Engage Large Teams in Maintaining Food Safety Standards
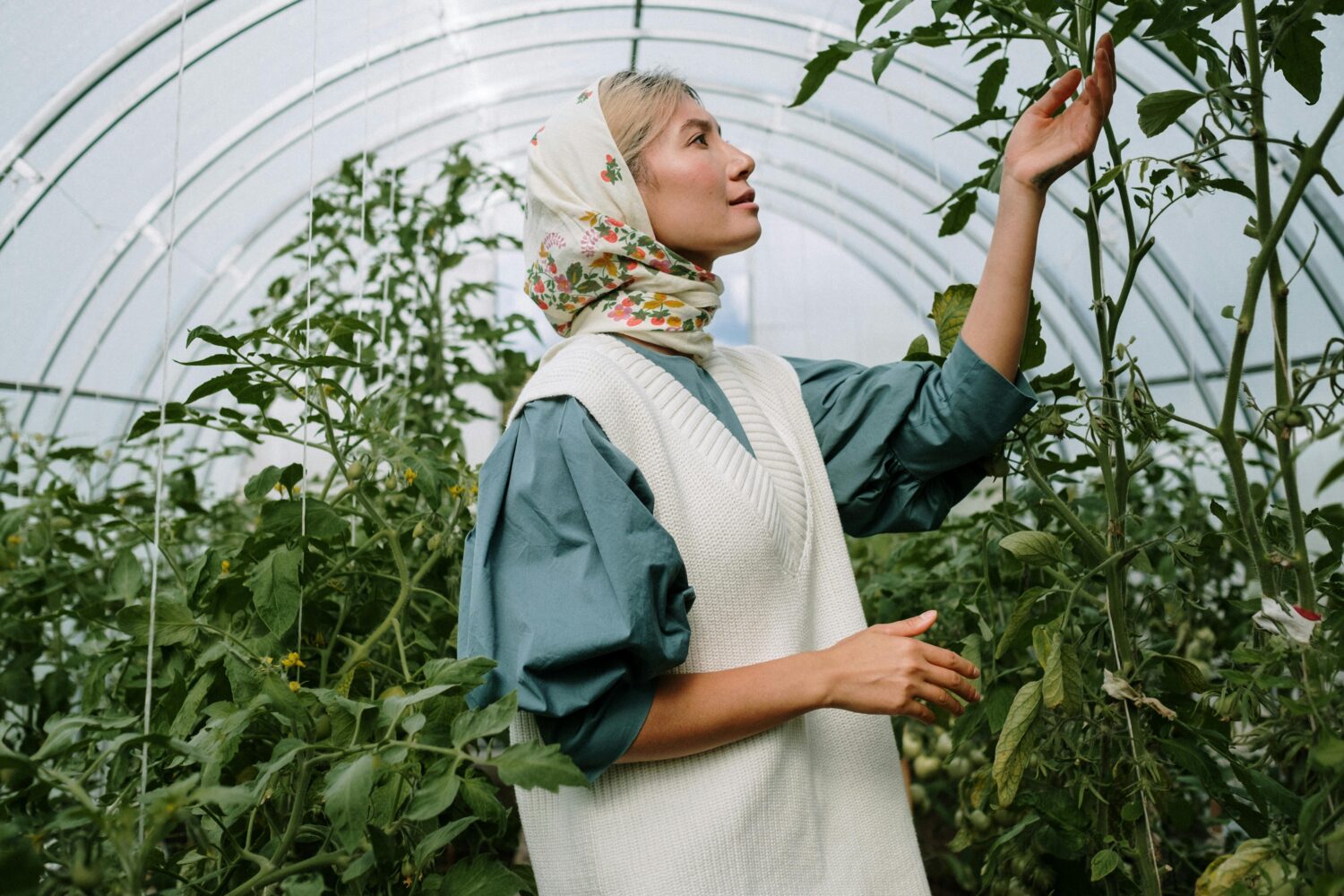
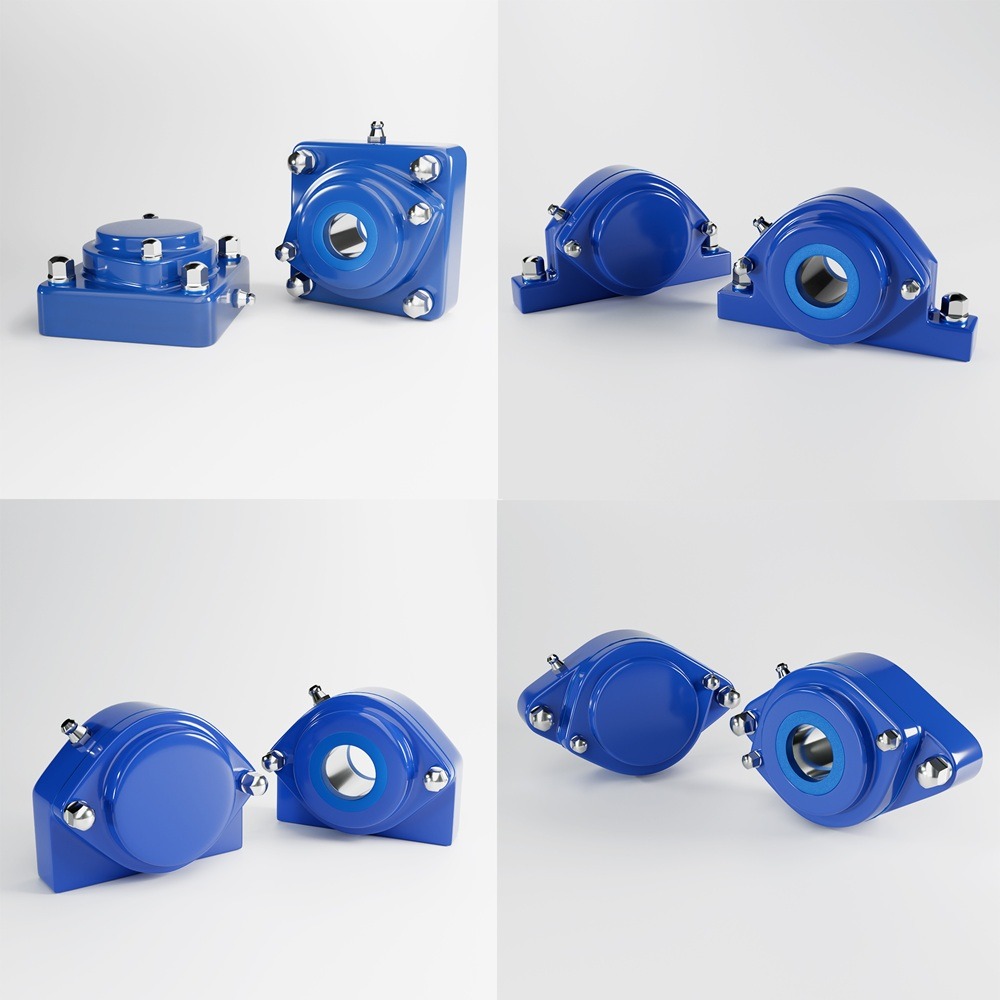
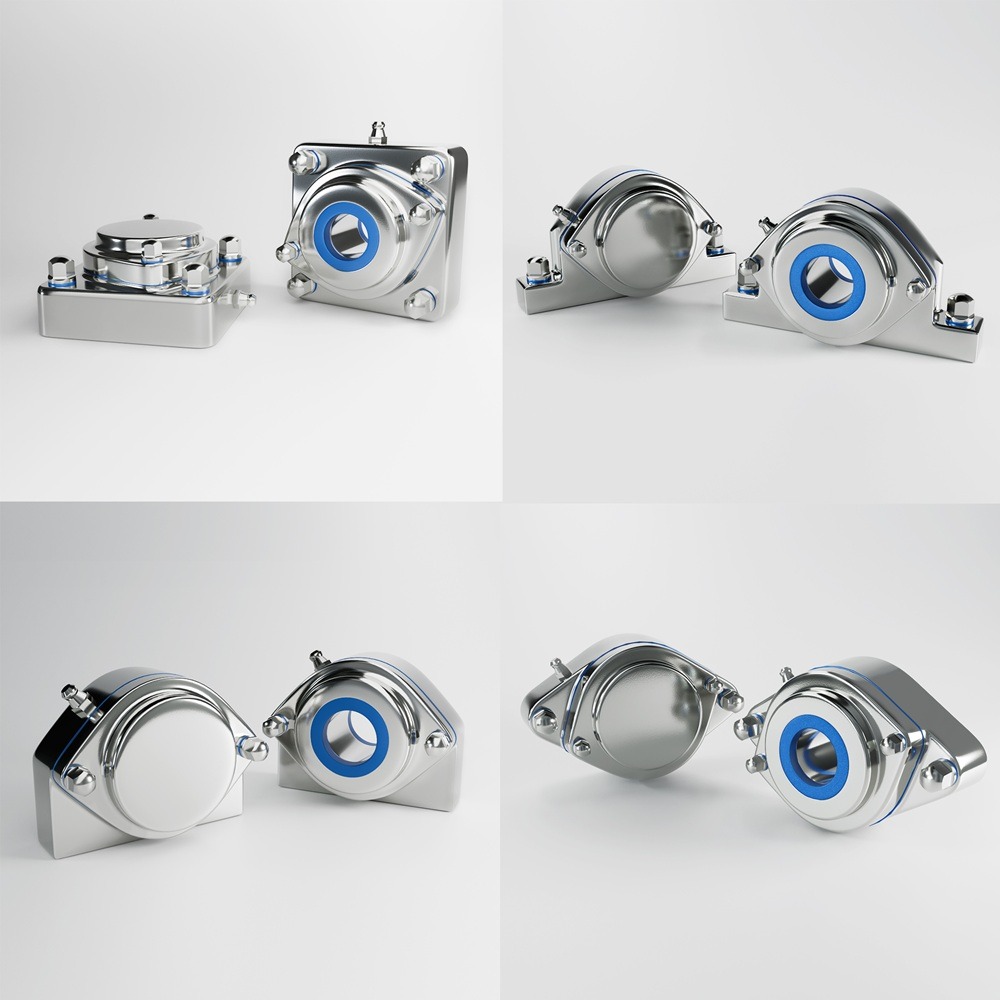
Food safety is the cornerstone of any food processing or manufacturing operation. With increasing regulatory requirements and consumer demand for hygienic products, maintaining food safety standards is not just a compliance issue but also a strategic priority. Engaging large teams in this mission, however, can be challenging. This article delves into practical and effective strategies to ensure your workforce is aligned, motivated, and committed to upholding food safety standards. Maintaining food safety standards in operations involving large teams requires a coordinated approach. Large groups often face challenges such as inconsistent communication, varying levels of commitment, and knowledge gaps among employees. These hurdles can compromise safety protocols and expose the organization to risks, including contamination, regulatory penalties, and loss of consumer trust. Creating a culture where food safety is a shared responsibility is crucial for engagement. Leadership must prioritize food safety as a core value and inspire employees to take ownership of their role in maintaining standards. Clear, consistent communication ensures that food safety standards are understood and implemented by all team members. Training is the backbone of an effective food safety strategy. A well-trained team is more likely to follow safety protocols and identify potential risks. Continuous monitoring of processes ensures accountability and adherence to food safety practices. Collaboration between departments promotes a holistic approach to food safety. Empowered employees feel more invested in the organization’s success. Technology can play a pivotal role in engaging large teams in food safety. From automated monitoring systems to training platforms, leveraging the right tools can simplify compliance and ensure consistent adherence to safety standards. Change management is essential when introducing new food safety initiatives. Resistance from employees is common but can be mitigated with a thoughtful approach. Tracking the effectiveness of your engagement strategies is critical for continuous improvement. Regular evaluations ensure that your efforts are aligned with food safety objectives. Engaging large teams in maintaining food safety standards is a complex yet achievable goal. By fostering a culture of accountability, leveraging technology, and investing in communication and training, organizations can create a workforce that is committed to excellence in food safety. Remember, the foundation of a successful food safety program is people, and empowering them is the key to long-term success. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Blocks and Direct Mount Bearings is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. Stainless Steel 440 and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Empowering Large Teams to Uphold Food Safety Standards: Strategies for Success
Get our catalogue here
See our product line here
The Importance of Food Safety in Large Teams
Key Challenges:
Strategies to Engage Large Teams in Food Safety
1. Build a Strong Food Safety Culture
2. Effective Communication is Key
3. Comprehensive Training Programs
4. Implement Robust Monitoring Systems
5. Foster Collaboration Across Departments
6. Empower Employees with Responsibility
Get our catalogue here
See our product line here
Technology’s Role in Food Safety Engagement
Examples of Technology in Action:
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Steps to Address Resistance:
Measuring the Impact of Engagement
Key Metrics to Track:
How to Effectively Engage Large Teams in Maintaining Food Safety Standards


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards