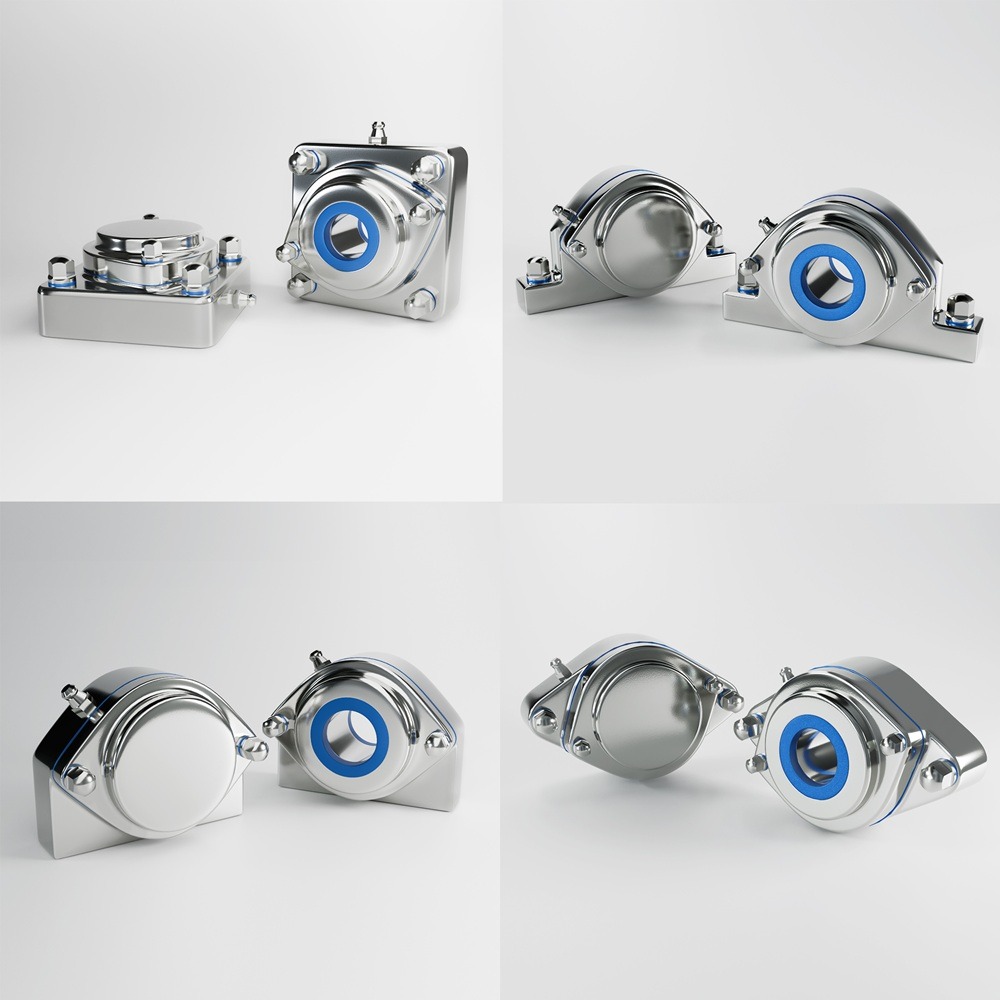
The global food industry is constantly evolving, driven by new scientific discoveries, consumer demands, and, most importantly, regulatory changes. Adapting to new food regulations, labeling requirements, and compliance standards is critical for businesses to maintain market access and consumer trust. This article explores the impact of these regulatory changes, the importance of compliance, and how companies are successfully navigating these challenges. Regulatory compliance ensures the safety, quality, and transparency of food products. As governments and international bodies update food regulations, companies must stay informed and adapt quickly to remain compliant. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including fines, product recalls, and reputational damage. The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) represents the most significant overhaul of U.S. food safety laws in over 70 years. Enacted to prevent foodborne illnesses, the FSMA imposes strict requirements on food producers and processors. Companies must implement hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls (HARPC), ensure proper sanitation, and maintain comprehensive records. Example: A major U.S. dairy producer invested heavily in updating its facilities and training staff to comply with FSMA regulations. By adopting advanced monitoring systems and improving traceability, the company not only met regulatory requirements but also enhanced its overall product quality, resulting in increased consumer trust and market share. In the European Union, the Food Information to Consumers (FIC) Regulation mandates clear and accurate food labeling to help consumers make informed choices. This includes allergen labeling, nutritional information, and origin labeling. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties. Example: A European snack manufacturer faced challenges with the new allergen labeling requirements. By investing in comprehensive ingredient tracking and updating their labeling processes, the company ensured compliance and avoided costly fines. Additionally, transparent labeling improved customer confidence and loyalty. China’s Food Safety Law, revised in 2015, imposes stringent standards on food production, distribution, and importation. Companies must implement rigorous quality control measures and ensure traceability throughout the supply chain. Example: A global beverage company operating in China had to revamp its entire supply chain to comply with the updated Food Safety Law. By enhancing supplier audits, implementing real-time monitoring systems, and improving product traceability, the company not only complied with the regulations but also achieved a competitive advantage by demonstrating superior quality assurance to Chinese consumers. Japan’s food labeling standards require detailed information about ingredients, allergens, and nutritional content. These regulations are designed to protect consumers and promote healthy eating habits. Example: A multinational confectionery brand encountered challenges with Japan’s stringent labeling requirements. By collaborating with local experts and investing in advanced labeling technology, the company successfully navigated the regulatory landscape. Compliance not only facilitated smooth market entry but also enhanced the brand’s reputation for quality and transparency. Adapting to new food regulations, labeling requirements, and compliance standards is an ongoing challenge for the global food industry. However, companies that proactively embrace these changes can turn compliance into a competitive advantage. By investing in technology, enhancing traceability, and prioritizing consumer safety, businesses can build trust, improve product quality, and secure their position in the market. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Block Bearings and Flange Mounted Units is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. Type 440 Steel and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Adapting to New Food Regulations, Labeling Requirements, and Compliance Standards Globally
The Importance of Regulatory Compliance in the Food Industry
H2: Case Study 1: The Impact of the FSMA in the United States
H2: Case Study 2: The EU’s Food Information to Consumers Regulation
H2: Case Study 3: Adapting to China’s Food Safety Law
H2: Case Study 4: Navigating Japan’s Food Labeling Standards
Prioritizing consumer safety


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards