Hygienic Design of Equipment in Food Processing
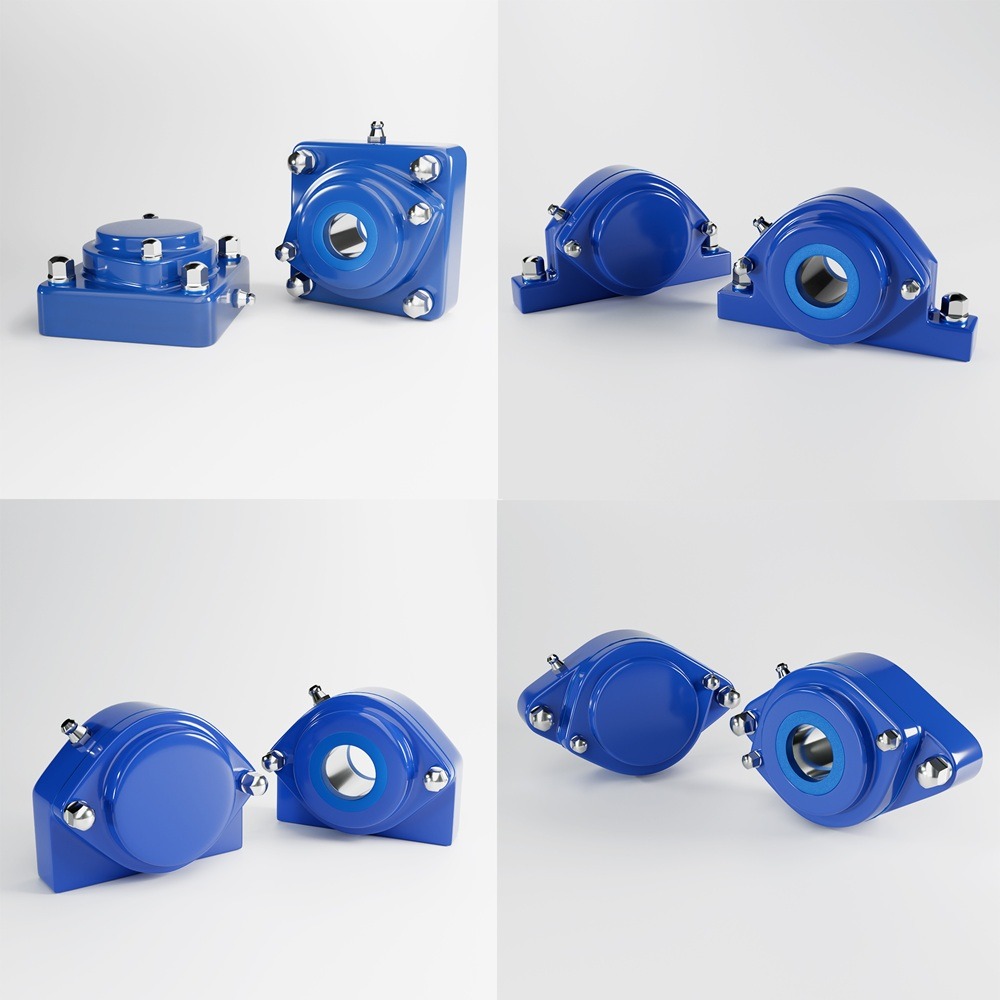
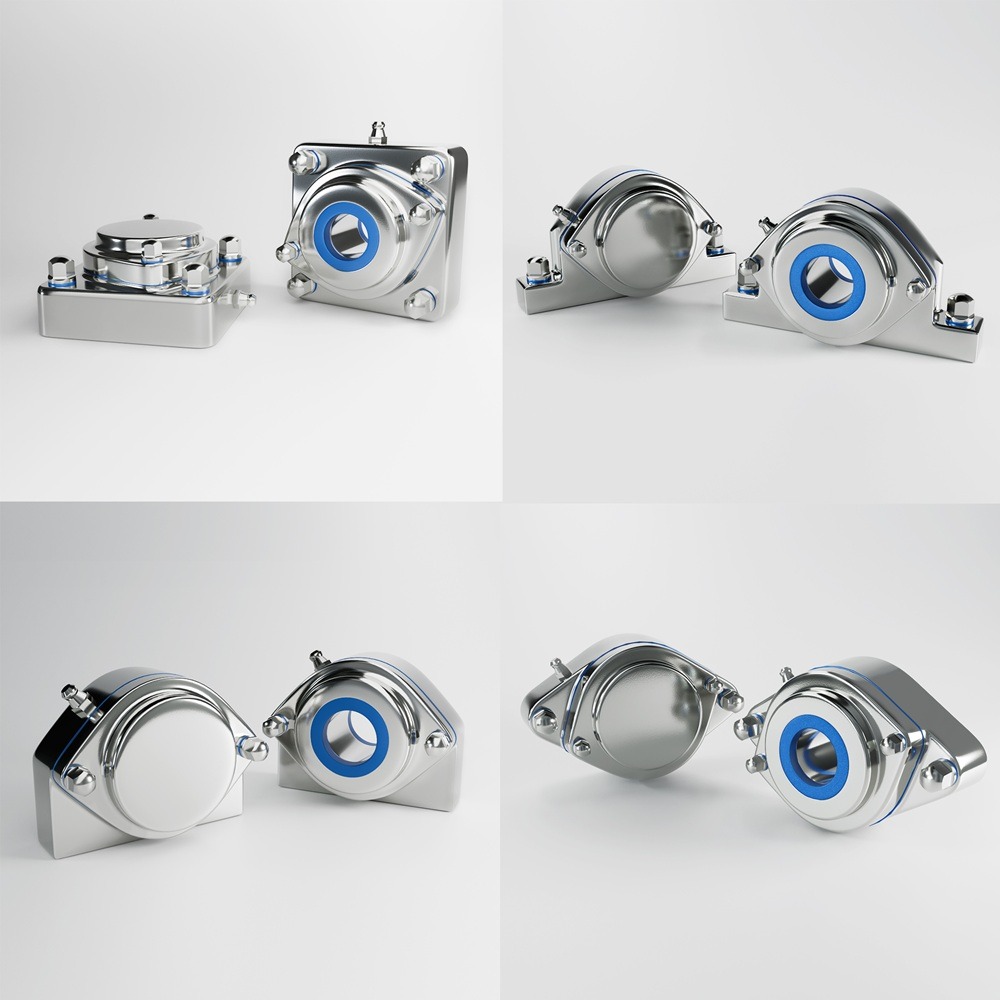
In the food processing industry, hygiene is paramount. The design of food processing equipment plays a crucial role in ensuring food safety, preventing contamination, and complying with strict industry regulations. Poorly designed equipment can harbor bacteria, lead to cross-contamination, and increase downtime due to inefficient cleaning processes. Hygienic design principles focus on creating equipment that is easy to clean, resistant to bacteria, and built with food-safe materials. This article explores the fundamentals of hygienic design, key industry standards, and the benefits of implementing sanitary engineering practices in food processing. In the food processing industry, the hygienic design of equipment is crucial for ensuring product safety, maintaining quality, and complying with regulatory standards. Properly designed equipment minimizes contamination risks, facilitates effective cleaning, and enhances operational efficiency. This article delves into the key principles of hygienic design, relevant industry standards, and the benefits of implementing such designs in food processing facilities. Adherence to established standards and guidelines is essential for ensuring the hygienic design of food processing equipment: While the benefits are clear, implementing hygienic design principles can present challenges: Investing in the hygienic design of food processing equipment is not merely a regulatory requirement but a fundamental aspect of producing safe, high-quality food products. By adhering to established design principles and standards, manufacturers can minimize contamination risks, enhance operational efficiency, and build consumer trust. In an industry where safety and quality are paramount, hygienic design stands as a cornerstone of successful food processing operations. Food safety regulations have become increasingly stringent worldwide. Organizations such as the European Hygienic Engineering and Design Group (EHEDG), Sanitary Standards, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) set guidelines to ensure equipment used in food production meets hygienic standards. Hygienic design minimizes risks associated with: By integrating sanitary design into food processing machinery, manufacturers reduce risks, comply with regulations, and enhance overall product quality. Hygienic design is guided by several core principles to ensure food processing equipment meets industry standards. These principles help maintain cleanliness, efficiency, and long-term durability. Materials used in food processing equipment must be: 304 stainless steel is commonly used in general food production, while 316 stainless steel is preferred in environments exposed to harsh chemicals and high salinity (e.g., seafood processing). Food contact surfaces must be smooth and free from cracks, crevices, and sharp edges. Rough or porous surfaces allow bacteria to accumulate and are difficult to clean. Equipment should be self-draining to prevent the accumulation of water, which can encourage bacterial growth. Food processing equipment should be designed for easy cleaning, ensuring all surfaces can be reached for sanitation. Hygienic design should eliminate cross-contamination risks from microbial, chemical, and physical hazards. Traditional bolts and screws can create contamination points in food processing equipment. Hygienic design is regulated by multiple organizations that establish food safety standards for equipment manufacturers: EHEDG provides design guidelines for food equipment, ensuring they meet hygiene and cleanability standards. Equipment carrying EHEDG certification is recognized in European food processing facilities. Sanitary Standards ensure that food and dairy processing equipment meets strict sanitary requirements. Compliance with sanitary standards is mandatory in industries like dairy, meat, and beverage processing. In the U.S., food processing equipment must comply with FDA 21 CFR regulations, ensuring all materials and components in direct contact with food are safe and non-toxic. NSF certifies food processing equipment based on safety, sanitation, and cleanability, focusing on materials, design, and microbial resistance. This international standard outlines hygiene requirements for machinery used in food processing, ensuring they meet safety and cleanliness expectations. Compliance with these standards helps food manufacturers meet legal requirements while maintaining a clean and efficient processing environment. Investing in hygienic food processing equipment provides multiple advantages: By preventing bacterial contamination, hygienic design reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses and costly recalls. Well-designed equipment reduces cleaning time by up to 30%, saving water, chemicals, and labor costs. Hygienic design minimizes equipment breakdowns and extends service life by preventing corrosion and buildup of food residues. Adhering to EHEDG, Sanitary standards, and FDA guidelines ensures equipment meets global food safety standards, reducing the risk of regulatory fines. Although hygienic design may require a higher initial investment, long-term savings are achieved through reduced contamination risks, lower maintenance costs, and fewer equipment failures. Despite its benefits, hygienic design can present challenges: However, the long-term advantages outweigh these challenges, making hygienic design a critical investment for food processors. The hygienic design of food processing equipment is essential for food safety, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. By incorporating food-grade materials, smooth surfaces, self-draining designs, and easy-to-clean structures, manufacturers can prevent contamination, streamline cleaning processes, and reduce maintenance costs. As food safety regulations continue to evolve, adopting hygienic design principles ensures food manufacturers stay ahead of compliance requirements while protecting consumers and improving overall efficiency. Investing in hygienic food processing equipment isn’t just about compliance—it’s about ensuring the safety, quality, and sustainability of food production for the future. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Blocks and Flange Bearing Units is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. Stainless Steel 440 and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.A Key to Food Safety and Efficiency
Challenges in Implementing Hygienic Design
Key Principles of Hygienic Design
Industry Standards and Guidelines
Benefits of Hygienic Design
Challenges in Implementing Hygienic Design
The Importance of Hygienic Design in Food Processing
Key Principles of Hygienic Equipment Design
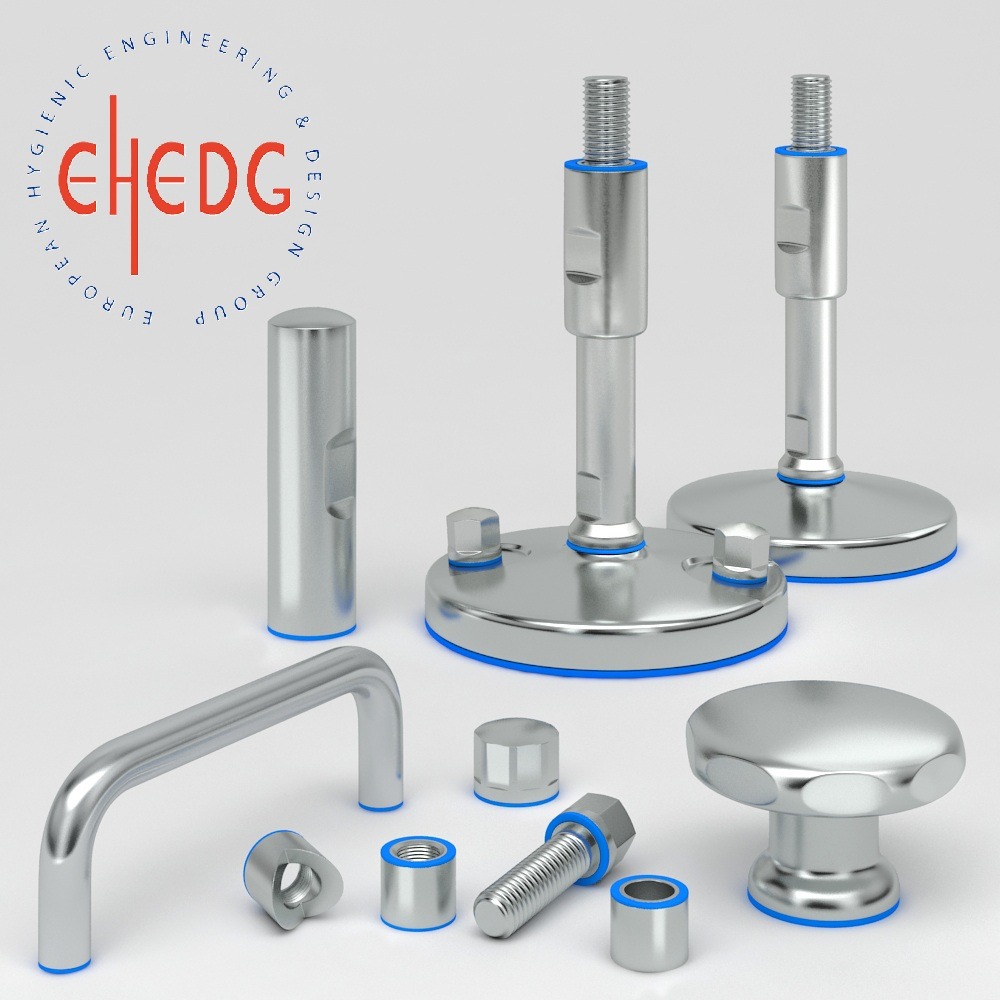
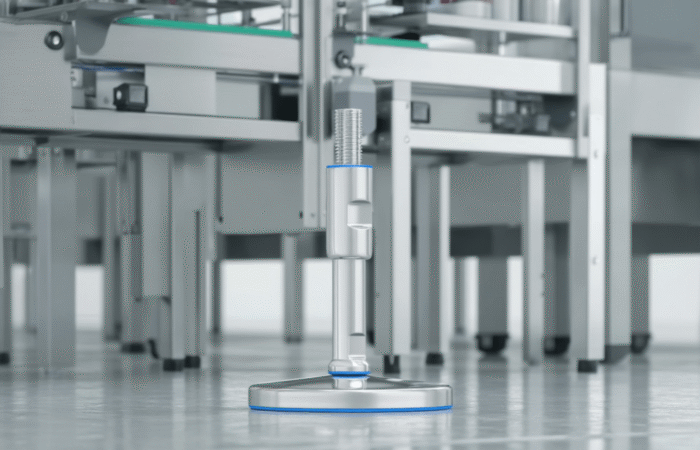
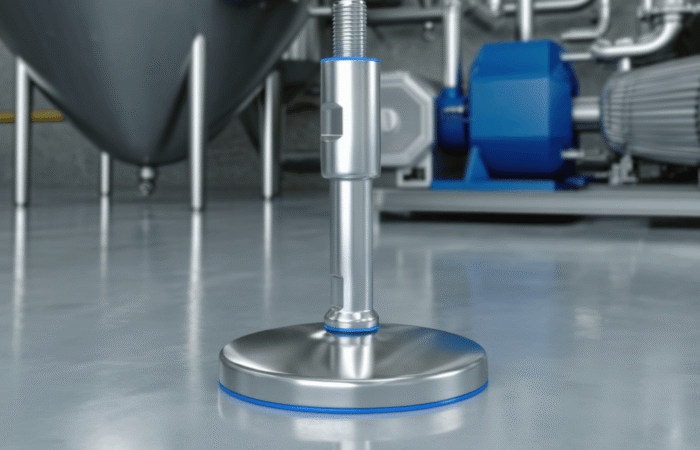
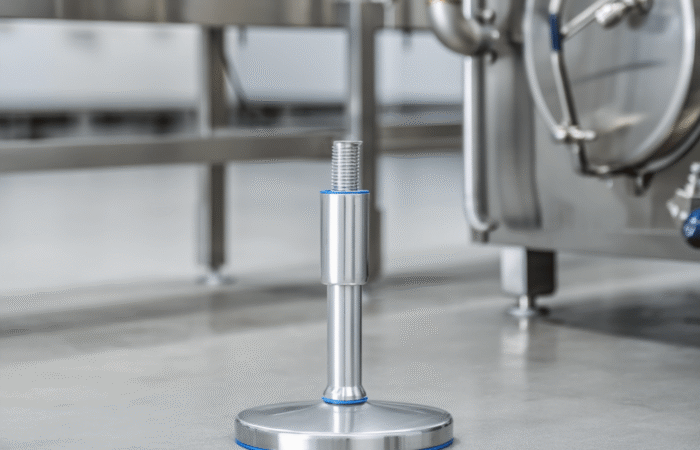
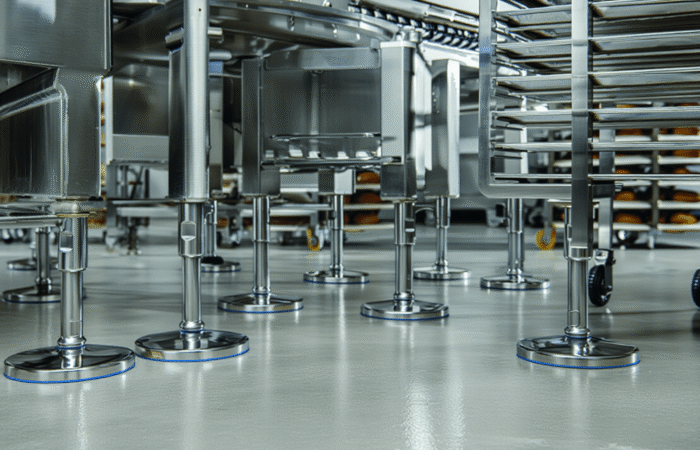
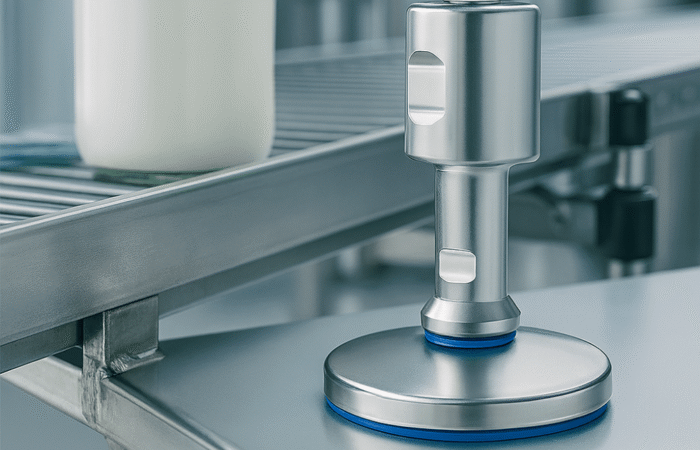
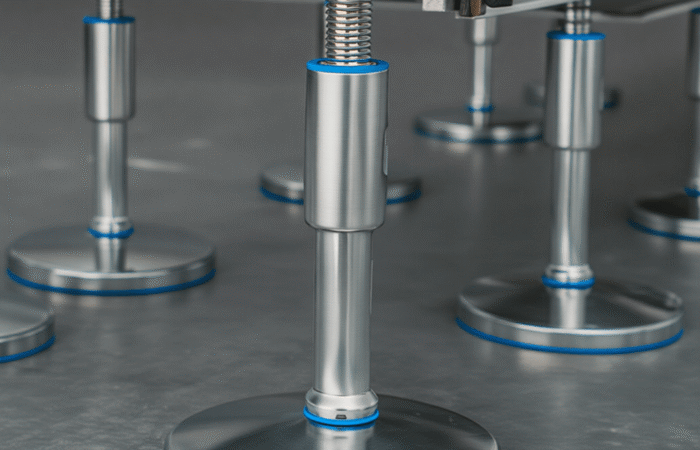
1. Selection of Food-Grade Materials
2. Smooth Surfaces and No Crevices
3. Drainability and Water Resistance
4. Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
5. Prevention of Contamination
6. Use of Hygienic Fasteners and Connections
Industry Standards and Certifications for Hygienic Design
1. EHEDG (European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group)
2. Sanitary Standards (USA)
3. FDA (Food and Drug Administration) Compliance
4. NSF International Certification
5. ISO 14159: Hygienic Design of Machinery
Benefits of Hygienic Equipment Design
1. Improved Food Safety
2. Increased Cleaning Efficiency
3. Reduced Downtime and Maintenance
4. Compliance with Food Safety Regulations
5. Lower Total Cost of Ownership
Challenges in Implementing Hygienic Design
Enhancing Safety, Efficiency and Compliance




Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards