How to Prioritize and Address Food Safety Concerns Effectively
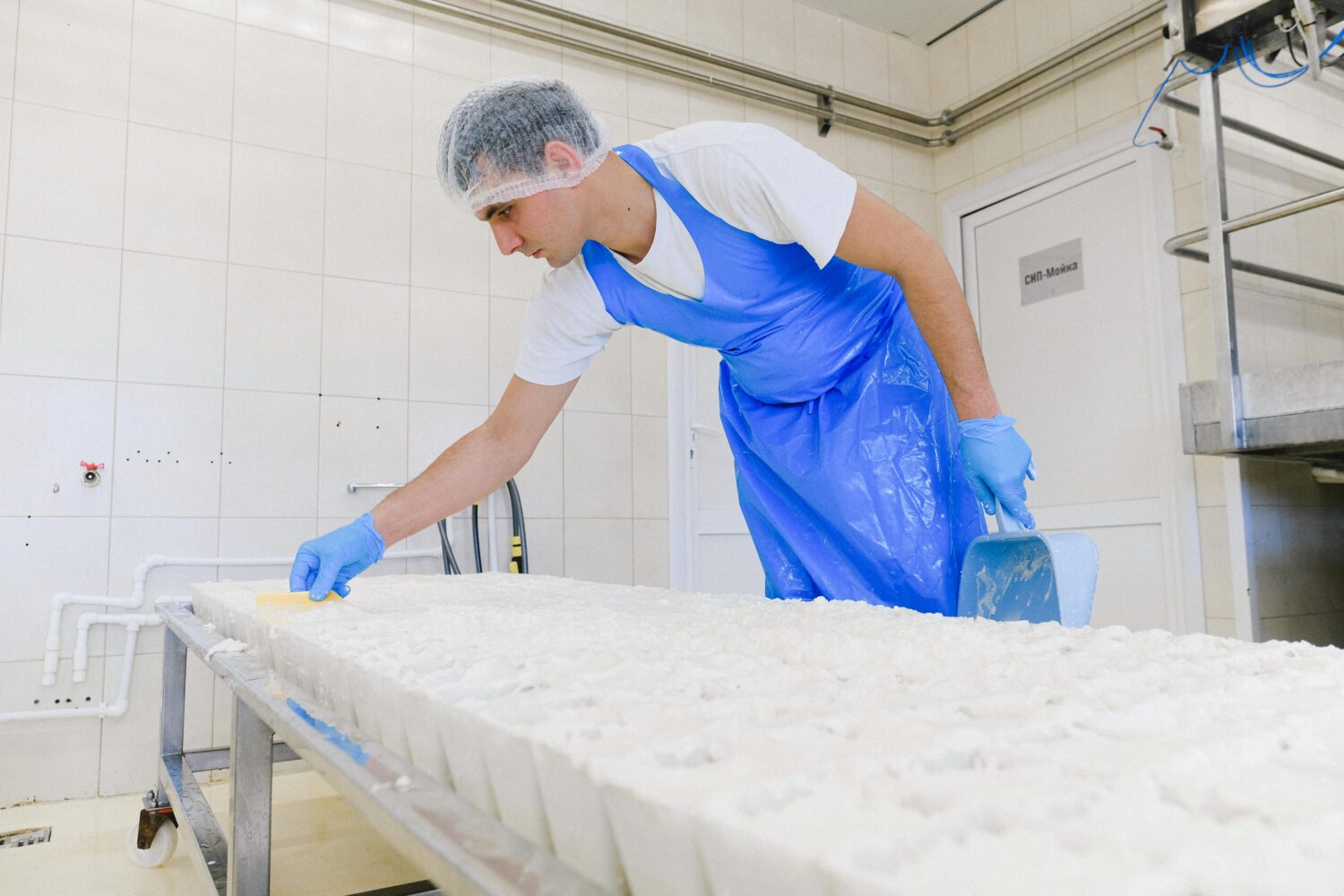
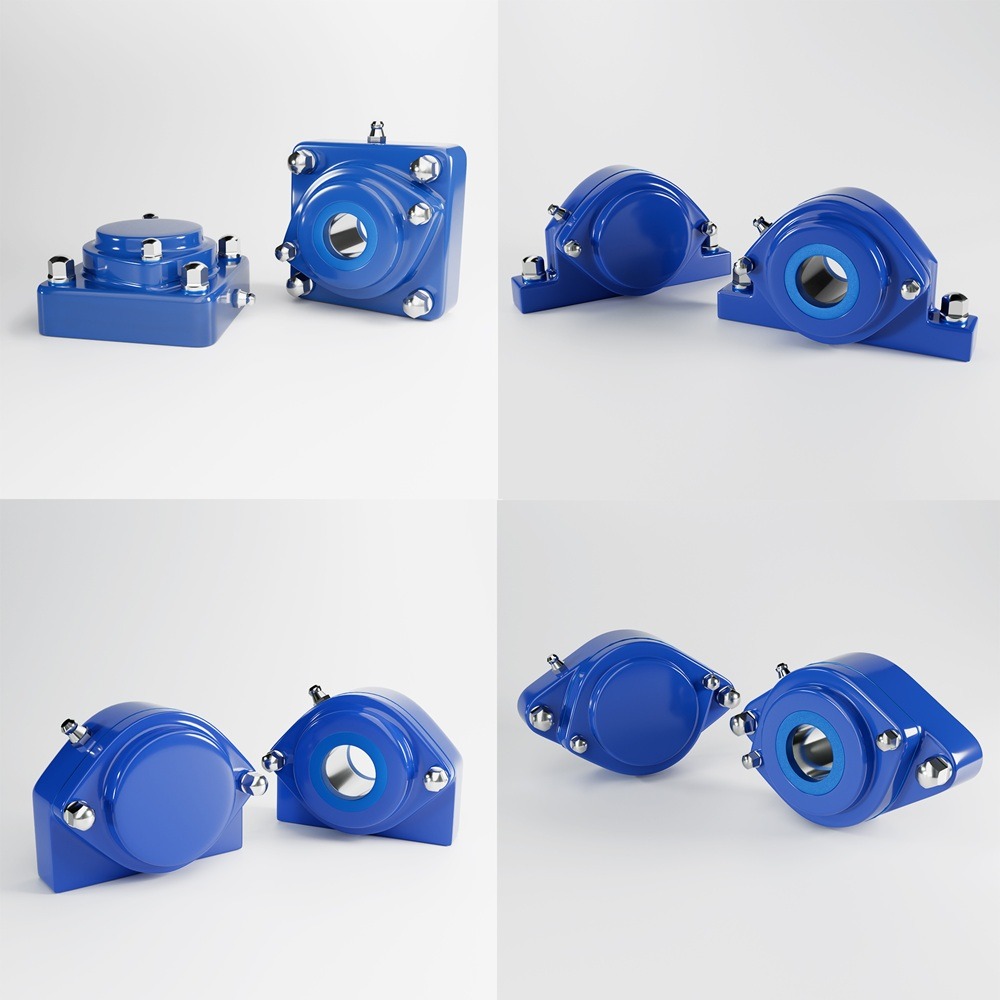
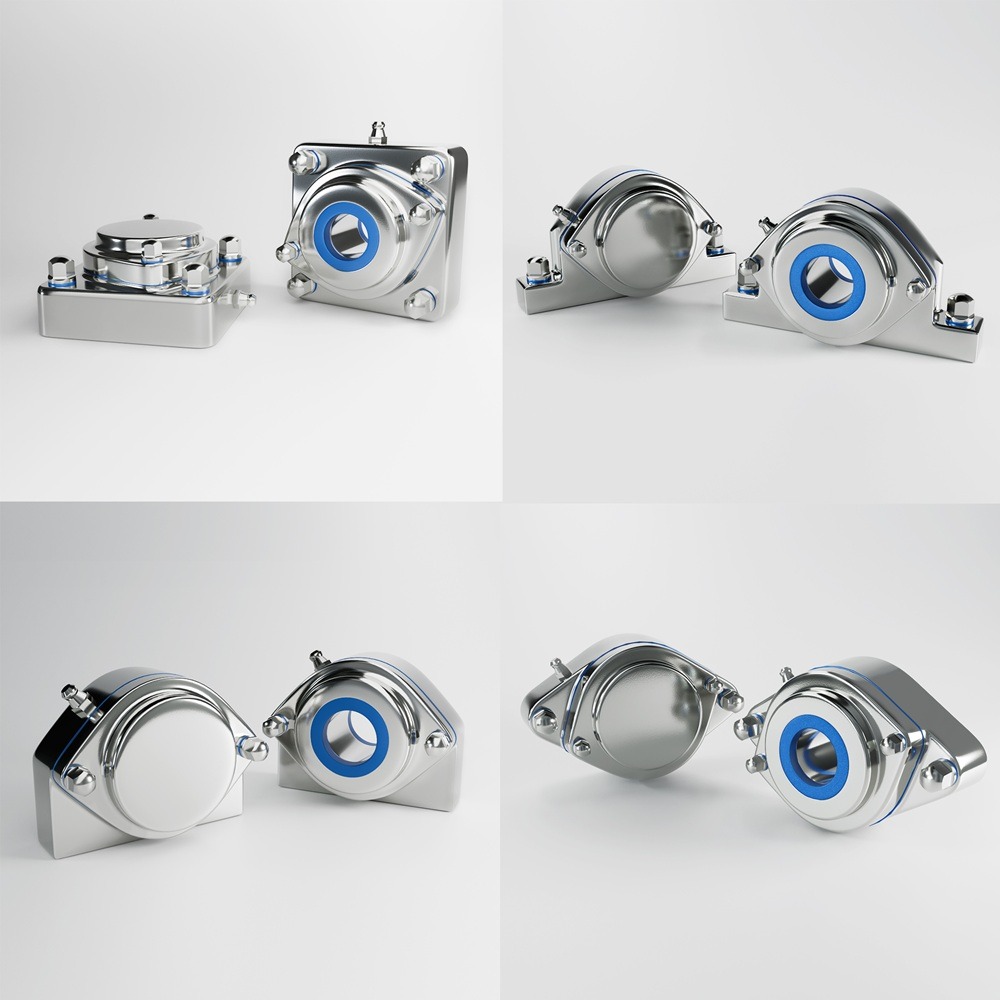
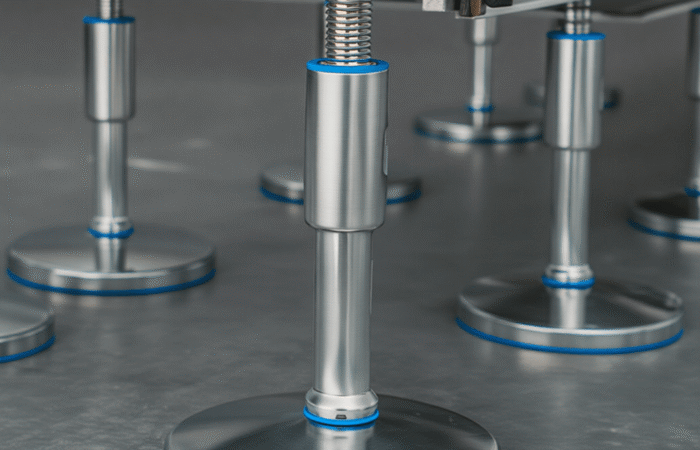
Food safety has never been more critical than in today’s interconnected global food supply chain. Consumers demand transparency, while regulatory bodies enforce stringent compliance standards. Foodborne illnesses, product recalls, and legal liabilities can result in severe financial losses and reputational damage. Addressing these challenges requires proactive strategies that prioritize food safety at every stage of the production and supply chain. Several critical food safety concerns can impact both consumers and businesses: To mitigate risks and maintain a safe food supply, businesses must implement a robust food safety management plan. Below are the top strategies to prioritize food safety effectively: Adopt a comprehensive FSMS based on globally recognized standards like HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points). An FSMS identifies potential hazards, establishes critical control points, and provides guidelines for continuous monitoring. State-of-the-art hygienic machinery plays a critical role in preventing contamination. Components such as stainless steel leveling feet, waterproof bearings, and sanitary conveyor belts are essential for maintaining cleanliness in food production facilities. Well-trained employees are your first line of defense against food safety risks. Regular training programs should emphasize proper hygiene, handling practices, and equipment usage to reduce contamination risks. Routine inspections and audits help identify and address vulnerabilities in your processes. Engage third-party auditors to ensure impartial evaluations and compliance with industry standards. Digital technologies like blockchain, IoT, and AI can enhance traceability and transparency in the supply chain. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of ingredients and finished products, ensuring quality and safety at every step. Regularly monitoring factors such as humidity, temperature, and cleanliness in production facilities can help prevent microbial growth and contamination. Modern sensors and automated systems can provide continuous data to help you make timely adjustments. Innovation is reshaping how companies address food safety challenges. Here are some groundbreaking solutions: Automated cleaning systems and advanced sanitization tools ensure equipment is thoroughly cleaned with minimal downtime. These technologies reduce labor costs while maintaining strict hygiene. Using antimicrobial materials in machinery components, such as leveling feet and conveyor parts, can minimize microbial growth and enhance overall hygiene. Data analytics tools can predict food safety risks by analyzing historical data, helping businesses address potential issues before they arise. Sustainability aligns with food safety by reducing waste and improving operational efficiency. For example, eco-friendly packaging can prevent contamination while meeting consumer demands for sustainable products. Despite best practices, businesses often face challenges in achieving optimal food safety, including: To overcome these challenges, businesses should adopt scalable solutions and collaborate with trusted suppliers and partners. Leadership plays a pivotal role in establishing a food safety culture within organizations. Executive teams must prioritize food safety in decision-making processes and allocate resources to meet compliance requirements. When leadership is committed to safety, employees are more likely to follow suit, creating a unified approach to risk mitigation. Prioritizing food safety offers numerous benefits, including: Addressing food safety concerns requires a proactive and holistic approach. By adopting best practices, leveraging innovation, and fostering a culture of safety, businesses can protect consumers, comply with regulations, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. Investing in food safety isn’t just a regulatory obligation—it’s a strategic advantage that builds trust and ensures long-term success. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Bearing Housings and Direct Mount Bearings is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. Stainless Steel 440 and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.The Importance of Food Safety in Today’s World
Get our catalogue here
See our product line here
Understanding Key Food Safety Concerns
Contamination can occur through physical, chemical, or biological agents. From raw materials to the final product, each stage carries potential risks if not carefully managed.
In food processing environments, cross-contamination is a significant concern. This occurs when pathogens or allergens are unintentionally transferred from one surface, food item, or piece of equipment to another.
Many foodborne pathogens thrive in the “danger zone” (40°F – 140°F). Ensuring proper refrigeration, freezing, and cooking temperatures is essential to prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms.
With ingredients often sourced globally, maintaining visibility across the supply chain is vital. Traceability can prevent issues related to adulteration, fraud, and recalls.
Failing to adhere to food safety certifications such as HACCP, ISO 22000, or BRC Global Standards can lead to fines, recalls, and brand damage.Strategies to Prioritize Food Safety
1. Implement a Food Safety Management System (FSMS)
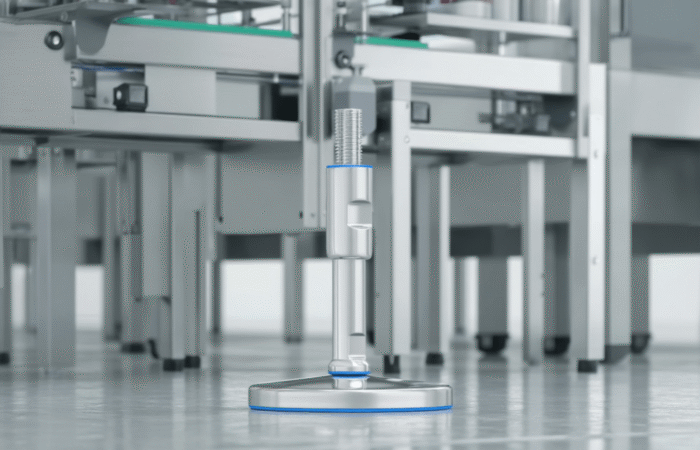
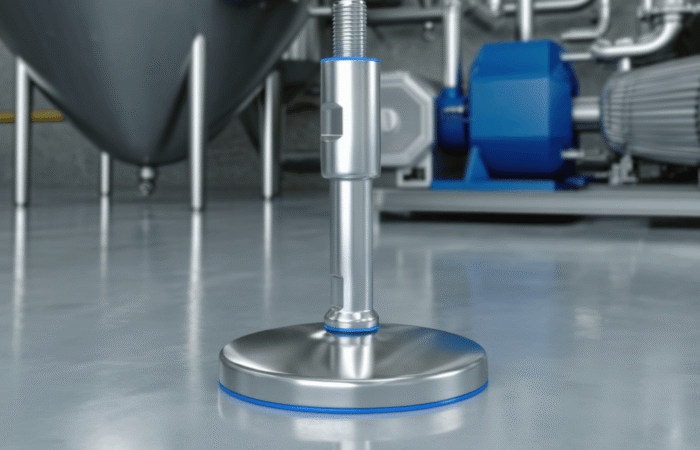
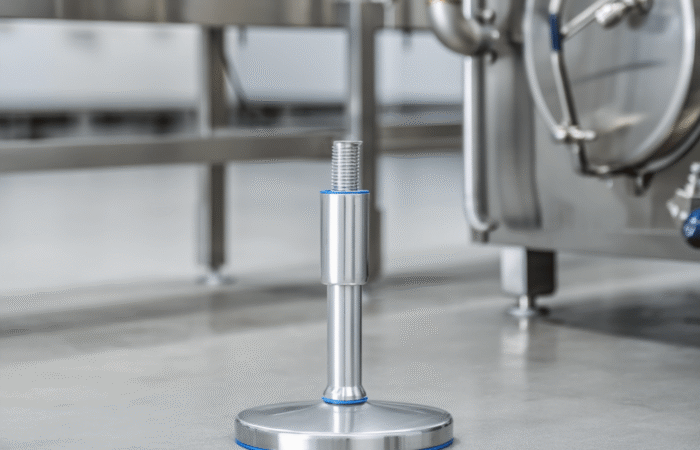
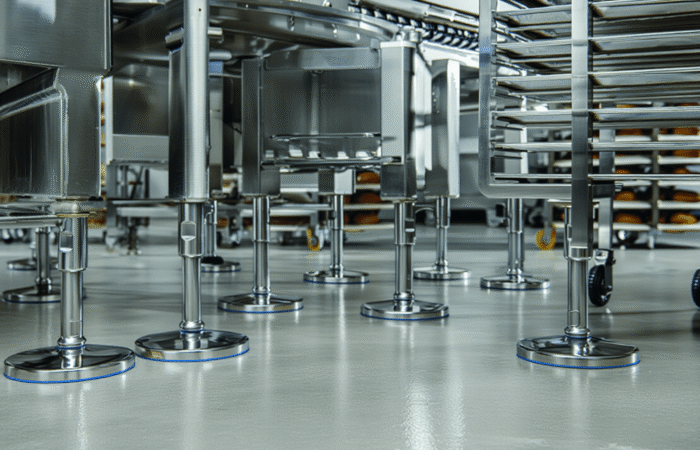
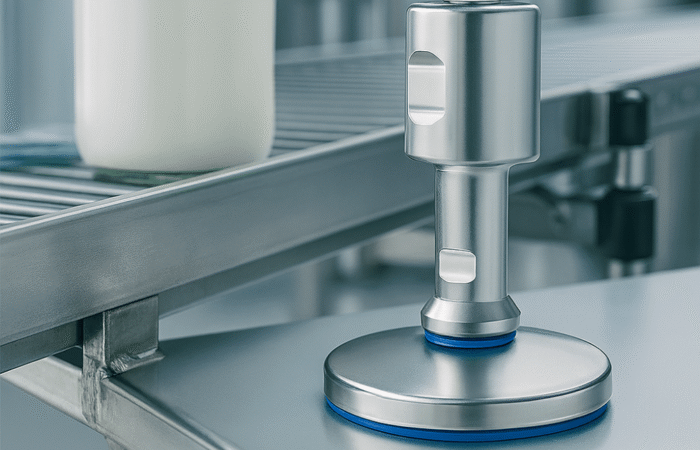
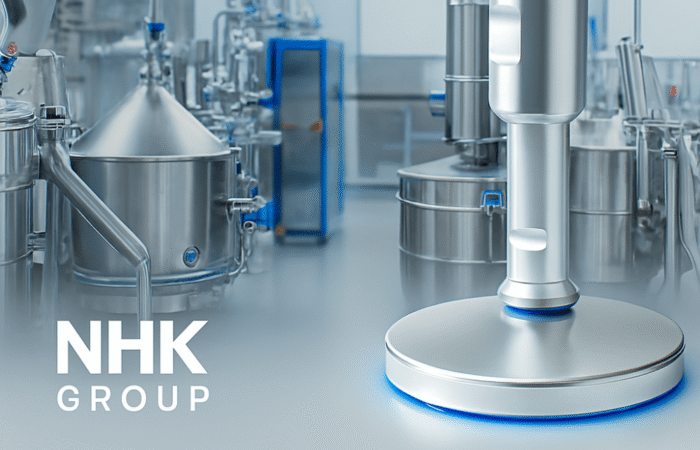
2. Invest in Hygienic Equipment
3. Ensure Employee Training
4. Conduct Regular Audits and Inspections
5. Leverage Technology for Traceability
6. Monitor Environmental Conditions
Addressing Food Safety Concerns Through Innovation
Advanced Cleaning Technologies
Antimicrobial Materials
Predictive Analytics
Sustainable Practices
Common Challenges in Maintaining Food Safety
The Role of Leadership in Food Safety
Benefits of Prioritizing Food Safety
Mastering Food Safety: Effective Strategies to Protect Consumers and Build Trust


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards