Designing a Food-Grade Hygienic Conveyor System
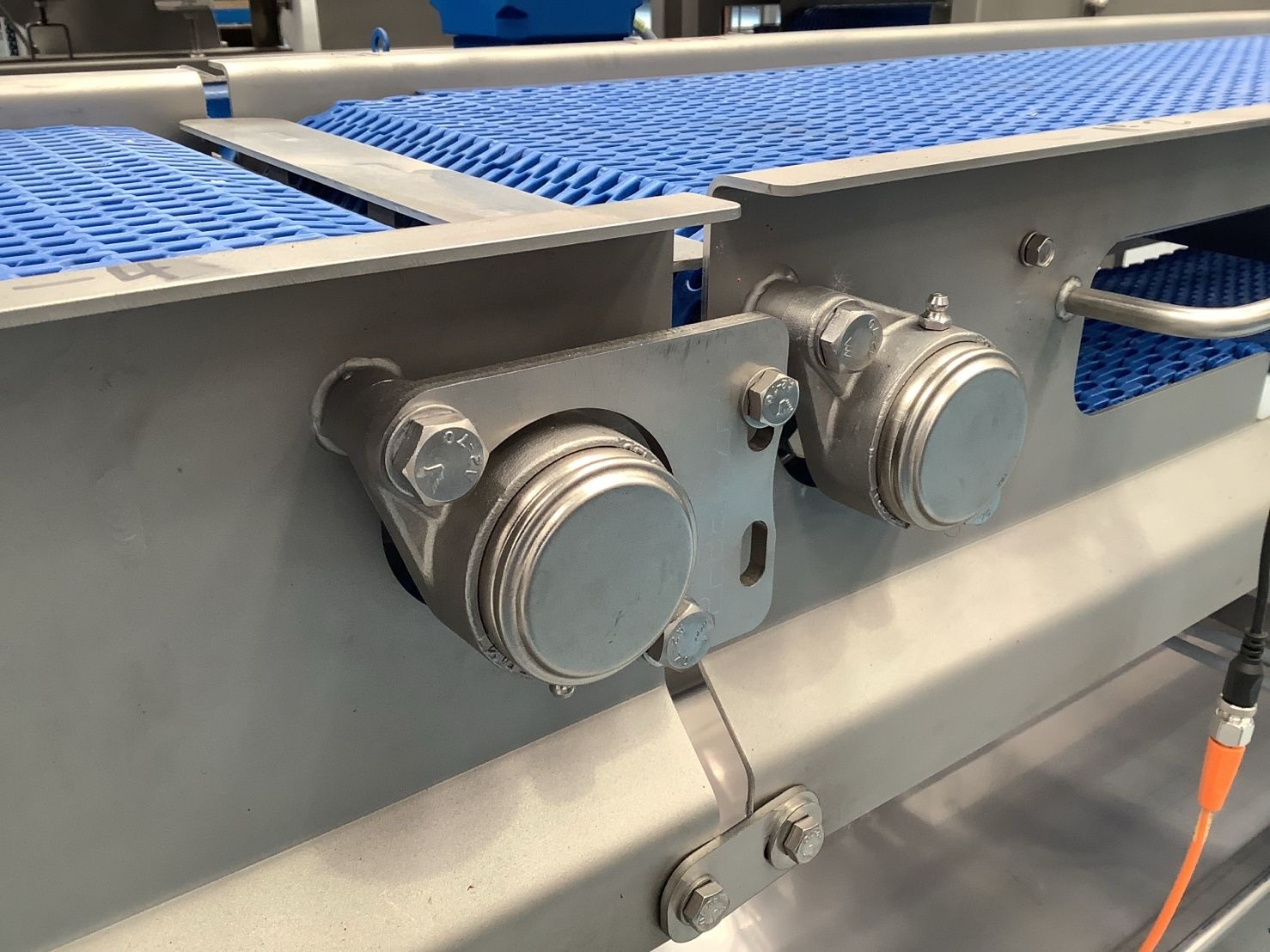
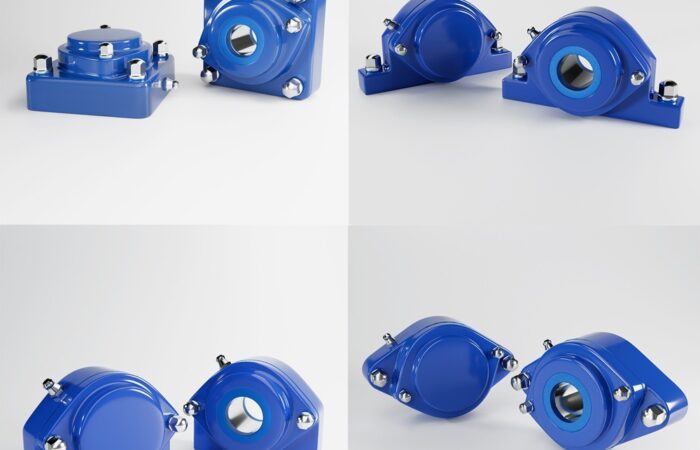
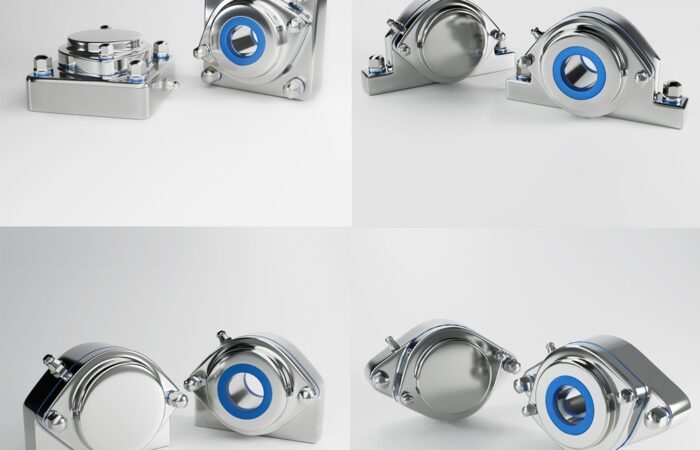
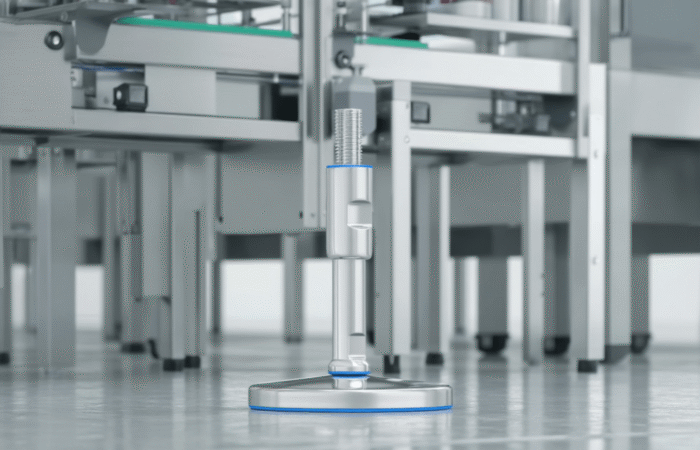
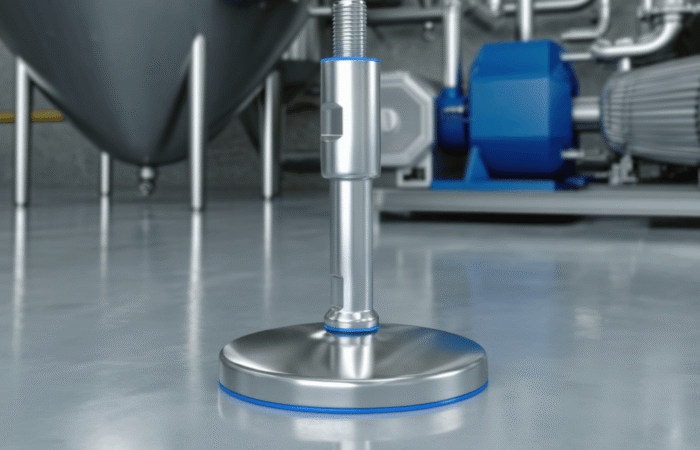
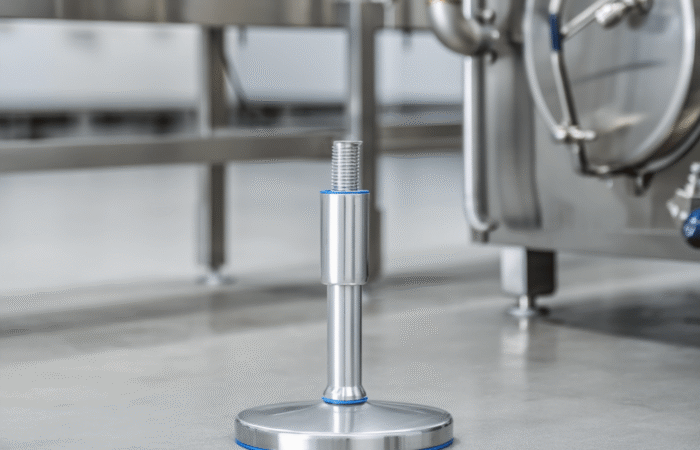
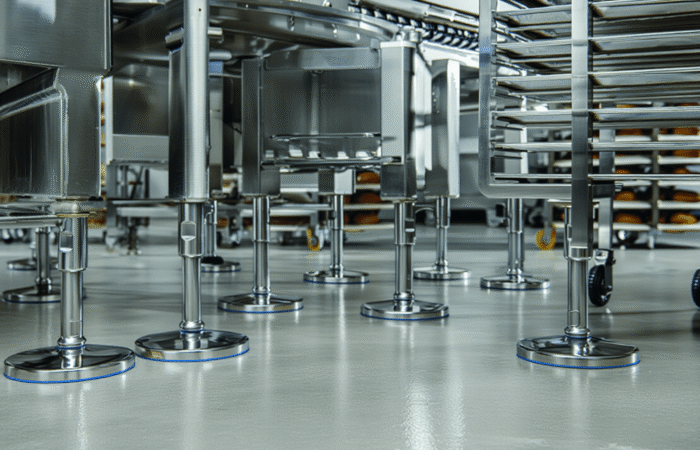
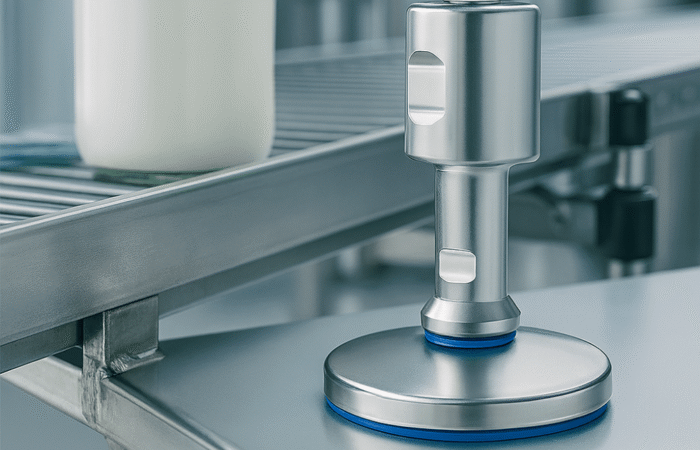
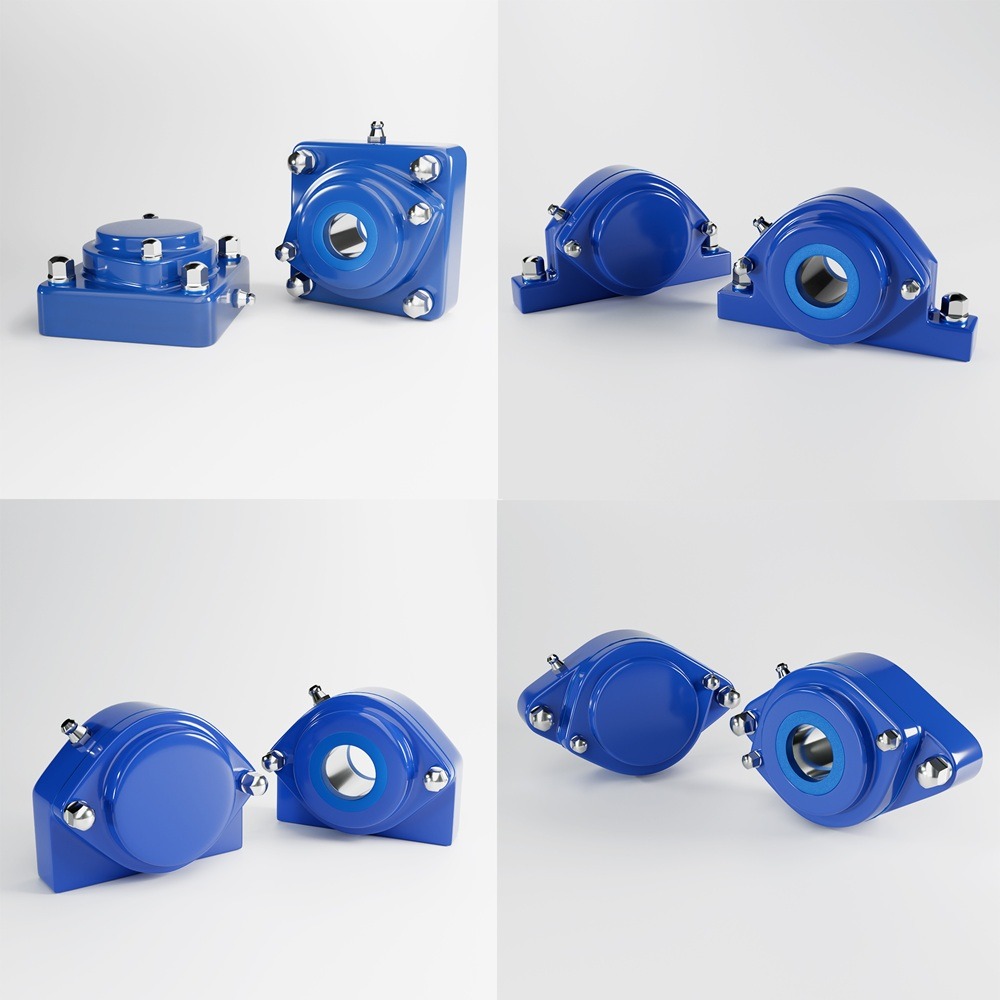
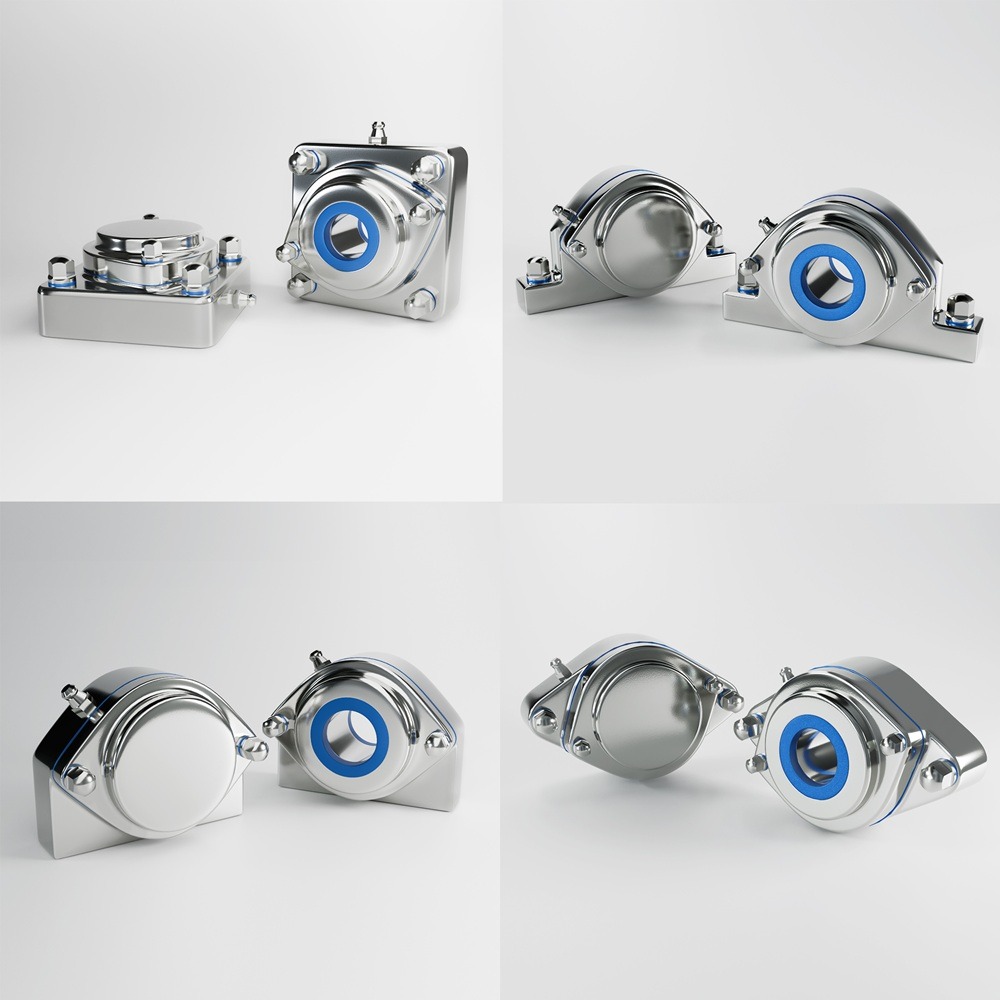
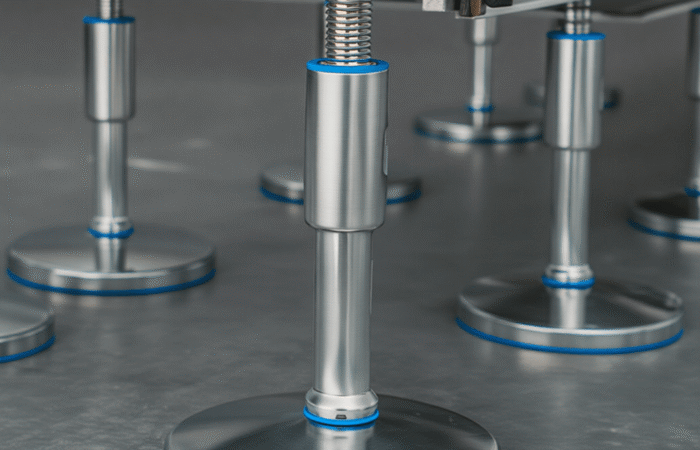
Designing a food-grade hygienic conveyor system with sleek, stainless steel construction involves several critical considerations to ensure compliance with food safety standards and efficiency in operation. Here’s an outline of the key features and considerations: By incorporating these features and following a thorough design process, you can create a food-grade hygienic conveyor system that meets stringent hygiene standards and ensures efficient, safe, and reliable operation. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Blocks and Flange Bearings is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. Stainless Steel 440 and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Compliance with food safety standards and operational efficiency
Food safety standards and efficiency in operation.
Key Features:
Example Components:
Design Process:


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards