Food Security and Access
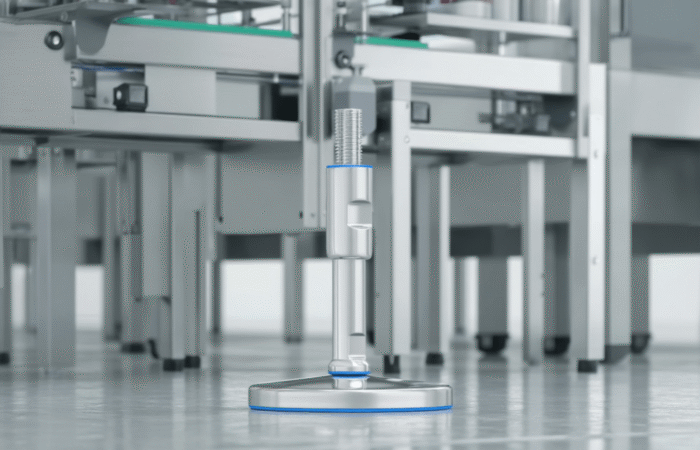
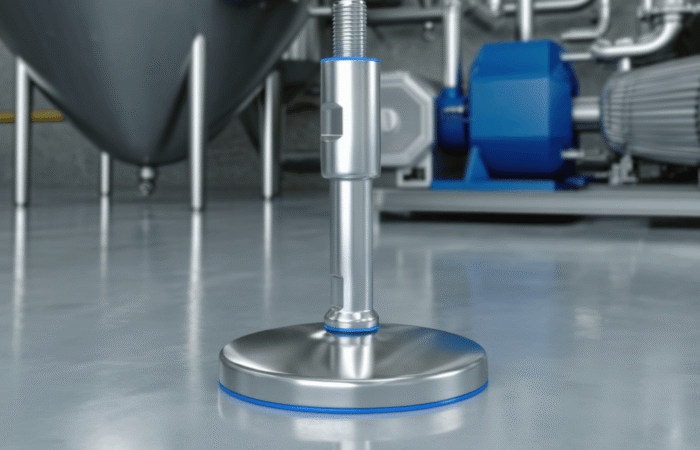
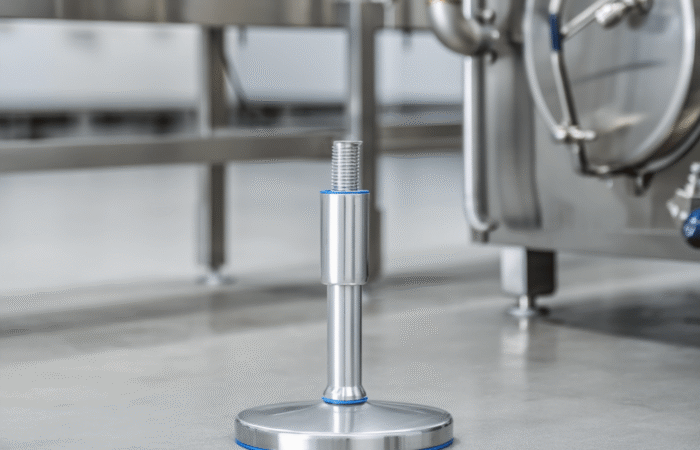
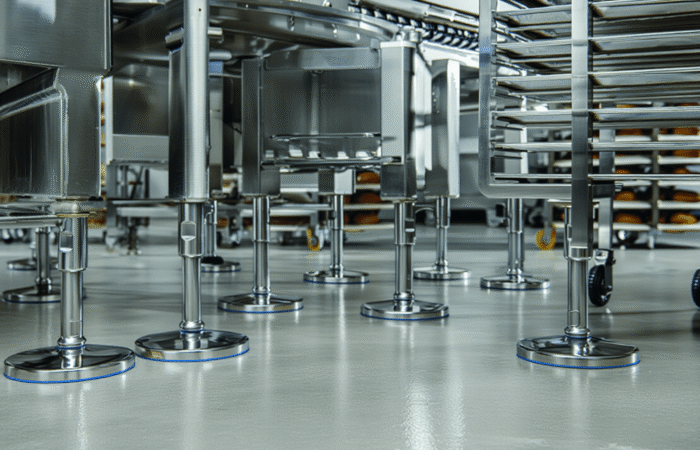
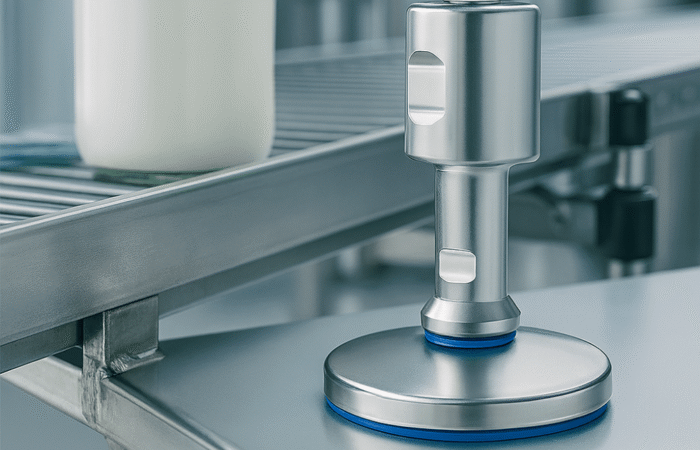
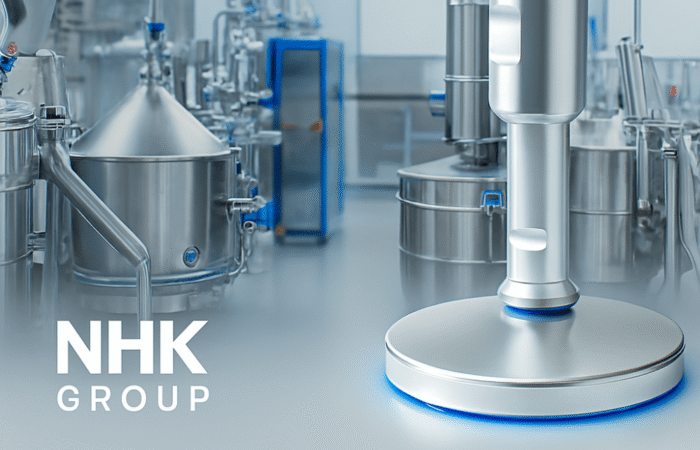
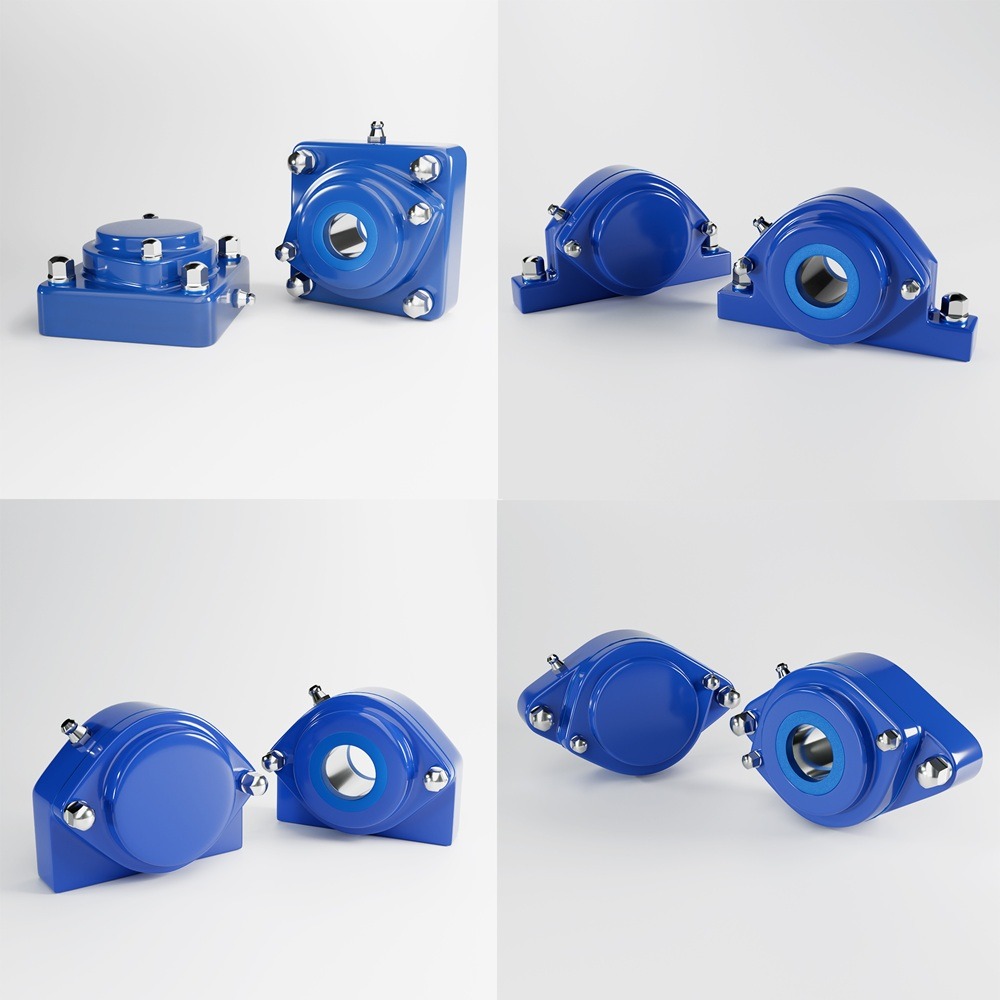
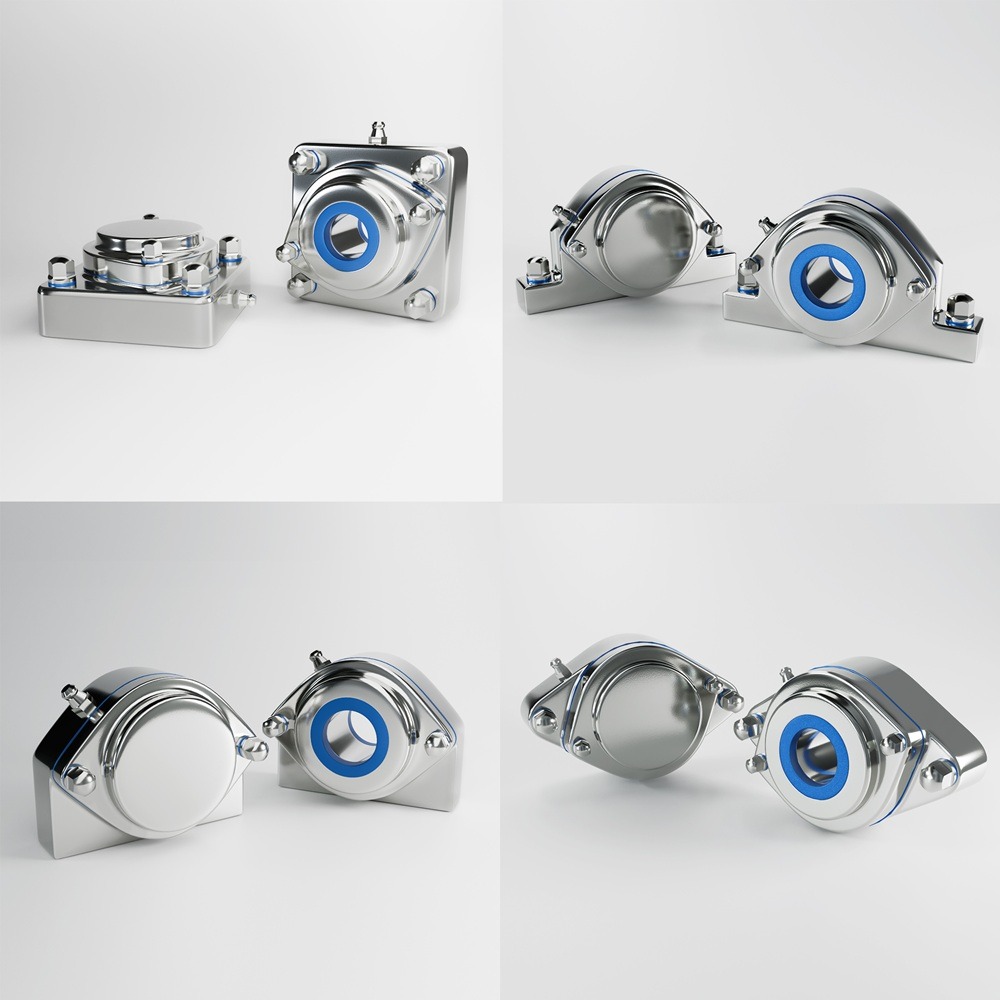
Food security and access to nutritious foods are critical issues affecting millions of people worldwide. As populations grow and climates change, these challenges become increasingly complex, necessitating multifaceted solutions. This article delves into the key challenges related to food security, affordability, and access to nutritious foods, and explores potential strategies to address these issues in various regions. Food security exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs for an active and healthy life. The concept encompasses four key dimensions: Climate change significantly impacts agricultural productivity through extreme weather events, changing precipitation patterns, and rising temperatures. These changes can lead to reduced crop yields, affecting food availability and pushing up prices, making food less affordable for vulnerable populations. Economic inequality is a major barrier to food access. In many regions, particularly in developing countries, poverty limits the ability of individuals and families to purchase sufficient and nutritious food. This disparity is often exacerbated by political instability and economic policies that do not prioritize food security. Inadequate infrastructure, such as poor roads and storage facilities, hampers the efficient distribution of food. This can result in significant food losses, particularly in perishable goods, further straining food availability and access. Rapid population growth in certain regions places additional pressure on the food system. Increasing demand for food can lead to higher prices and reduced availability, making it difficult for low-income households to afford nutritious options. Promoting sustainable agricultural practices can enhance food security by increasing productivity while conserving resources. Techniques such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and integrated pest management can improve yields and resilience to climate change. Governments can implement policies to reduce economic disparities and enhance food security. Social safety nets, such as food subsidies and cash transfer programs, can help low-income families afford nutritious food. Additionally, investment in rural development can create job opportunities and improve access to food. Investing in infrastructure, such as roads, storage facilities, and market systems, can enhance food distribution and reduce losses. This investment ensures that food produced in rural areas can reach urban markets, maintaining stability in supply and prices. Education programs that promote nutritional awareness and food safety can improve food utilization. By understanding the importance of a balanced diet and safe food handling practices, communities can make better food choices and reduce health risks. In Africa, food security is challenged by a combination of climate change, political instability, and poverty. Initiatives such as the Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP) aim to improve agricultural productivity and food security through coordinated efforts across the continent. Asia faces significant food security challenges due to rapid population growth and urbanization. Innovations in technology, such as precision agriculture and genetically modified crops, are being explored to increase productivity and ensure food availability. In Latin America, food security is often hindered by economic inequality and social unrest. Programs focused on rural development and poverty reduction are essential for improving access to nutritious foods in the region. While food security is generally high in North America and Europe, pockets of food insecurity still exist, particularly among low-income populations. Efforts to reduce food waste and promote local food systems are key strategies in these regions. Food security is a fundamental issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Ensuring that everyone has access to affordable, nutritious food is crucial for the well-being and development of societies. However, numerous challenges impede food security, particularly in developing regions. These challenges include economic disparities, climate change, political instability, and logistical issues. This article delves into these challenges and examines four case studies that highlight various aspects of food security and access across different regions. Food security is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) as the condition when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life. This multifaceted issue is influenced by several factors: In Sub-Saharan Africa, food security is a persistent challenge exacerbated by climate change. Droughts and floods significantly impact agricultural productivity. Programs such as the World Food Programme’s (WFP) efforts to provide drought-resistant seeds and irrigation systems have shown promise. These initiatives help farmers maintain crop yields despite adverse weather conditions, thus improving food availability. South Asia faces significant issues related to food affordability. A large portion of the population lives below the poverty line, making it difficult to afford nutritious food. India, for example, has implemented the Public Distribution System (PDS), which provides subsidized grains to low-income families. While effective in theory, the PDS faces challenges such as corruption and inefficiency, which hinder its impact. In Latin America, urbanization and economic inequality contribute to food insecurity. In Brazil, the “Zero Hunger” program aims to eradicate hunger through a combination of direct food assistance, income support, and agricultural development. This multi-faceted approach has led to a significant reduction in hunger, demonstrating the importance of comprehensive policies that address both immediate and long-term needs. Even in developed regions like North America, food insecurity exists, particularly among low-income households. The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) in the United States provides financial assistance for purchasing food. However, stigma and administrative barriers sometimes limit its effectiveness. Efforts to streamline the application process and reduce stigma have been critical in improving access to nutritious food for vulnerable populations. Addressing food security and access requires a holistic approach that considers economic, environmental, and social factors. The case studies of Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, Latin America, and North America illustrate that while the challenges vary by region, the need for coordinated and innovative solutions is universal. By implementing targeted programs and policies, it is possible to make significant strides toward ensuring that all people have access to affordable, nutritious food. Addressing food security and access to nutritious foods requires a comprehensive approach that considers the unique challenges of each region. By promoting sustainable agricultural practices, implementing supportive economic policies, investing in infrastructure, and raising awareness about nutrition, we can move closer to a world where everyone has access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food. Ensuring food security is not just a matter of meeting dietary needs; it is fundamental to achieving overall health, economic stability, and social well-being. Collaborative efforts between governments, international organizations, and local communities are essential to creating sustainable solutions that address the root causes of food insecurity. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Block Units and Flange Bearing Units is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. 440C Steel and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Addressing Challenges Related to Food Security, Affordability, and Access to Nutritious Foods
Understanding Food Security
Challenges to Food Security
1. Climate Change
2. Economic Disparities
3. Infrastructure and Logistics
4. Population Growth
Addressing Food Security Challenges
1. Sustainable Agricultural Practices
2. Economic Policies and Social Safety Nets
3. Improved Infrastructure
4. Education and Awareness
Regional Perspectives
Africa
Asia
Latin America
North America and Europe
Food Security and Access
Understanding Food Security and Its Challenges
Case Study 1: Sub-Saharan Africa
Case Study 2: South Asia
Case Study 3: Latin America
Case Study 4: North America
Ensuring food security and access


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards