Adapt to Industry Trends for Success in Hygienic Manufacturing
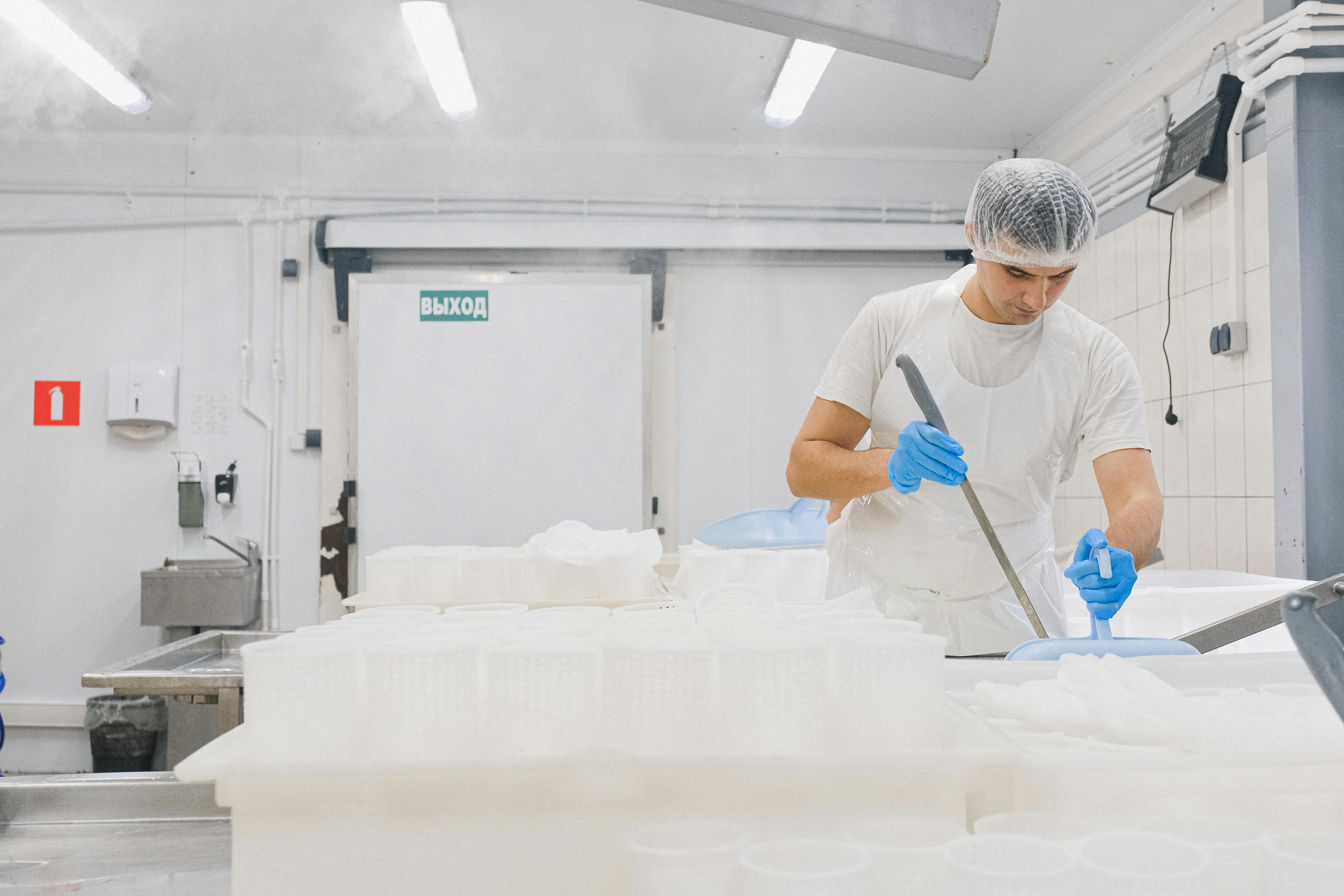
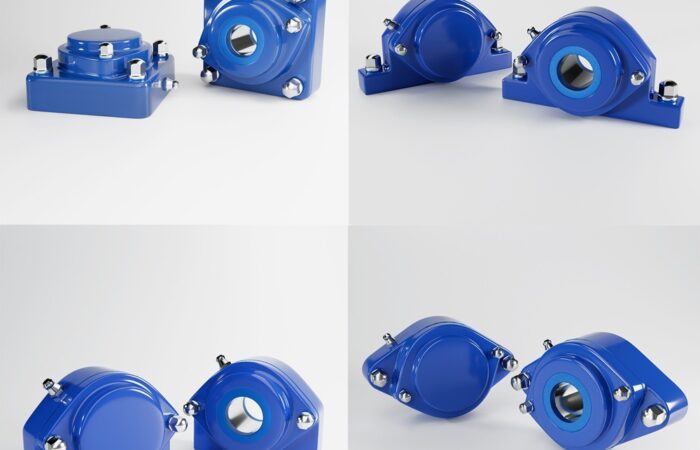
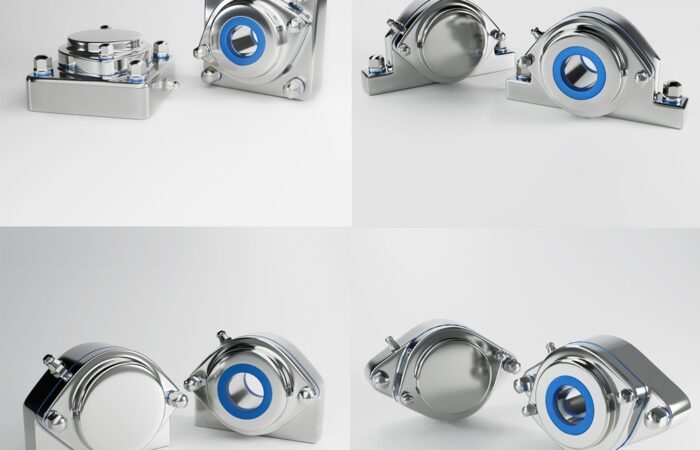
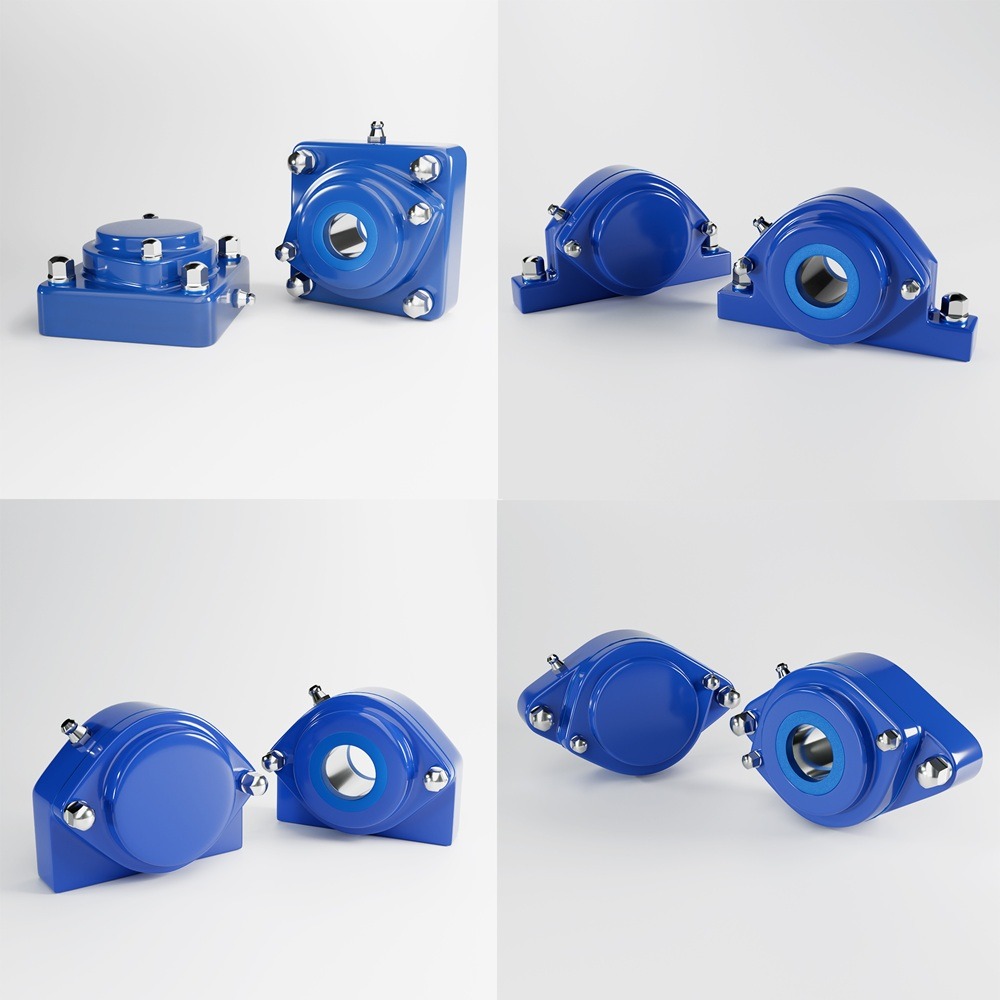
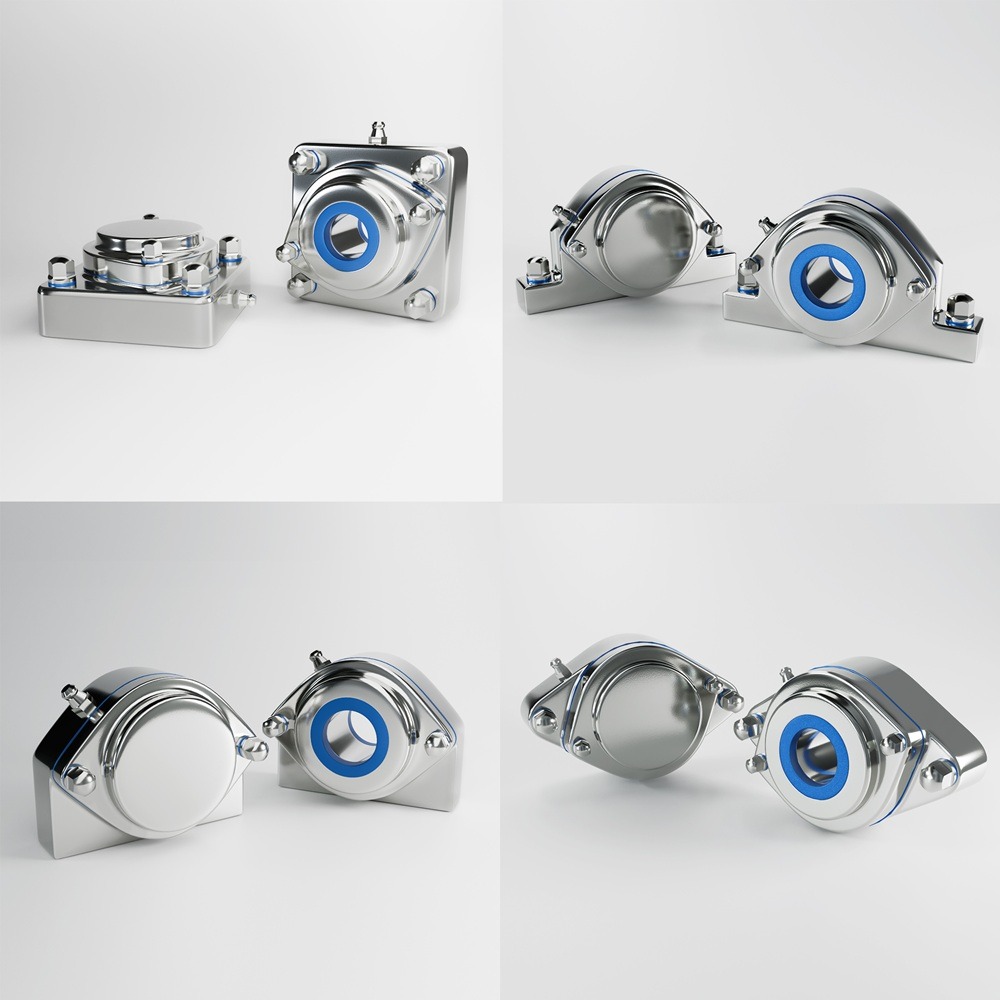
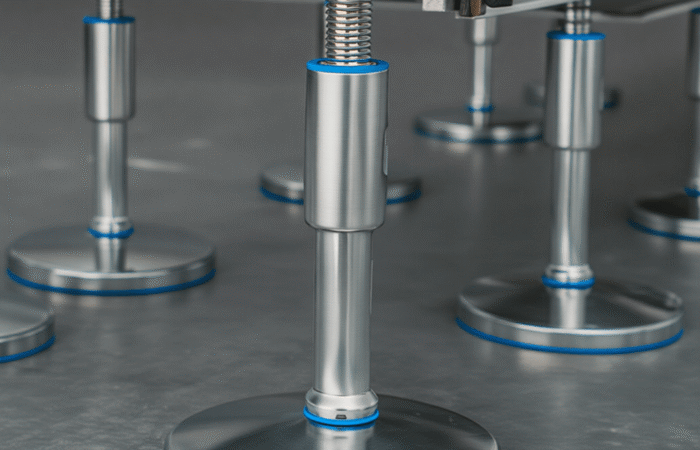
In the field of hygienic manufacturing, success hinges on staying ahead of industry trends that enhance product safety, efficiency, and compliance. This article explores key trends that are shaping the future of hygienic manufacturing and how businesses can adapt to these changes to maintain their competitive edge. The adoption of advanced sanitization technologies is critical in maintaining the highest standards of cleanliness, use certified hygienic components. UV sterilization, automated cleaning systems, and electrostatic spray technologies are becoming more prevalent. These methods provide effective and efficient cleaning solutions that reduce the risk of contamination and increase the overall reliability of the manufacturing process. Automation is transforming hygienic manufacturing by minimizing human contact with products during the production process. Robotics are being employed for tasks ranging from mixing ingredients to packaging finished products. This not only enhances cleanliness but also improves precision and reduces labor costs, making operations more scalable and less prone to errors. Traceability is paramount in ensuring transparency and compliance in manufacturing. Advanced traceability systems allow manufacturers to track every component from procurement through to the finished product. This is crucial for quality control, recall efficiency, and consumer trust, as it provides clear accountability and facilitates quicker responses to any issues that may arise. Packaging plays a crucial role in maintaining the hygiene and integrity of products. Innovations in packaging technologies, such as active packaging that can extend shelf life, and intelligent packaging that provides information about the condition of the product, are becoming more widespread. These technologies not only enhance product safety but also appeal to the environmentally conscious consumer by improving sustainability. The design of manufacturing equipment and facilities plays a foundational role in maintaining cleanliness. Equipment should be designed for easy cleaning and minimal maintenance, with smooth surfaces and minimal crevices where bacteria can accumulate. Additionally, the layout of facilities should facilitate optimal hygiene practices and workflows. Continual employee training in the latest hygiene and safety protocols is essential. Regular training ensures that all personnel are aware of the best practices and the latest technological advancements in hygiene. This is critical not only for compliance but also for fostering a culture of cleanliness and safety that permeates every level of the organization. As environmental sustainability becomes a priority for consumers and regulatory bodies alike, hygienic manufacturers must integrate eco-friendly practices into their operations. This includes using sustainable materials, reducing waste, and conserving energy. Sustainable practices not only improve the environmental footprint of a company but also enhance its public image and consumer appeal. By understanding and integrating these trends, companies in the hygienic manufacturing sector can improve their operational efficiency, comply with rigorous standards, and ultimately gain a substantial competitive advantage in the marketplace. Maintaining the highest standards of cleanliness requires clear protocols, comprehensive staff training, and the use of high-quality cleaning products and equipment. Regular and deep cleaning schedules, proper waste management, and rigorous personal hygiene practices are essential. Continuous monitoring, feedback mechanisms, and meticulous documentation ensure consistency. Adherence to health and safety regulations, obtaining relevant certifications, and adopting new cleaning technologies further uphold standards. This process ensures a safe, healthy environment, vital for settings like hospitals, schools, and workplaces, where cleanliness is crucial for preventing infection and promoting well-being. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Plummer Blocks and Flange Bearings is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. 440 Stainless Steel and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Harness Industry Trends for Success in Hygienic Manufacturing
Advanced Sanitization Technologies
Automation and Robotics
Traceability Systems
Innovative Packaging Solutions
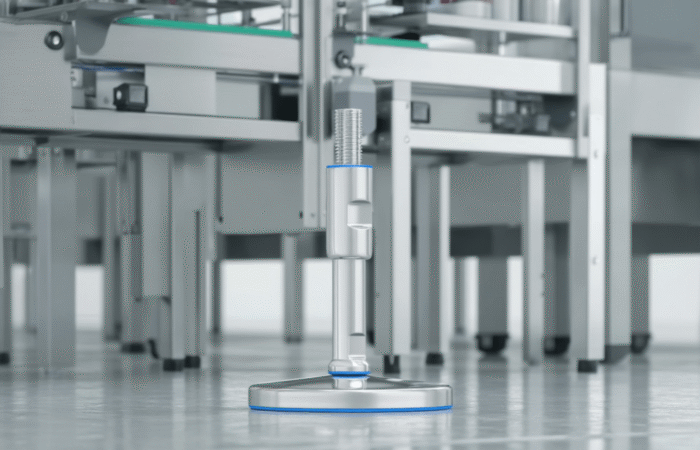
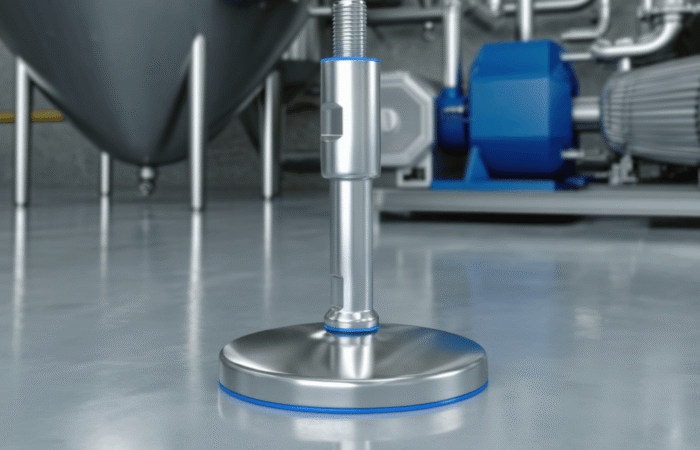
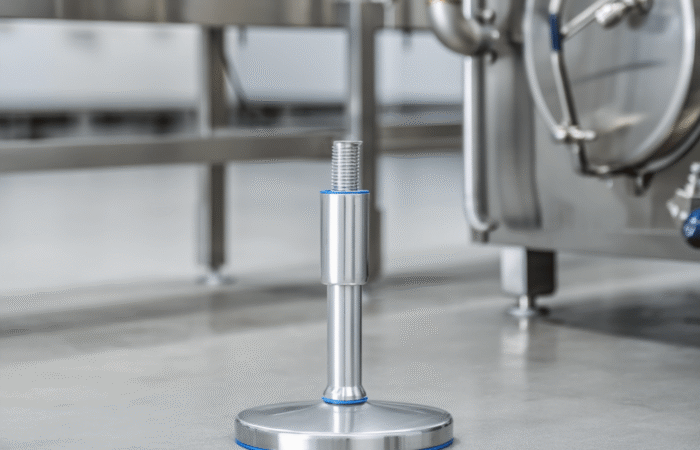
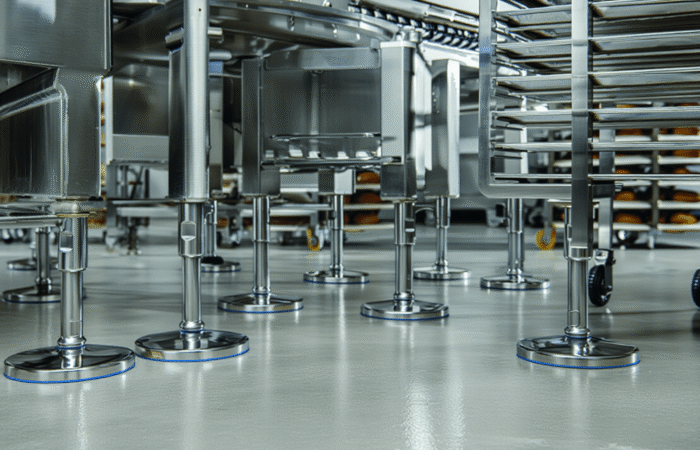
Hygienic Design Principles
Employee Training and Development
Sustainable Practices
Understanding and Integrating
Critical maintenance of the highest standards of cleanliness


Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards