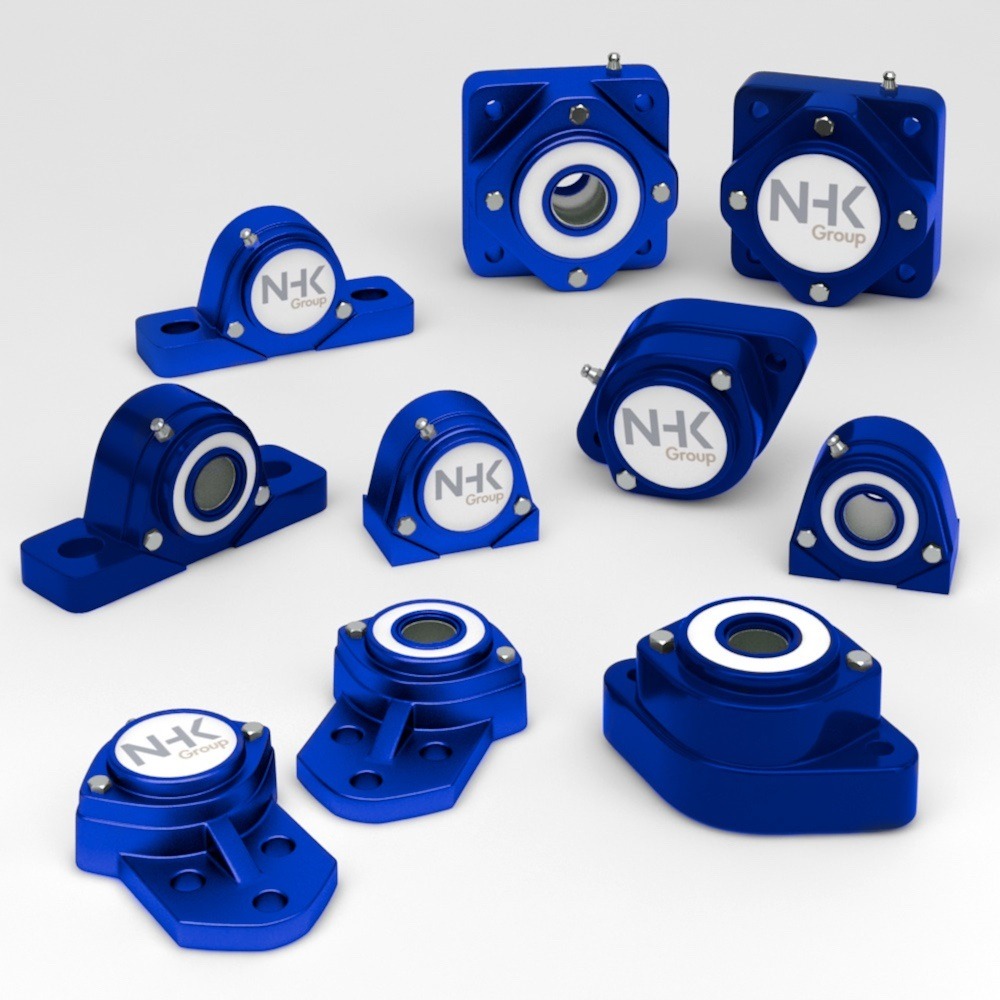
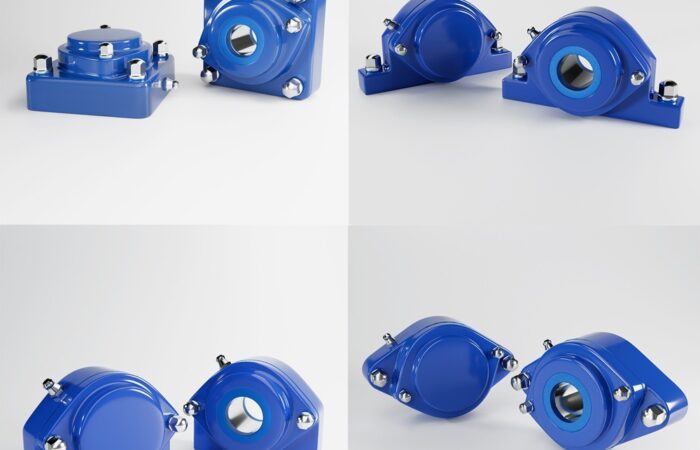
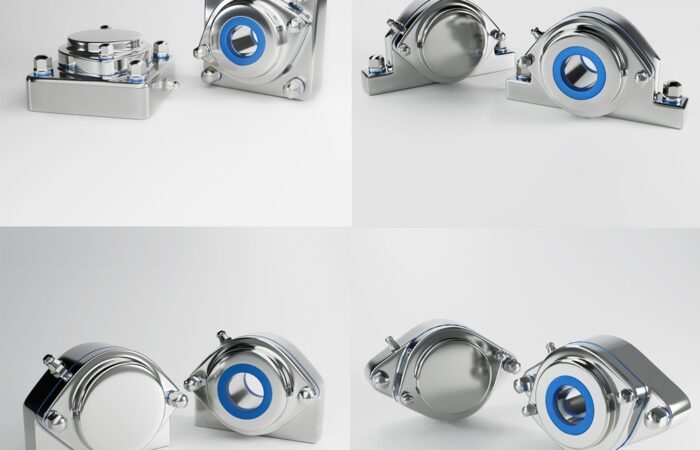
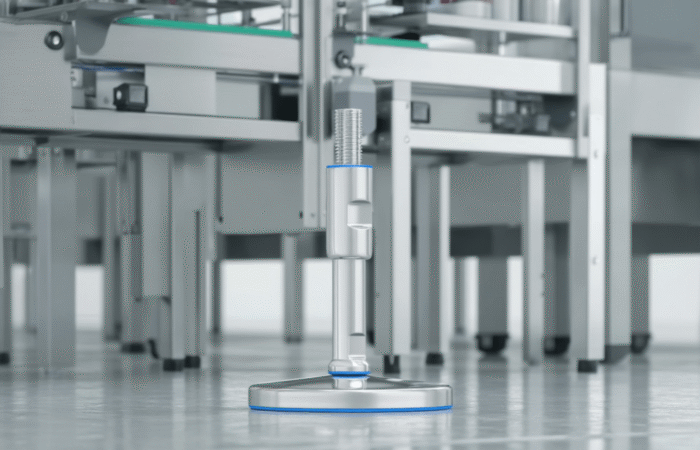
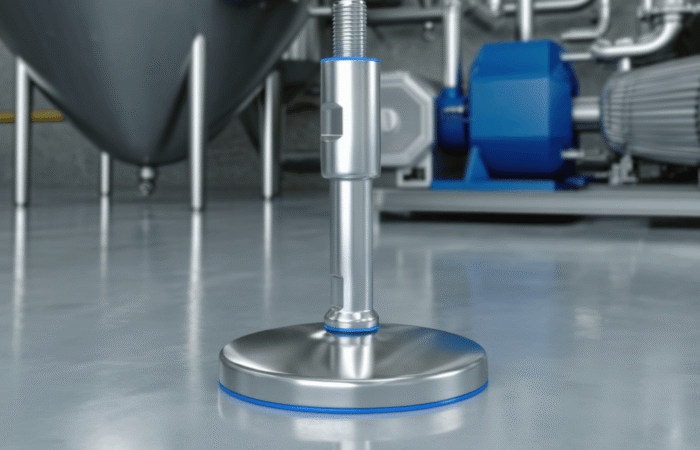
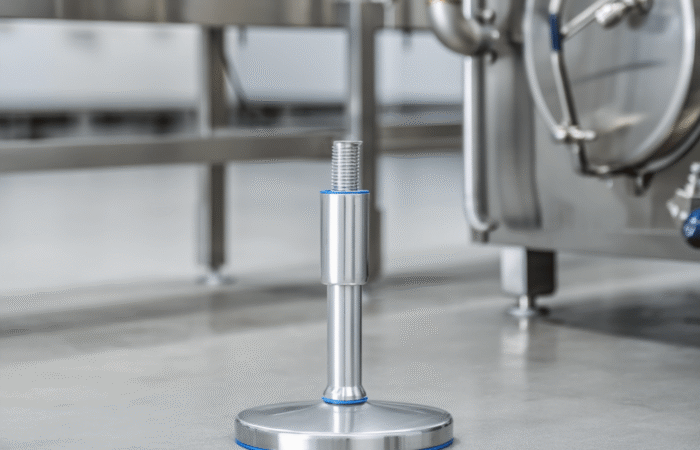
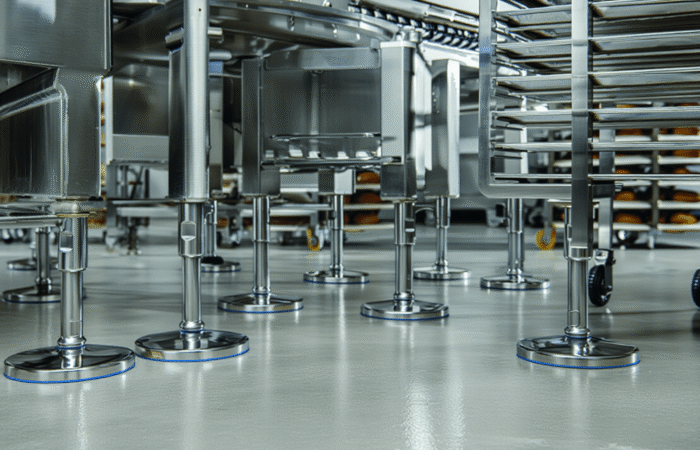
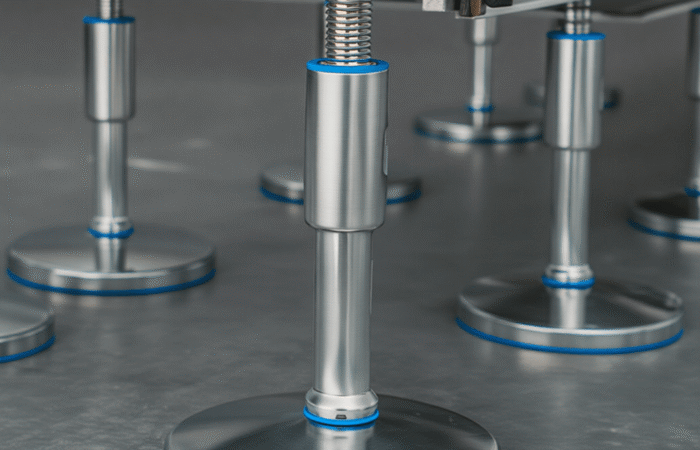
Bearing Unit Engineering: 420 vs. 440 Stainless Steel
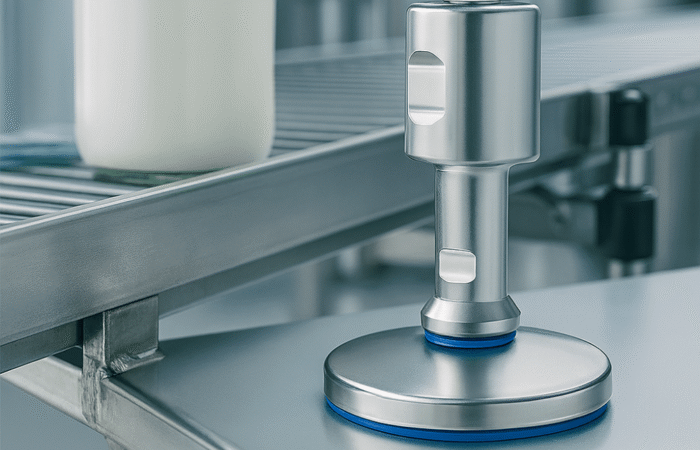
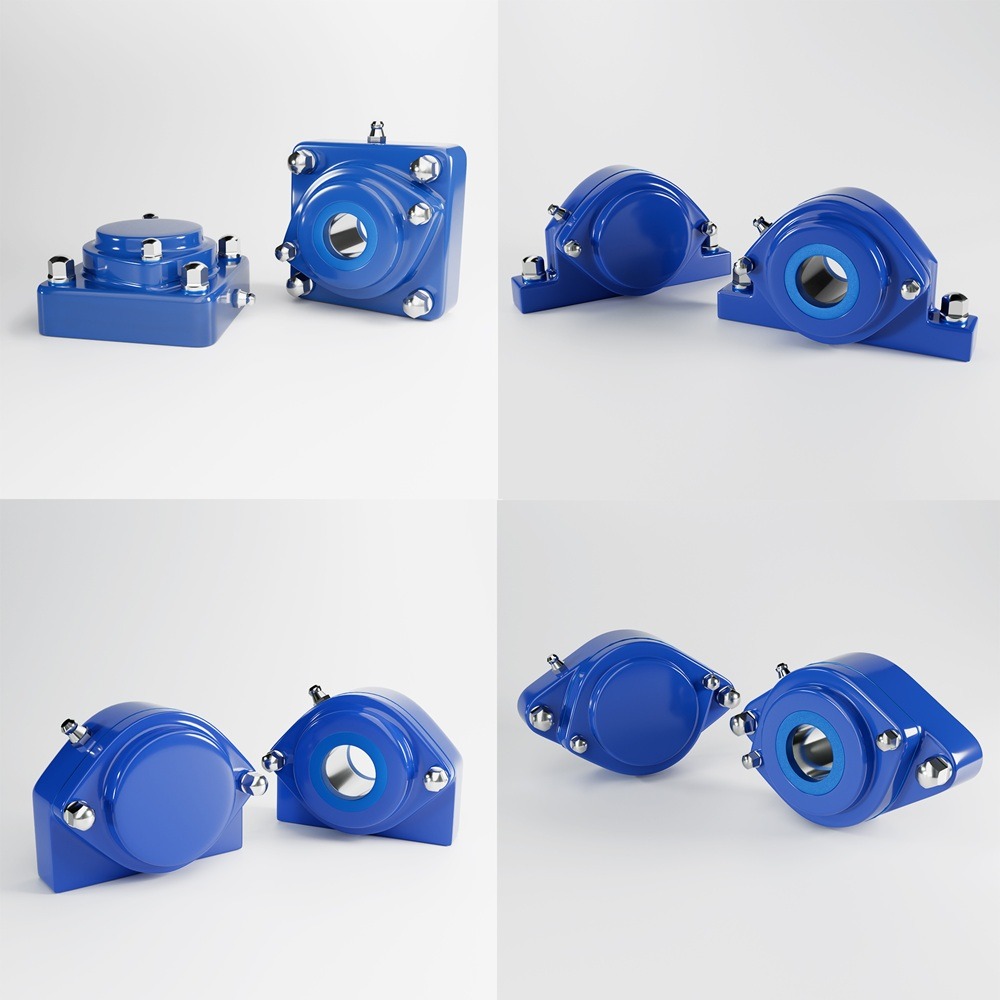
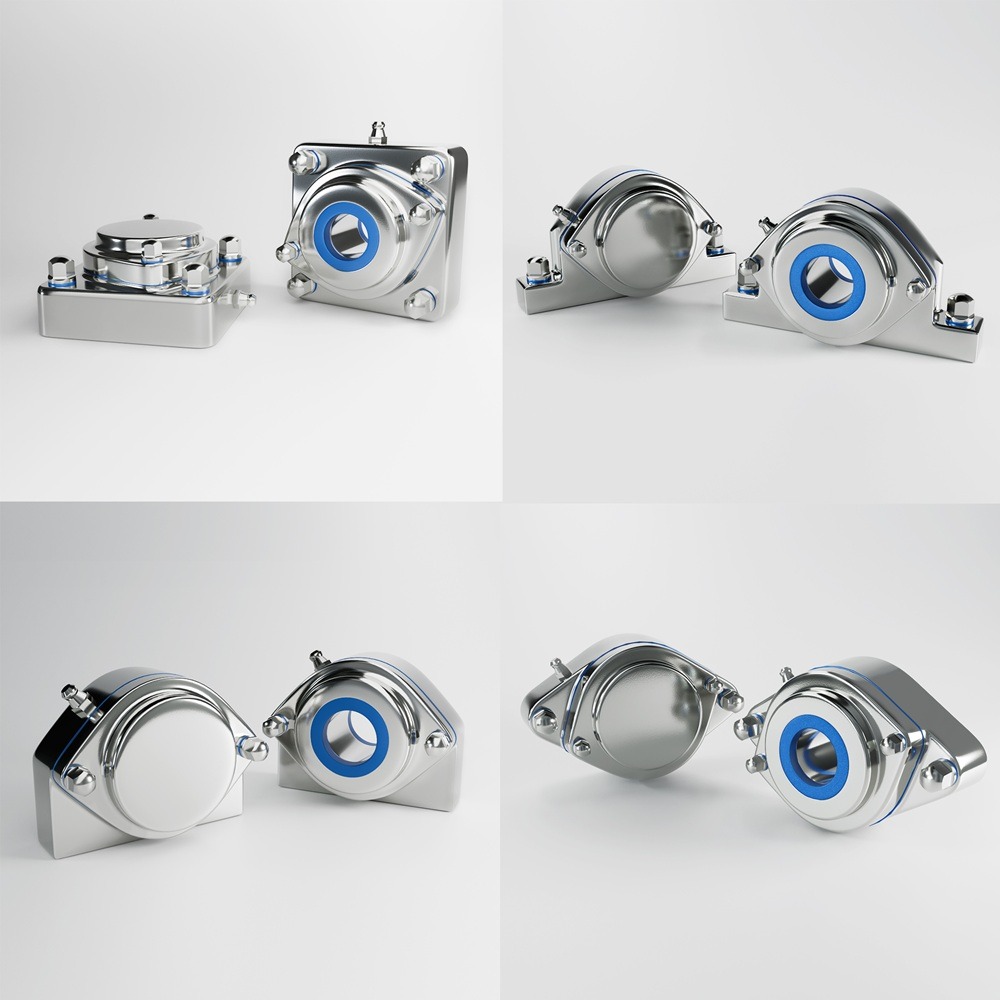
In an era where machinery performance and durability define industrial success, strategic planning in bearing unit engineering has become paramount. Industries such as food processing, pharmaceutical, and packaging demand components that not only meet stringent hygiene standards but also offer longevity and resistance to wear. Among the essential materials for bearing units, 420 and 440 stainless steel have emerged as popular choices. Understanding their differences, strengths, and ideal applications is vital for manufacturers and facility operators looking to future-proof their operations. Bearing units are crucial in supporting rotational and linear movement in machines, ensuring smooth operation, reduced friction, and optimal performance. Their role extends beyond mechanics as they also contribute to energy efficiency, safety, and compliance with hygiene regulations. The selection of materials for these components significantly impacts their reliability, particularly in extreme environments. 420 stainless steel, a martensitic steel, is well-regarded for its excellent hardness and corrosion resistance. It contains approximately 12-14% chromium, which forms a protective layer against oxidation. When heat-treated, 420 stainless steel achieves high levels of strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for applications where sharp edges, cutting surfaces, or high contact pressure exist. 440 stainless steel is part of the high-carbon martensitic stainless steel family. It contains higher levels of chromium (16-18%) and carbon (0.95-1.20%) compared to 420 stainless steel. This composition results in superior corrosion resistance, hardness, and edge retention. Commonly used in bearing units for harsh or extreme environments, 440 stainless steel offers long-term durability in conditions involving high moisture, chemicals, or sanitation protocols. Sealed stainless steel 420 vs 440 bearing units Mounted stainless steel 420 vs 440 bearing units Future-proofing bearing units is not solely about material selection but also about aligning production needs with industry trends, regulatory demands, and long-term sustainability goals. Here are strategic considerations for bearing unit engineering: Strategic planning in bearing unit engineering is shifting towards smart, sustainable, and predictive maintenance models. The following trends are driving innovation: Strategic planning in bearing unit engineering involves a comprehensive approach to material selection, hygiene compliance, and lifecycle cost analysis. While 420 stainless steel is an economical option for moderate applications, 440 stainless steel delivers unparalleled corrosion resistance and durability for harsh, hygienic environments. Each has its strengths, and the choice should be guided by operational needs, regulatory compliance, and long-term cost considerations. Forward-thinking manufacturers are now integrating IoT technology and predictive maintenance strategies to extend the life of bearing units, reduce costs, and support sustainability. Whether the goal is to optimize performance in food production, pharmaceutical processing, or marine applications, selecting the right stainless steel is a pivotal step toward future-proofing machinery and ensuring operational success. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Block Units and Flange Bearing Units is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. 440 Stainless Steel and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Future-Proof Bearing Unit Engineering
Get our catalogue here
See our product line here
The Role of Bearing Units in Modern Industry
The Composition and Characteristics of 420 Stainless Steel
Key Benefits of 420 Stainless Steel for Bearing Units:
The Composition and Characteristics of 440 Stainless Steel
Key Benefits of 440 Stainless Steel for Bearing Units:
420 Stainless Steel vs. 440 Stainless Steel: A Comparative Analysis
Feature 420 Stainless Steel 440 Stainless Steel Chromium Content 12-14% 16-18% Carbon Content 0.15% 0.95-1.20% Corrosion Resistance Moderate High Hardness High after heat treatment Higher, even in untreated state Wear Resistance Excellent Superior Cost Lower cost Higher cost Applications Dry environments, moderate hygiene Harsh, wet, and highly hygienic areas 420 Stainless Steel vs. 440 Stainless Steel: Hardness and Wear Resistance
420 Stainless Steel:
440 Stainless Steel:
Strategic Planning for Bearing Unit Engineering
Risk Mitigation in Material Selection
Compliance with Hygiene Standards
Performance in Extreme Environments
Lifecycle Cost Analysis
Technology Integration
Applications of 420 and 440 Stainless Steel Bearing Units
420 Stainless Steel Applications
440 Stainless Steel Applications
Future Trends in Bearing Unit Engineering
Strategic Planning and Future-Proof Bearing Unit Engineering


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards