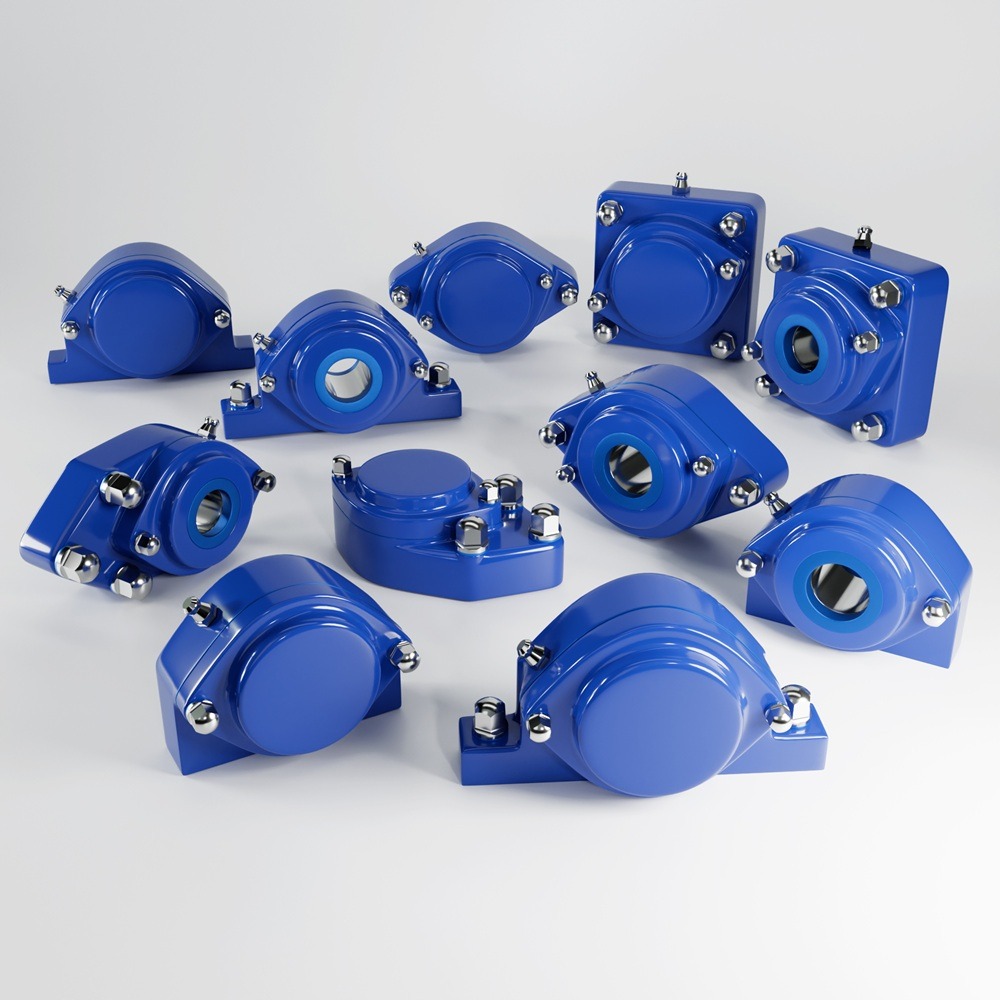
Pillow Block vs Flange Bearing Comparison
When a rotating shaft fails in production, it’s rarely the rolling elements alone—more often, the housing choice (mounting rigidity, alignment tolerance, sealing, washdown resistance, and material compatibility) determines whether uptime is measured in months or in missed shifts. This guide is a practical pillow block vs flange bearing explained for engineers, OEMs, and maintenance teams who need a repeatable way to pick the right mounted unit for real-world machinery. A mounted bearing unit is a bearing insert pre-fitted into a housing that’s bolted to a structure. The housing influences: Structural stiffness & load path (how loads travel into the frame) Misalignment handling (shaft/frame tolerances and deflection) Seal performance (contaminants in, lubricant out) Serviceability (access to fasteners, relube points, replacement time) Corrosion resistance & cleanability (washdown, chemicals, hygiene requirements) Manufacturers describe pillow blocks as housings that can be bolted to a support surface, typically for straightforward base mounting. A pillow block is a base-mounted housing: it sits on a flat foundation and is bolted down from above. pillow block bearing housing types and uses Common reasons to choose a pillow block: You have a flat mounting base (machine bed, conveyor stringer, welded frame) You want easy shaft height control via shims or machined pads You expect moderate frame misalignment and want simpler alignment procedures You need fast swap-out on long conveyor lines or general industrial machinery SKF notes pillow block units are an insert bearing mounted in a housing, bolted to a support surface—exactly why they’re popular for general machinery. A flange unit is face-mounted: the housing bolts to a vertical or perpendicular surface (think end plates, bulkheads, machine sidewalls). flange bearing housing for harsh environments Common reasons to choose a flange unit: Your structure is a wall/plate rather than a base (gearbox face, end shield, tank wall, side plate) Je hebt nodig compact mounting where base space is restricted You want better control of shaft position relative to a wall/guard You need a robust “bolt-through-the-flange” assembly commonly used in industrial layouts Timken’s flanged mounted units are described as assembled and ready for mounting using bolts through the flange, and many designs help compensate for misalignment via spherical outside diameters. Pillow blocks often excel on long bases where radial loads dominate (conveyors, fan shafts, general line shafts). Flange units can be ideal when the housing must react loads close to a plate or end wall (end-of-shaft support, compact assemblies, motors/gearbox-adjacent mounting). Many mounted bearings use insert designs intended to tolerate small misalignment. Timken explicitly highlights misalignment compensation in several flanged unit styles. If the environment involves spray, foam cleaning, dust, or product fines, sealing and enclosure performance become central. While IP ratings apply to enclosures (not bearings per se), the Ingress Protection (IP) rating system is defined under IEC 60529 and is often used as a shorthand for dust/water resistance of protected assemblies. Pillow block “sweet spots” Conveyors in packaging and logistics Fans/blowers and general rotating equipment Agricultural and general industrial machinery (also commonly listed by major suppliers) Flange unit “sweet spots” Compact machines with side plates/end walls (cartoners, case packers, form/fill/seal) End-of-shaft support where base mounting is impractical Motor/gearbox-adjacent arrangements and plate-mounted assemblies Pros: stiffness, vibration damping, broad availability. Pros: washdown resistance, chemical resistance, hygienic design potential (smooth, cleanable geometries). If you build for food handling, remember standards and guidance focus on cleanability and contamination risk reduction. EHEDG publishes hygienic design principles to prevent contamination and improve cleanability. Pros: corrosion resistance, light weight, sometimes chemical resilience. Problem: Bearings fail early due to moisture ingress and corrosion at the housing and fasteners. Problem: No room for a base footprint; shaft support must mount to a vertical plate. Problem: Debris, vibration, and occasional misalignment destroy seals and overheat bearings. Problem: Painted cast housings corrode; maintenance time is high and failures are unpredictable. Top bearing suppliers like SKF, Schaeffler (FAG/INA), En Timken provide broad mounted-unit ranges (pillow block and flanged) with standardized housings, insert bearings, and sealing options—helpful because it reduces engineering risk and speeds replacement. bearing housing selection for machinery builders If your equipment enters regulated or hygiene-critical environments, your housing choice should support compliance arguments: EHEDG hygienic design principles for cleanability and contamination prevention ISO 14159 hygiene requirements for machinery design EN 1672-2 hygiene and cleanability requirements for food processing machinery 3-A guidance (where applicable) outlining sanitary design expectations and criteria language used in sanitary standards Here are anonymized, representative comments consistently reported by maintenance leads and OEM builders when housings are correctly selected: “The biggest win wasn’t longer life—it was predictable maintenance. We stopped getting surprise washdown failures.” “Switching to a plate-mounted flange design cut replacement time because techs could access bolts without dismantling guards.” “A more robust seal choice reduced relube frequency and kept contamination out during peak season.” “Standardizing on one housing family simplified spares and training across multiple lines.” Mounting plane: base (pillow) or wall/plate (flange)? Omgeving: dust, washdown, chemicals, temperature swings? Materiaal: cast iron vs stainless vs polymer—match corrosion and cleanability needs. Misalignment & deflection: welded frames and long shafts need tolerance. Seals & lubrication: choose based on contaminants and cleaning regime. Standards: if food/pharma, align design rationale with EHEDG / ISO 14159 / EN 1672-2. Choosing between a pillow block and a flange housing isn’t a style preference—it’s a mechanical decision about mounting geometry, load path, sealing strategy, and environment. Use pillow blocks when the base is king and serviceability matters; use flanges when space is restricted or you need plate-mounted support. Then refine the decision with material, seals, lubrication, and standards alignment—and you’ll reduce downtime, simplify maintenance, and increase confidence in every new build.How to Choose the Right Bearing Housing (and Why It Matters)
What a bearing housing actually does (beyond “holding a bearing”)
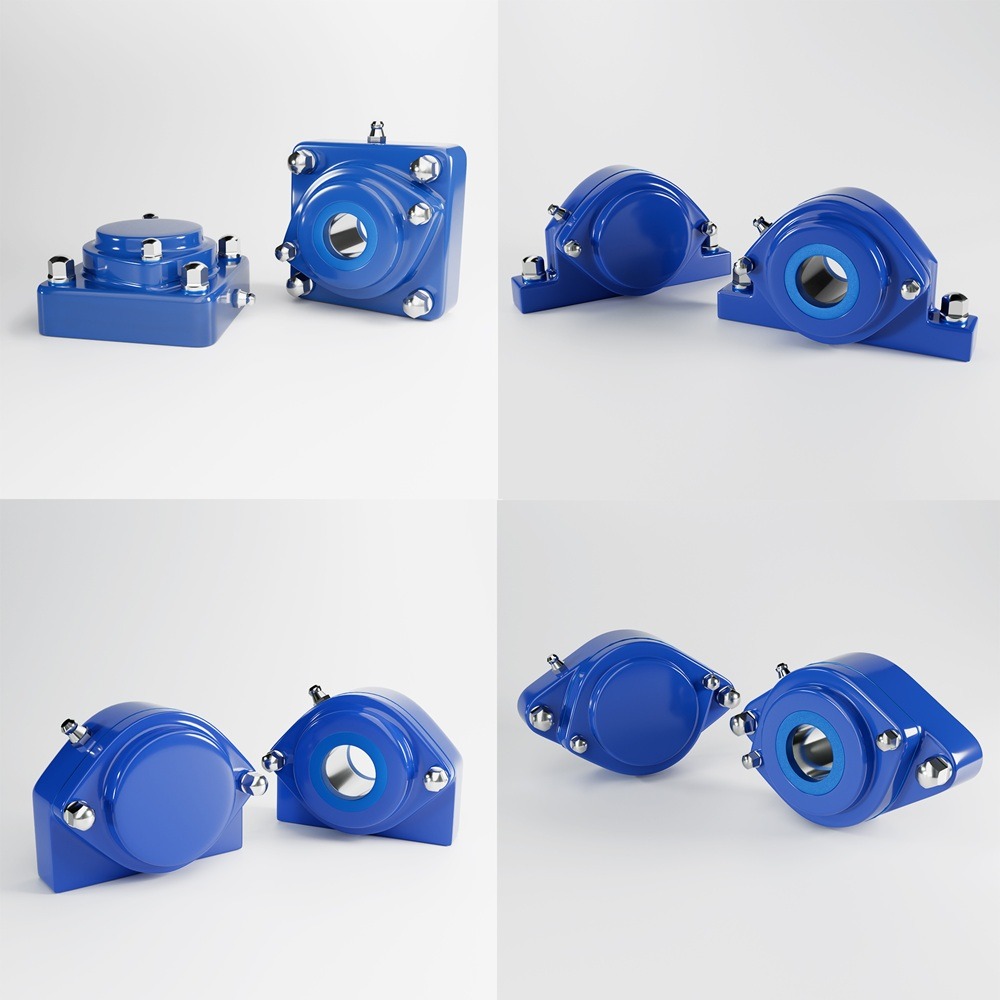
Pillow block vs flange: the simplest mental model
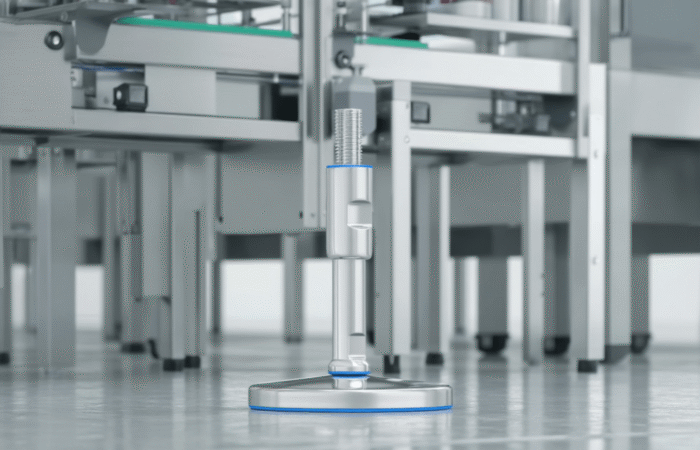
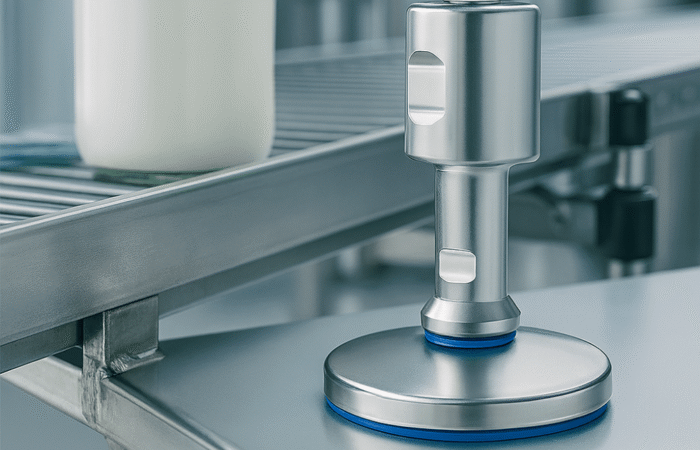
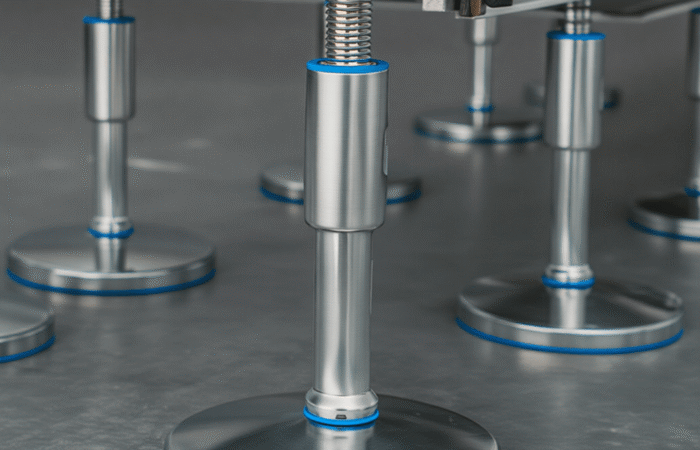
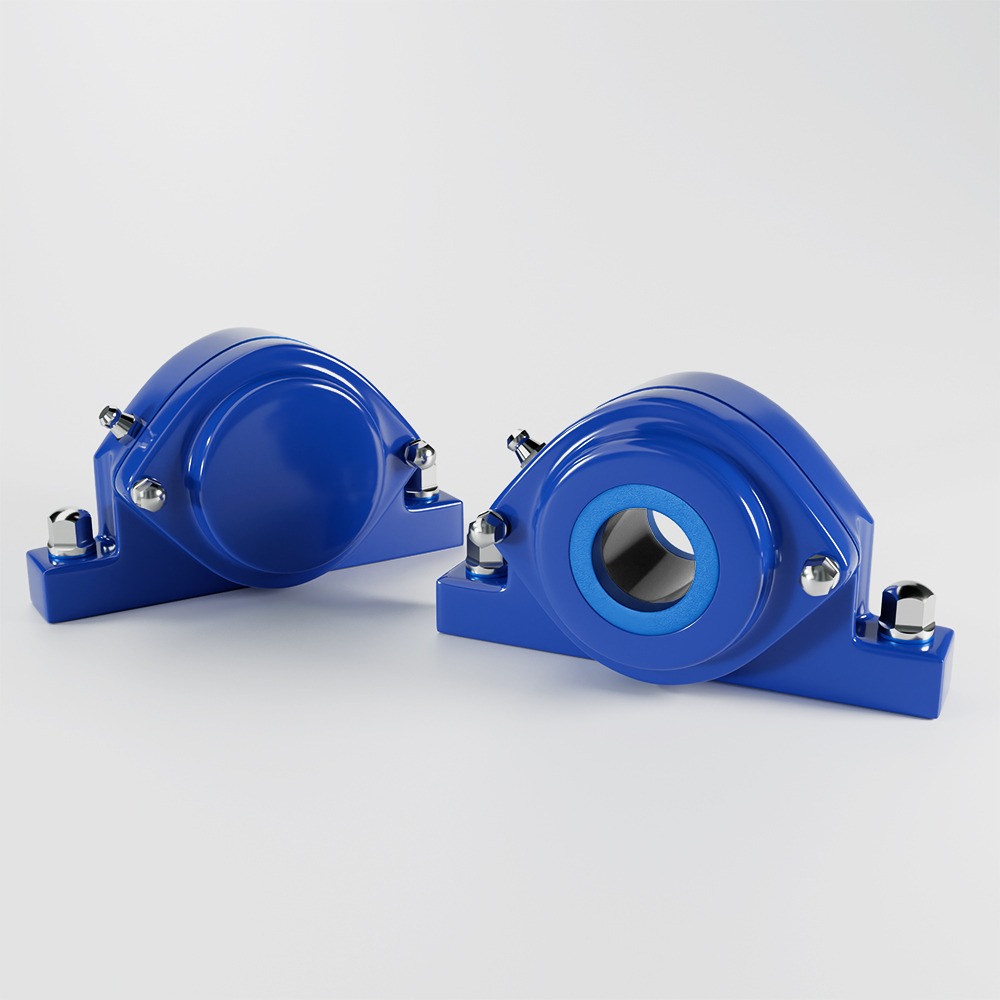
Pillow block (plummer block) housings
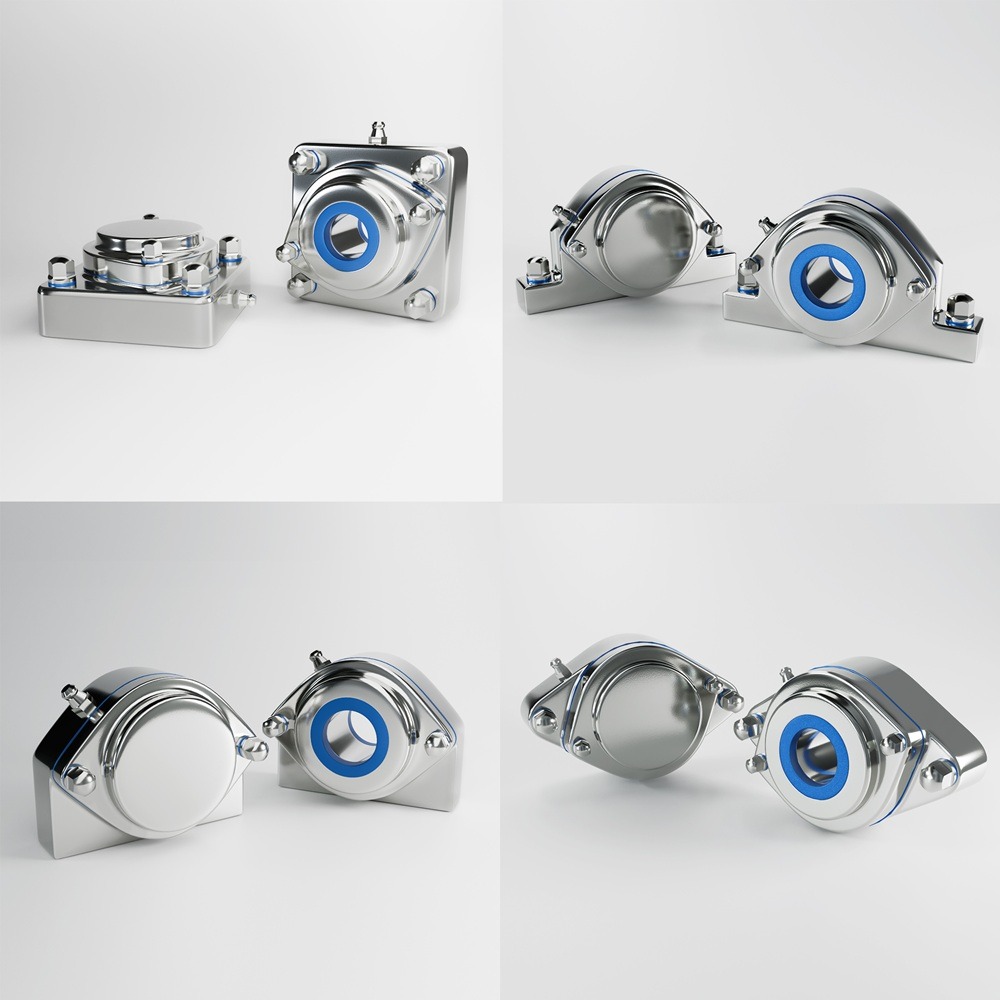
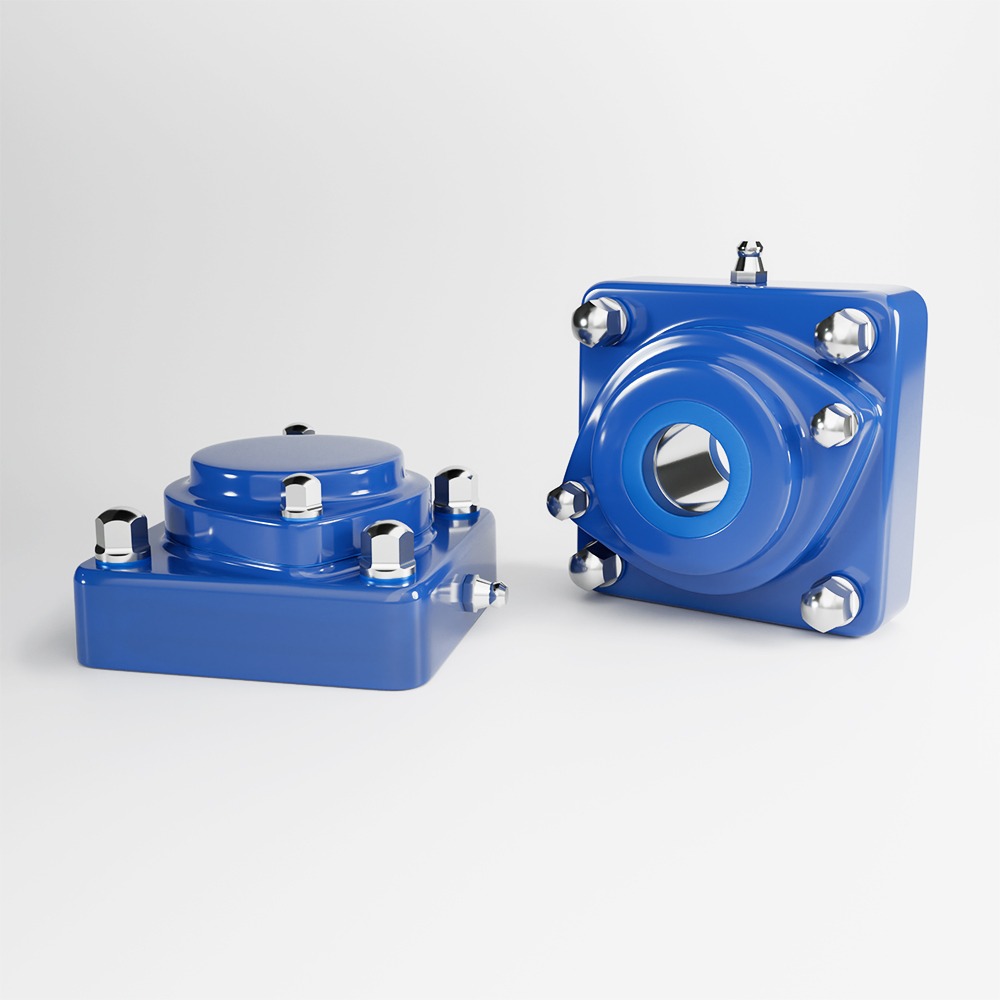
Flange housings (2-bolt / 3-bolt / 4-bolt)
Schaeffler (FAG/INA) catalogs also position flanged housings as a go-to adjacent construction for many machines, simplifying design and maintenance in certain layouts.Usage: what changes in the machine when you pick one vs the other?
1) Load direction and frame stiffness
2) Alignment tolerance and installation reality
Practically: if your fabrication tolerances are “industrial” (welded frames, field drilling), choose designs that tolerate misalignment and allow quick adjustment.3) Hygiene, washdown, and ingress
In washdown food/pharma zones, you’re usually engineering for repeatable cleanability, corrosion resistance, and seal integrity—not just “it spins.”Industries: where each housing type tends to win
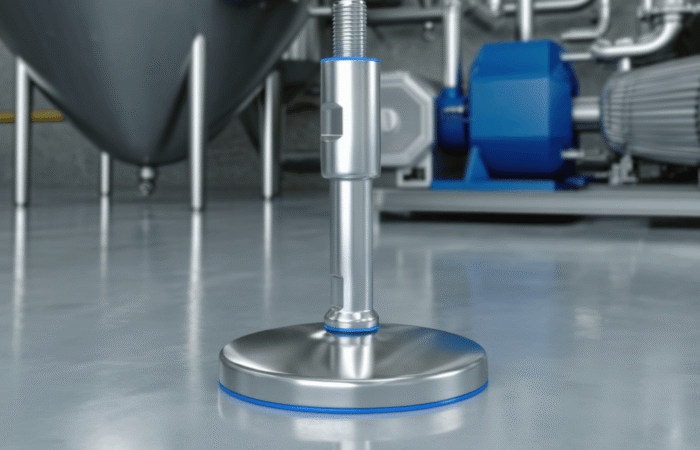
Material choices: what the housing is made from changes everything
Cast iron (common, cost-effective)
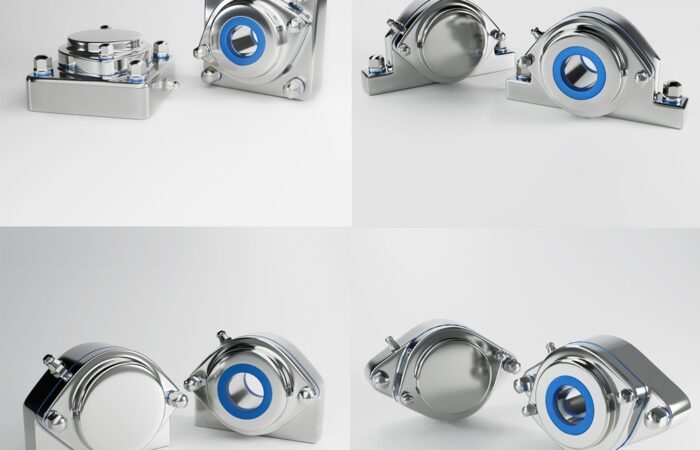
Cons: corrosion risk in wet/chemical environments; coating damage can become a failure accelerant.Stainless steel (hygienic and corrosion-resistant)
Cons: higher cost; correct grade selection and surface finish matter.
ISO 14159 also specifies hygiene requirements for machinery design where hygiene risks can occur.
For food processing machinery, EN 1672-2 is widely referenced for hygiene and cleanability requirements.Thermoplastic / polymer housings (special cases)
Cons: temperature limits, creep under load, and application-specific compatibility checks required.Experience: 4 real-world selection cases (what actually drives the decision)
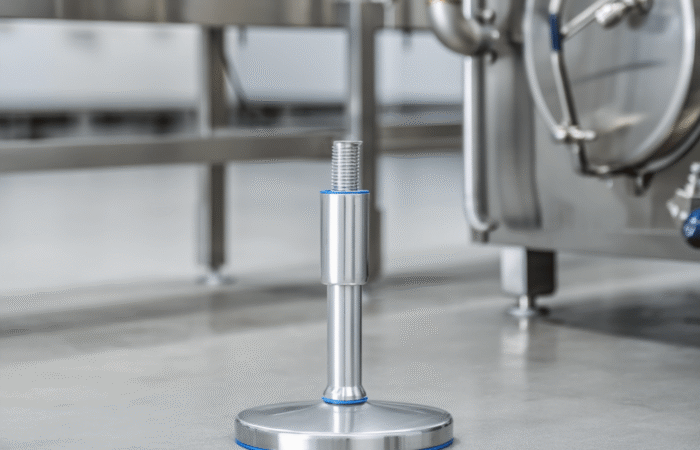
Case 1 — Washdown conveyor in a dairy zone (frequent caustic + hot rinse)
Choice: Stainless housing + high-performance seals; often a flange or pillow block depending on conveyor frame geometry.
Why: Hygienic design principles emphasize cleanability and contamination control; stainless and smooth geometries reduce harborage points.Case 2 — Packaging machine with tight side-plate space (cartoner end-shaft support)
Choice: 2-bolt flanged unit.
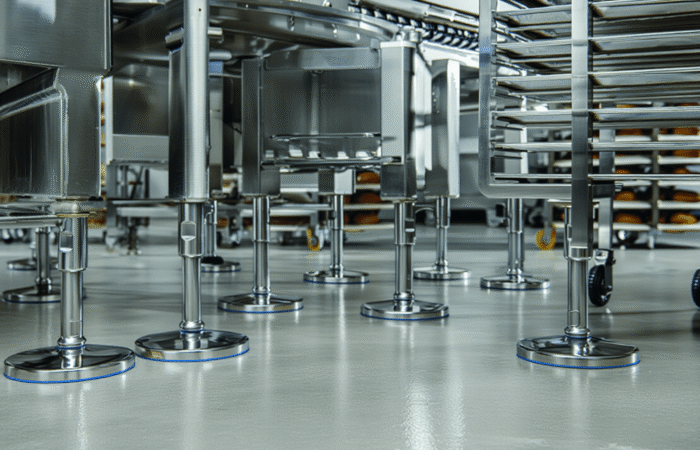
Why: Flanged units are made for bolt-through mounting on restricted areas and plate-mounted assemblies.Case 3 — Quarry/aggregate conveyor (dust + shock + misalignment)
Choice: Heavy-duty pillow block style with robust sealing and relube strategy (often spherical roller unit style).
Why: Pillow blocks are common on rugged conveyor frames; supplier catalogs emphasize contaminant protection and durability features in housed units.Case 4 — Chemical plant transfer line (splash zone + cleaning chemicals)
Choice: Corrosion-resistant housing material (often stainless) + seal/lube selection aligned to exposure; flange or pillow block based on mounting plane.
Why: The environment dictates material compatibility and sealing more than the “shape” alone; IEC’s IP framework is often used when specifying protected assemblies in wet zones.Expertise: what leading manufacturers typically offer (and why it helps you)
When you’re designing machinery for scale, a deep catalog matters: consistent part numbering, availability, and predictable performance data.Authoritativeness: certifications and standards you can cite in specifications
Trustworthiness: what customers actually care about (testimony from the field)
Practical selection checklist (fast and reliable)
Conclusion: the “best” housing is the one that fits your machine reality



Contact
Industriemachinedelen en Beschermingsnormen
De voedselindustrie en verpakkingsmachines vereisen nauwkeurig gemaakte componenten die volledig voldoen aan internationale beschermings-, duurzaamheids- en hygiëne-standaarden strenge. De IP-classificatie is absoluut fundamenteel voor het bepalen van geschiktheid van componenten in vochtige, corrosieve of hogedruk-wasomgevingen veeleisend. IP67 biedt volledige bescherming tegen stof en tijdelijke onderdompeling in water, terwijl IP69K het hoogste beschermingsniveau vertegenwoordigt, speciaal ontworpen voor intensieve industriële reinigingsomgevingen en processen. De keuze van roestvrijstalen materialen is cruciaal en essentieel voor de fabricage van hygiënische machines modern. Roestvrijstaal 440 en 420 vertonen verschillende eigenschappen uitstekend aangepast aan specifieke toepassingen diverse. Roestvrijstaal 440 biedt superieure hardheid uitzonderlijke en uitzonderlijke snijkantbehoud, ideaal voor snijgereedschap en onderdelen met hoge slijtage. Roestvrijstaal 420 levert betere corrosieweerstand en wordt voorkeur gegeven in voedselverwerkingsapparatuur. Precisielagers zijn essentieel en onmisbaar voor optimale machineprestaties uitstekend. De internationale standaarden blijven zich voortdurend ontwikkelen om aan de groeiende eisen van de moderne industrie te voldoen volledig. Innovatie en technologie zijn sleutelwoorden voor succes industrieel. De betrouwbaarheid van apparatuur hangt af van kwaliteitscomponenten altijd. Bedrijven profiteren aanzienlijk van investeringen in superieure onderdelen.