A Detailed Guide: Machine Casters vs. Leveling Feet
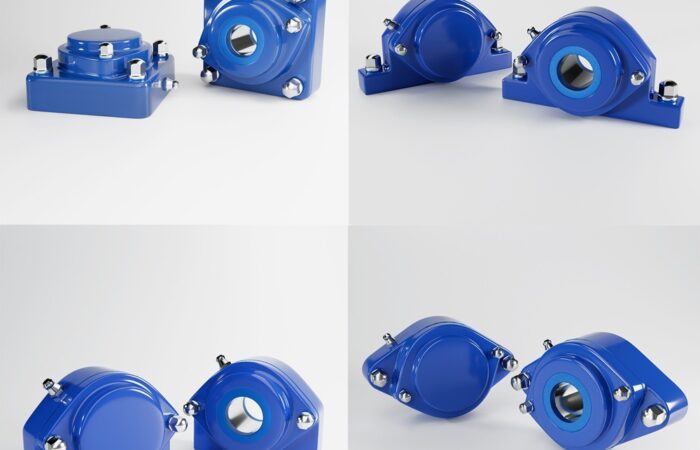
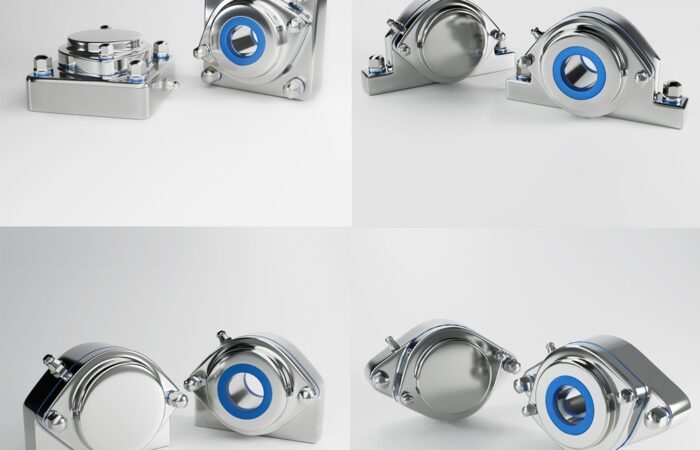
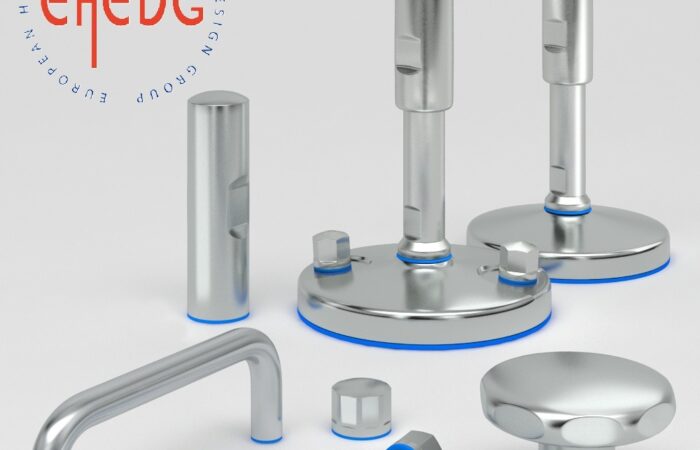
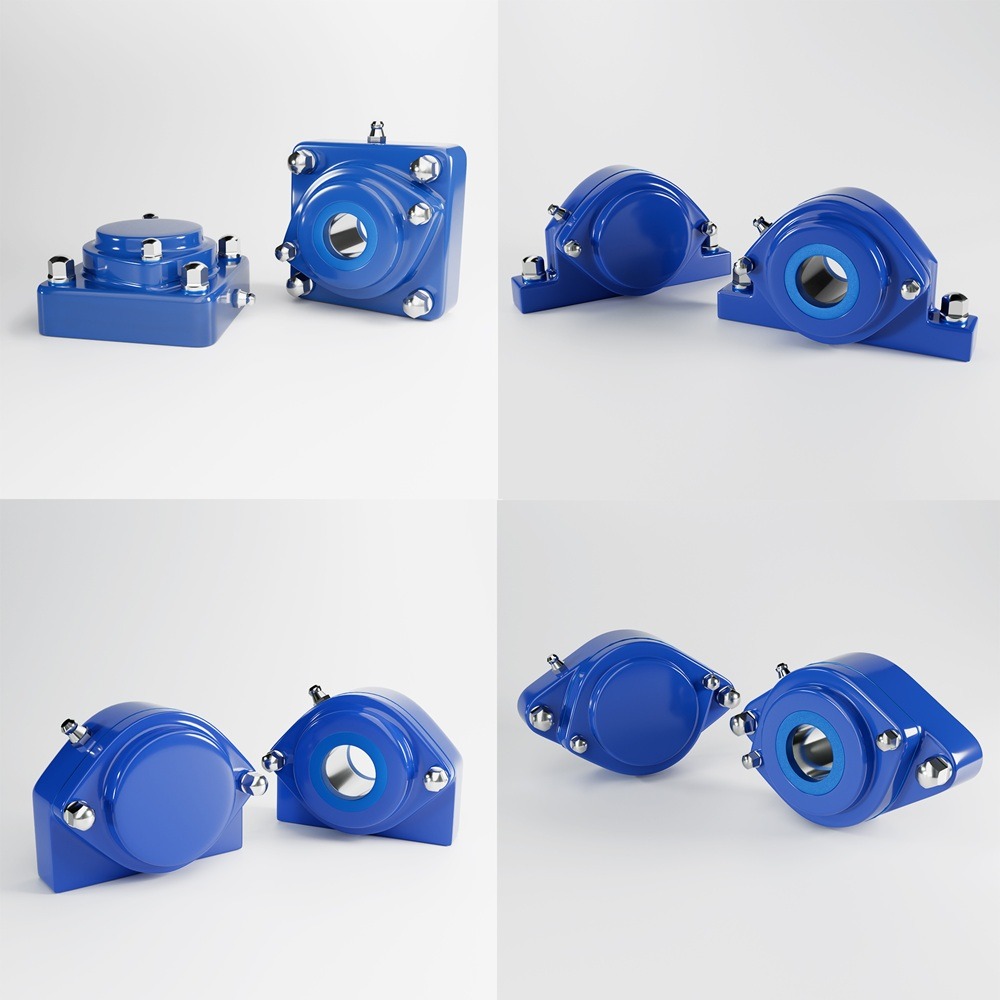
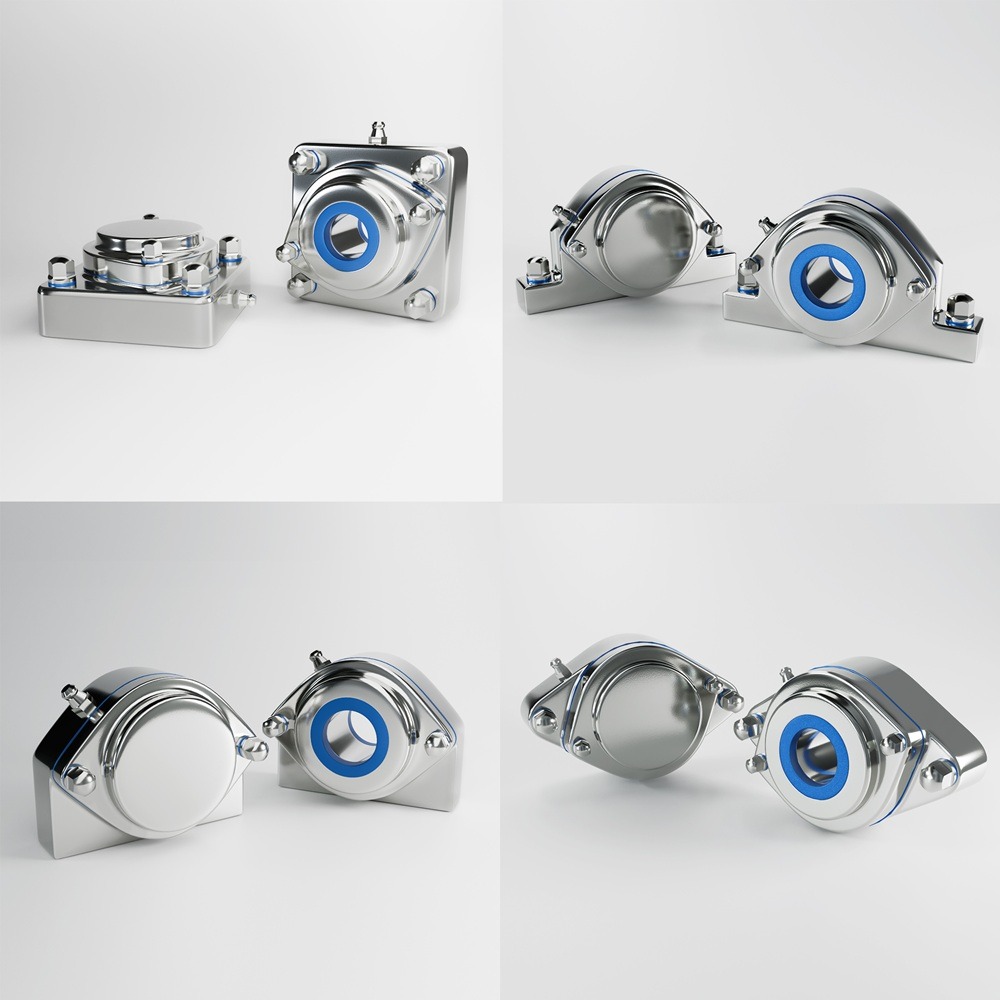
When setting up industrial machinery, workstations, or heavy equipment, choosing the right support system is critical for performance, safety, and efficiency. Two of the most commonly used options are machine casters and leveling feet. Each option has specific advantages and limitations, making it crucial to understand their differences to select the best fit for your industry and application. This guide covers: Machine casters are wheel-based support systems that provide mobility to industrial equipment. They are commonly used in environments where machines need to be frequently repositioned or moved for maintenance, cleaning, or workflow changes. Leveling feet are stationary supports designed to stabilize machines, ensuring they remain level on uneven surfaces while reducing vibration. They are ideal for equipment that must stay in place for precise and consistent operation. ✔ Machine Casters – Ideal for machines that need frequent repositioning, such as conveyor systems and labelers. ✔ Machine Casters – Used for mobile food prep stations and reconfigurable equipment. ✔ Machine Casters – Best for mobile cleanroom equipment and lab storage units. ✔ Machine Casters – Suitable for flexible lab setups with frequently moved equipment. For industries that require both mobility and stability, leveling casters combine the advantages of casters and leveling feet. Leveling casters feature: ✔ Dual Functionality – Can be moved or locked in place. When deciding between machine casters and leveling feet, consider the following: Choosing between machine casters and leveling feet depends on stability, mobility, and environmental factors. By understanding these differences, industries can optimize efficiency, safety, and operational performance for long-term success. Industrial machinery requires precision-engineered components that meet exacting standards for durability, safety, and performance. This comprehensive guide explores the essential machinery parts that drive modern manufacturing across food processing, packaging, and chemical industries. Understanding the difference between Pillow Blocks and Flanged Bearings is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals seeking to optimize equipment longevity. Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer blocks, are self-aligning bearing units that simplify installation and significantly reduce maintenance costs. These versatile components mount on machine frames and support rotating shafts with exceptional precision, ensuring smooth operation in demanding industrial environments. Flange bearing units offer a more compact alternative, featuring integrated flanges that enable direct mounting to flat surfaces without additional hardware. Both designs come in various materials, including stainless steel grades optimized for corrosive environments and food-grade applications where hygiene is paramount. The importance of material selection cannot be overstated in machinery design. Stainless Steel 440 and 420 grades offer distinctly different properties suited to specific applications and environmental conditions. The 440 stainless steel variant provides superior hardness and exceptional edge retention, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-wear applications requiring maximum durability. Meanwhile, 420 stainless steel offers better corrosion resistance and is preferred in food processing equipment where chemical exposure is common. Hygienic stainless steel components have become essential in food machinery, meeting EHEDG standards and facilitating rapid equipment cleaning required in modern food production facilities. Understanding ingress protection ratings is equally critical for machinery durability and operational reliability. IP67 rating ensures protection against dust and temporary water immersion, while IP68 rating provides complete dust protection and sustained water immersion capabilities for submerged operations. The IP69K standard represents the highest protection level, specifically designed for high-pressure wash-down environments found in industrial food processing facilities. These ratings define how effectively machinery components withstand environmental challenges and maintain performance. Modern industrial facilities increasingly demand equipment that combines high performance with ease of maintenance and sanitation. The choice between different bearing types depends on operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Proper component selection ensures extended equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, and improved operational efficiency.Machine Casters vs. Leveling Feet
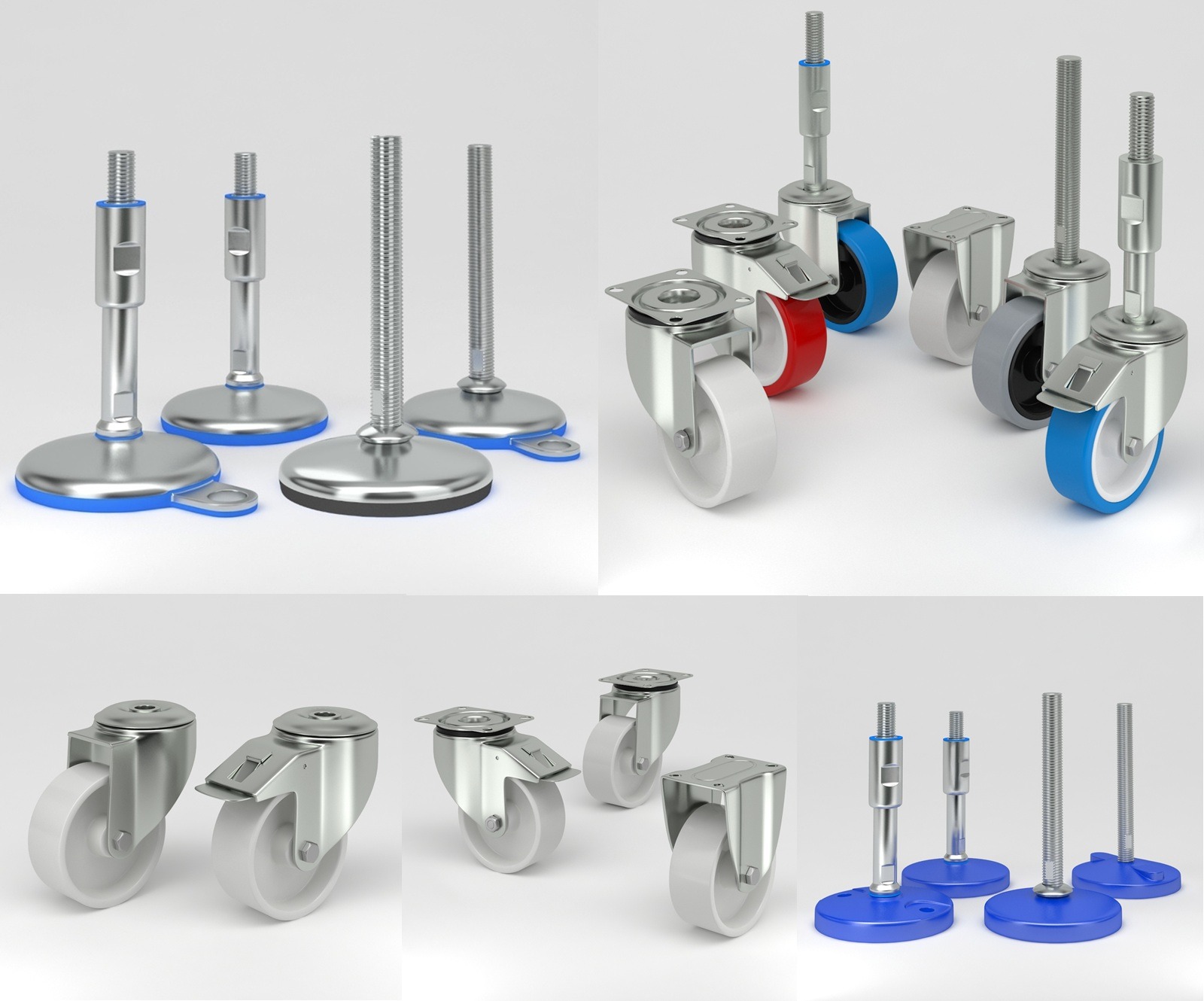
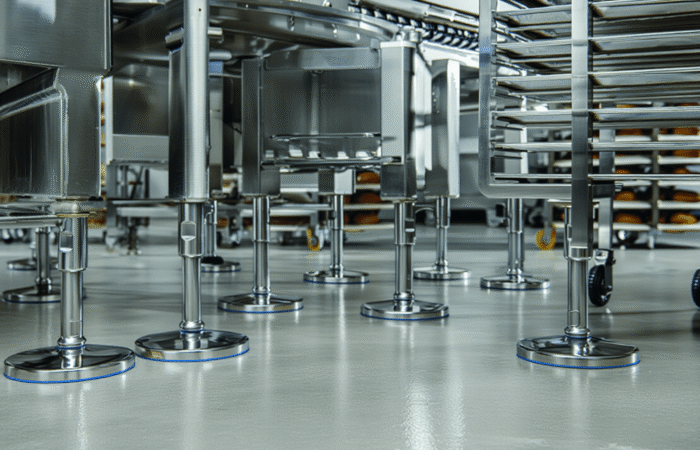
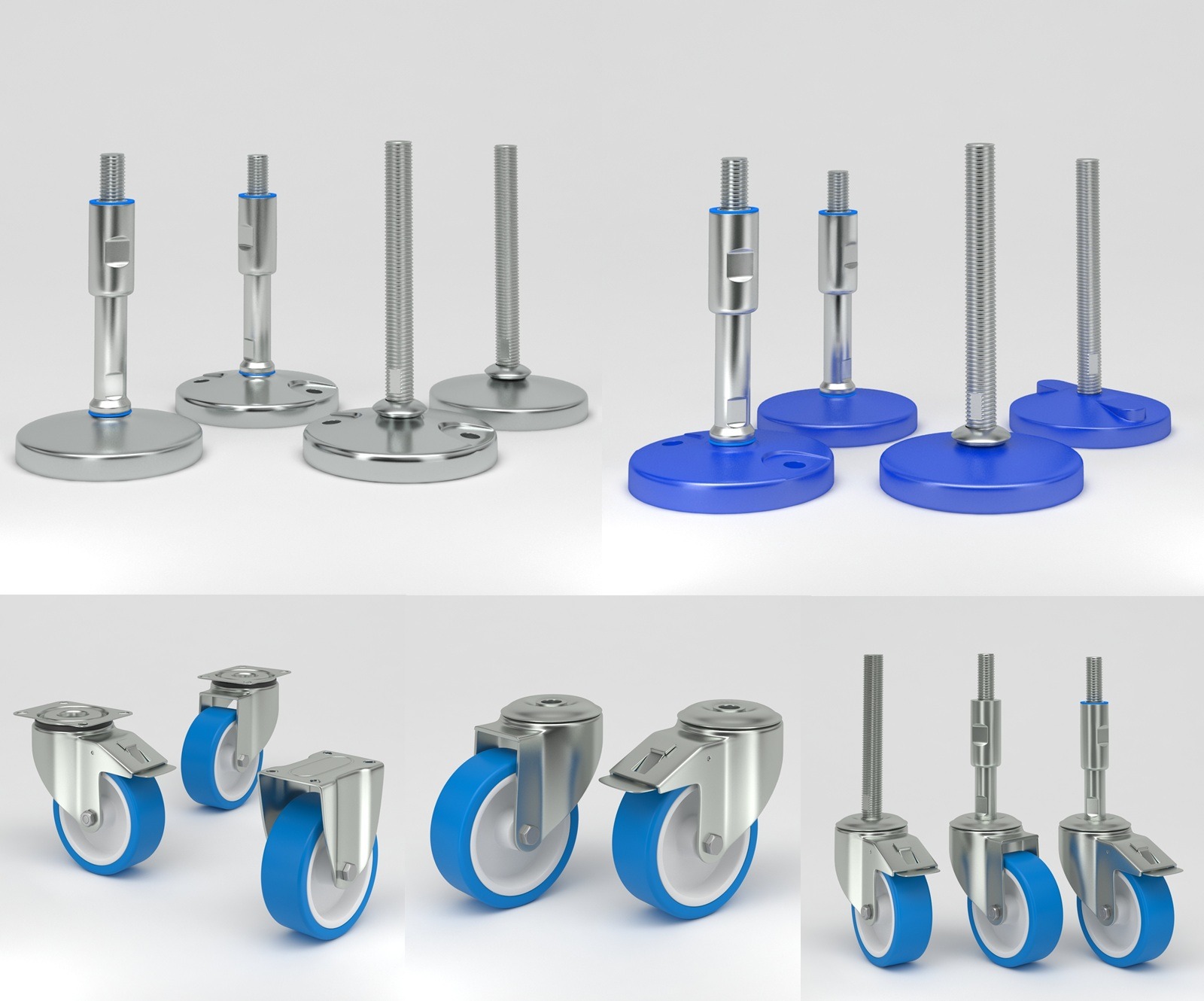
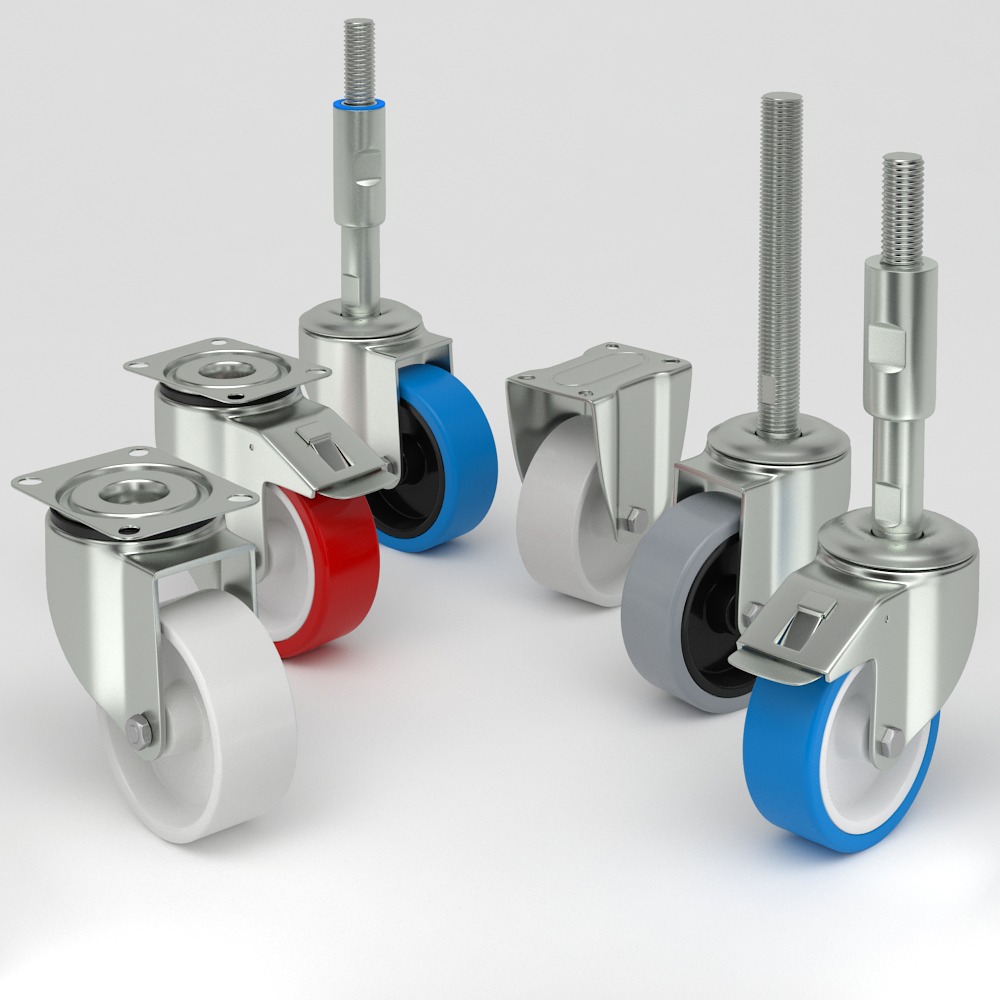
What Are Machine Casters?
Types of Machine Casters
Pros & Cons of Machine Casters
Pros Cons Allows movement & repositioning for flexible layouts. Less stability, even with locking mechanisms. Reduces manual labor when shifting machinery. Can introduce vibrations, affecting precision work. Facilitates maintenance & cleaning access. May damage floors if improper wheels are used. Available in various weight capacities & materials. Requires regular maintenance (e.g., checking wheel wear). Best Applications for Machine Casters
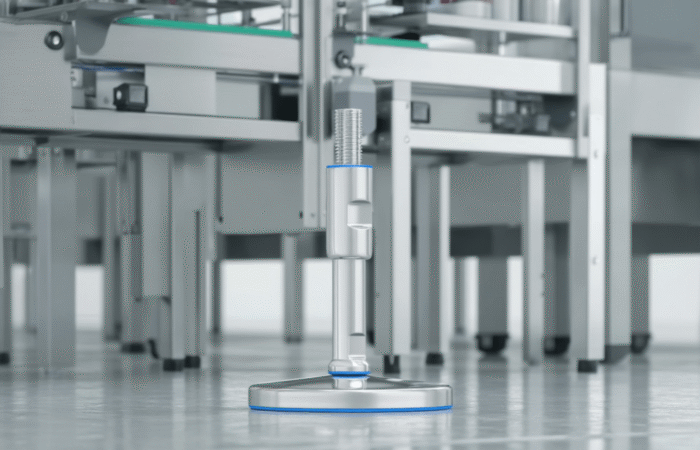
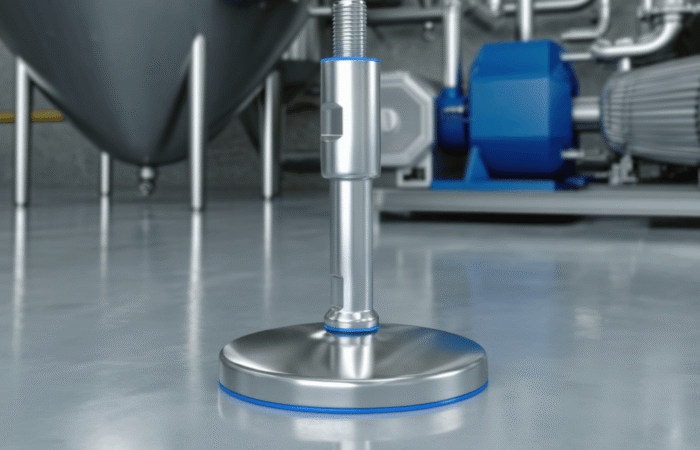
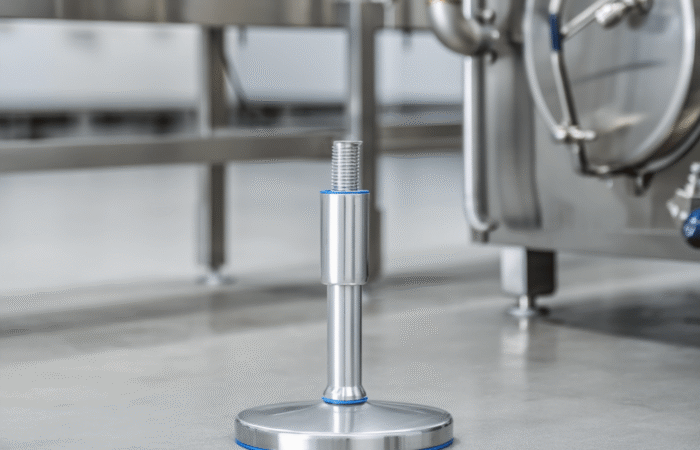
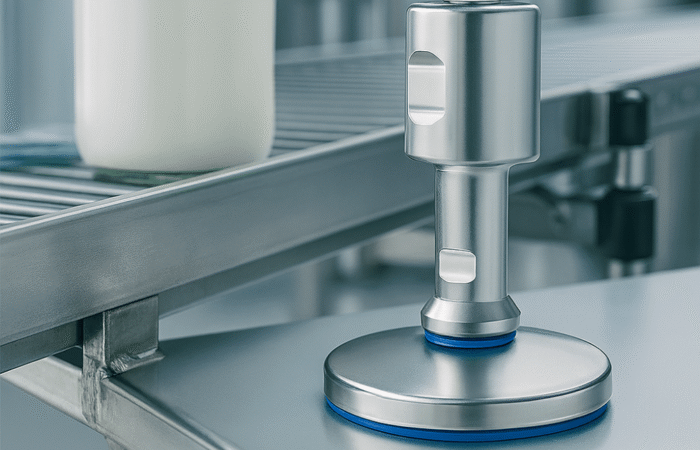
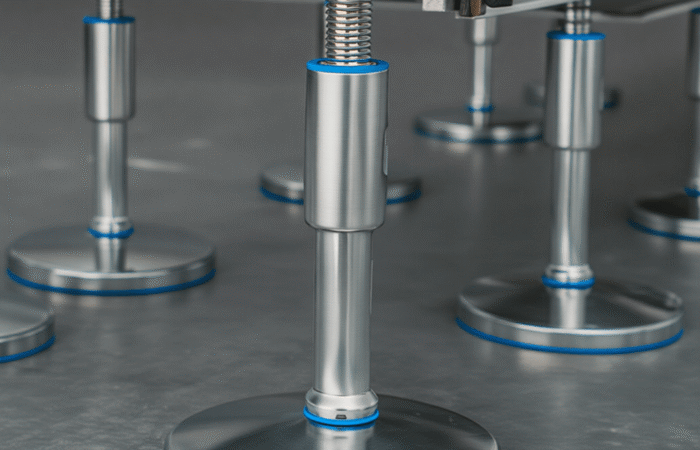
What Are Leveling Feet?
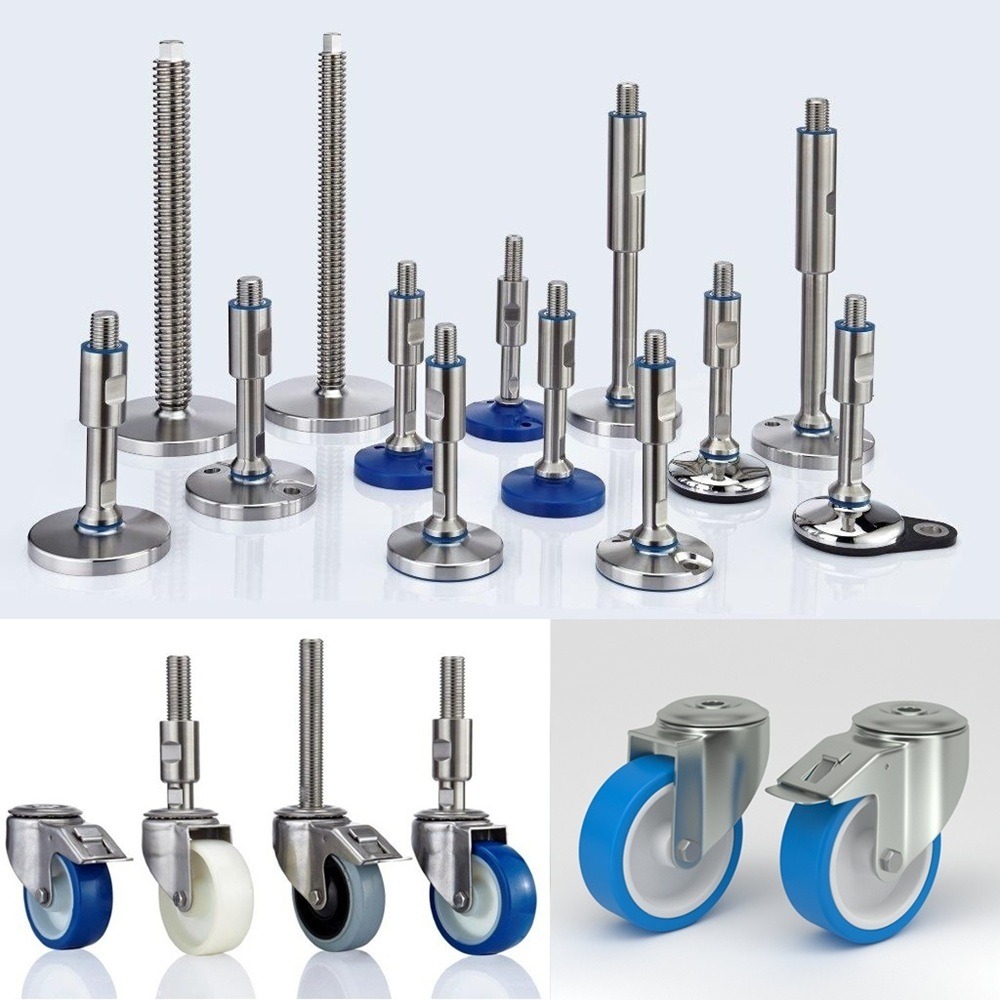
Types of Leveling Feet
Pros & Cons of Leveling Feet
Pros Cons Provides stability and vibration control for machinery. No mobility, requiring lifting equipment for relocation. Ensures precise machine alignment on uneven floors. Takes time to adjust properly during installation. Helps distribute weight evenly, reducing floor damage. Not suitable for frequently moved equipment. Hygienic options available for cleanroom environments. Can require additional support for extremely heavy loads. Best Applications for Leveling Feet
Machine Casters vs. Leveling Feet: Key Differences
Feature Machine Casters Leveling Feet Function Enables movement of machinery Stabilizes and levels stationary machines Best for Frequently repositioned equipment Fixed machinery requiring stability Mobility High – Machines can be moved easily Low – Once installed, machine stays in place Stability Moderate – Locking casters help but not as stable as feet High – Machines stay firmly in place Vibration Control Low – Can transfer vibrations to the floor High – Absorbs vibrations effectively Load Distribution Can cause uneven weight distribution Evenly distributes weight across feet Installation Time Quick setup, minimal adjustments needed Requires height adjustment for proper leveling Hygiene & Cleanability May have crevices that collect dirt Smooth surfaces available for cleanroom compliance Industry-Specific Considerations
Packaging Industry
✔ Leveling Feet – Essential for machines that require minimal movement, such as filling and capping machines.Food Processing Industry
✔ Leveling Feet – Required for stability in slicers, mixers, and pasteurizers to meet hygiene standards.Pharmaceutical Industry
✔ Leveling Feet – Necessary for precision devices like capsule filling and powder mixing machines.Biotechnology Industry
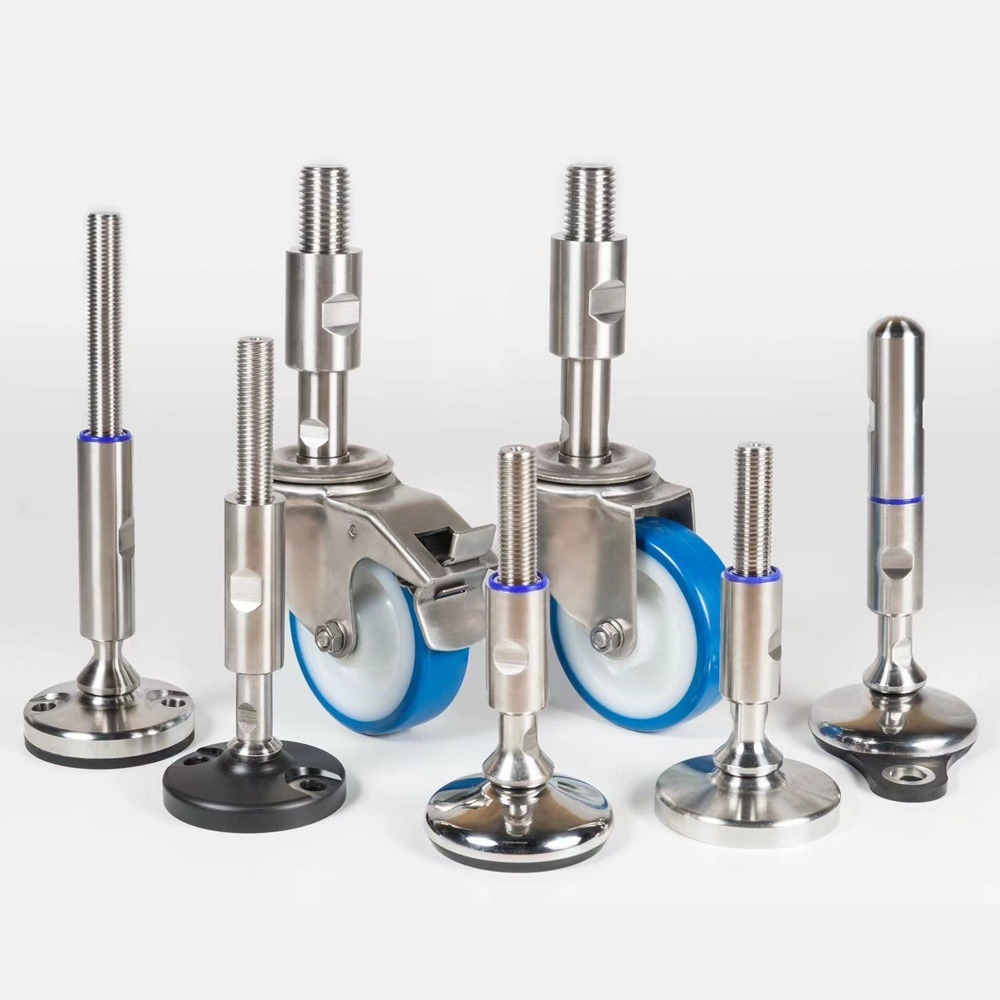
✔ Leveling Feet – Ideal for biosafety cabinets, incubators, and analytical balances where stability is essential.Hybrid Solution: Leveling Casters
What Are Leveling Casters?
Benefits of Leveling Casters
✔ Quick Repositioning – Reduces downtime in flexible workspaces.
✔ Vibration Reduction – Some models include anti-vibration properties.Best Use Cases for Leveling Casters
How to Choose Between Machine Casters and Leveling Feet
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Support for Industrial Machinery




Contact
Understanding Machinery Components & Protection Standards